PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH
advertisement

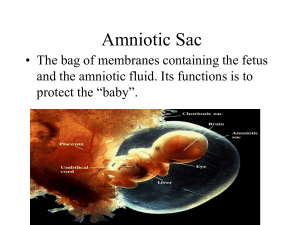
PREGNANCY AND CHILDBIRTH Beginning of life 1. Fertilization: Unite egg and sperm— becomes zygote 2. Implantation: zygote reaches uterus in 4-5 days and attaches to uterine wall—then is called an embryo when it attaches 3. After this happens you are pregnant and have HCG in your system Development in Uterus 1. Amniotic sac: fluid filled sac of thin tissue that develops around embryo for protection and temperature control 2. Placenta: lines the uterus during pregnancy and nourishes the embryo with substances from mothers blood---dangerous fluids can pass through this ie. Alcohol, tobacco and drugs 3. Umbilical Cord: develops between embryo and placenta—blood vessels carry nutrients and oxygen from placenta to embryo and wastes out Growing Embryo • First 2 months of development the body systems and organs start to form—heart beating, endocrine glands are examples FETUS • From 3rd moth to birth • 3rd to 6th month fetus starts to move— development of skeletal and muscular systems • Also sensitive to light and sound—nervous system • From 7th to 9th month—fetus continue to grow and accumulate fat, eyelids open and close • 9th month fetus ready to be born Healthy Pregnancy • Proper nutrition: Getting the right nutrients is most important because what you eat also feeds your baby • Exercise: reduces risk of diabetes • Avoiding alcohol and other drugs: even in small amounts they can harm your fetus and result in fetal alcohol syndrome, mental disabilities, heart defects and delayed growth • Avoid environmental hazards: x-rays, lead, mercury, and cat litter Prenatal Care • 3 trimesters: 3 months long each • Obstetrician: doctor specializes in pregnancy and childbirth • Monitoring tools -ultrasound: used to see baby -chorionic villus sampling: piece of placenta to determine any inherited disorders -amniocentesis: amniotic fluid to test for abnormalities Complications • Ectopic pregnancy: fertilized egg implants in fallopian tubfe instead of uterus—surgery is necessary to remove • Miscarriage: death of embryo in first 20 weeks-at least 15% of pregnancies end in miscarriage • Preeclampsia: high blood pressure, swelling of wrists and ankles and high levels of protein in urine-prevents oxygen to fetus • Gestational diabetes: high blood sugar levels— can result in big baby, hard delivery and breathing problems Birth Process • Labor: work performed by mother to push fetus out-strong contractions of muscles make cervix increase in width • Delivery of baby: contractions continue and push baby out of cervix and vagina usually head first • Delivery of afterbirth: push out placenta Postpartum period—period of adjustment for parents and their newborn beginnings first 6 weeks—periods of sadness could lead into postpartum depression Complications at Birth • Stillbirth: fetus passes away after the 20th week • Surgical delivery: cesarean section-surgery in lower abdomen into the uterus—done because mother not healthy, baby is breech (feet first), baby in distress • Premature birth: delivery before 37th week, baby not fully developed • Low birth weight: weighs less than 5.5 lbs., can also be premature, low birthweight happens for different reasons but drugs, alcohol and tobacco are a major cause