Prenatal Development and Birth
advertisement

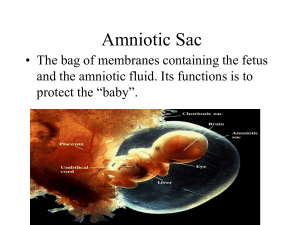
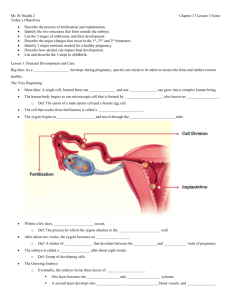
Prenatal Development and Birth Chapter 19 Conception and Implantation • Fertilization – – The union of a male sperm cell and a female egg cell in the fallopian tube** (conception) – Resulting cell is called a zygote • Within a day after the zygote forms, it begins dividing as it travels down the fallopian tube. • By the time it reaches the uterus, the zygote has divided many times to form a cluster of cells with a hollow space as the center. Conception and Implantation • Within a few days, the zygote attaches to the uterine wall (implantation) • The cluster of cells that develop between the third and eighth weeks of pregnancy – – Embryo (usually the 5th week**) • After about the eighth week, this developing groups of cells is called – – Fetus Embryonic Growth • As the embryo grows, its cells continue to divide, forming three tissue layers: – Respiratory and digestive system – Muscles, bones, blood vessels and skin – Nervous system, sense organs and mouth Embryonic Growth • During this time, two important structures form outside the embryo: – Amniotic sac: a thin, fluid-filled membrane that surrounds and protects the developing embryo. It also insulates embryo from temperature changes. – Umbilical cord: ropelike structure that connects the embryo and the mother’s placenta. • The placenta is a thick, blood-rich tissue that lines the walls of the uterus during pregnancy and nourishes the embryo. • Blood supply of the mother and developing embryo are kept separate, materials still diffuse from one blood supply to the other through the umbilical cord. – Harmful substances such as tobacco, alcohol or other drugs can cross the placenta and harm the embryo Fetal Development • 0-14 weeks – First Trimester • 15-28 weeks – Second Trimester • 28-40 weeks (birth) – Third Trimester • See Figure 19.2 in Textbook (pg. 488-489) Stages of Birth • Labor – – The final stage of pregnancy in which the uterus contracts and pushes the baby out of the mother’s body • Stage 1: Dilation • Stage 2: Passage through birth canal – Breech birth – baby enters the birth canal feet or buttocks first • Stage 3: Afterbirth (placenta) Proper Nutrition During Pregnancy • Calcium – helps build strong bones and teeth, as well as nerves and muscles. • Protein – helps form muscle and most other tissue. • Iron – makes red blood cells and supplies oxygen to cells. • Vitamin A – aids in cell and bone growth and eye development. • Vitamin B complex – aids in forming nervous system. • Folic acid – critical part of spinal fluid and helps close the tube that contains the central nervous system. **IMPORTANT THAT THIS BEGINS IN THE 2ND TRIMESTER** Proper Nutrition During Pregnancy • Weight gain is expected (25-35 lbs.) • Most only need an additional 300 calories per day, though. • Excess weight can be a health risk for mother and baby • Caffeine can increase risk of birth defects or low birth rate • Physical activity can be beneficial Tobacco and Pregnancy • It is estimated that smoking accounts for: – 30% of low birth weight – 14% of premature births – 10% of infant deaths • May also affect the growth, mental development and behavior of child until 11 years old • Secondhand smoke included in all this Alcohol and Pregnancy • Alcohol consumed during pregnancy quickly passes through the umbilical cord to the fetus. • The fetus breaks down alcohol much more slowly than an adult does, so the alcohol level in the fetus’s blood can be higher than that of the mother and remain higher for a longer period of time. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome A group of alcohol-related birth defects that includes both physical and mental problems • • • • • Mental retardation Learning disabilities Serious behavior problems Slowed growth Physical deformities including a small skull, abnormal facial features, and heart defects Medicines, Other Drugs, and Pregnancy • Using drugs can have serious consequences – Birth defects – Premature labor – Miscarriage • Even OTC medicines should only be taken with the approval of the doctor • A baby can be born addicted to the drugs the mother used during pregnancy. • The infant will suffer withdrawal symptoms: – hypersensitive and irritable and may cry for hours – tremble and jerk – May not bond with parents Complications During Pregnancy • Miscarriage – the spontaneous expulsion of a fetus that occurs before the 20th week • Stillbirth – dead fetus expelled from the body after the 20th week • Ectopic Pregnancy – zygote implants in the fallopian tube, abdomen, the ovary or the cervix. – Zygote can’t pass to the uterus – STD could be a reason – #1 cause of death of females in 1st trimester Sterility • Inability to reproduce – Males: may be due to stress, drug use or disease – Females: may be due to blocked fallopian tubes or severe scarring from STIs.