Introduction to EKG
advertisement

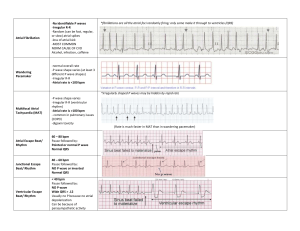
Introduction to EKG And then a little more • To get an accurate EKG, leads must be properly applied: aVR: RA(-) to [LA & LL(+)] I: RA(-) to LA(+) II RA(-) to LL(+) III:LA(-) to LL(+) Precordial lead is + aVL: LA(+) to [RA & LL(+)] aVF: LL(+) to [RA & LA(-)] • Normal activation • Interpretation: – Rhythm: look for P waves, regularity, reproducible intervals, PR interval, shape – Rate – Axis – Intervals: PR, QRS, QTc – Conduction – R wave progression – ST segments and T waves – Ectopic beats – Q waves: where they should and should not be – Other stuff • Some general guidelines: – P waves • Best seen in lead II • Upright or biphasic (neg component smaller) in V1-V2, upright in V4-V6 – QRS complex • • • • • • • V1 shows rS, V6 shows qR Size of r wave progressively increases, transition V3-V4 QRS duration < .120 sec One R wave in precordial leads should be > 8mm No R wave in precordial leads > 27mm Sum of tallest R in left leads and S in right leads should be < 35-40mm Precordial q waves should not exceed .04 sec nor have a depth greater than ¼ the height of the R wave following • R wave in aVL <12-13mm – ST segment • Should not be more than 1mm above or below baseline. Normal minor elevation in leads with large S waves ( V1-V3) and normal configuration is concave up. • T waves – Often inverted in V1. May be inverted in V2 if already inverted in V1. – Always upright in leads I, II, V3-V6 – Always inverted aVL • U waves – Amplitude usually < 1/3 T wave height in same lead – Direction is same as T wave in that lead • Axis – Frontal plane lead with the sum of r wave and s wave most closely approximates 0. – Look at QRS in the lead perpendicular to original lead – If QRS id positive, axis along that direction. If negative, axis in opposite direction. • Axis- cont Normal axis Left axis Right axis • Heart block – Normal PR interval < .2 sec – 1st degree AV block- prolonged PR • Heart Block – 2nd degree AV block- Wenchebach- Mobitz 1 • • • • Prolonged PR until dropped QRS 1st PR interval always the shortest 1 dropped QRS only RR intervals shorten • 2nd Degree- 2 to 1 block • 2nd degree type 2- mobitz 2 • Complete heart block • Bundle branch block – QRS > .120 sec – RBBB- R-R’ in V1-V2, s wave in lead 1 & V6 • LBBB – QRS >.120 sec – Neg QRS in V1 – Lack of small q in lead 1, V5-V6