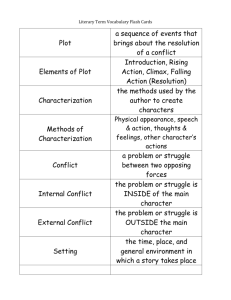
Elements of Literature Power Point Series
advertisement

Elements of Literature Power Point Series “It’s in the sauce.” Point of View: Where the Words are coming from. Function: Provides the reader with the _____ of _________ for the whole story. Establishes the ______ angle of the story. Determines the ______ of the story. 1st ______: “I” tells the story. We are inside a single person’s ____ and _____, so we see what they see, and the action is _______ to the perspective of one individual. The narrator then becomes one of the ____________ of the story. POV continued 3rd Person _______: A narrator tells the story but only reveals the ____ life of one character. The protagonist is referred to as “he” or “she.” (i.e. Harry Potter and Twilight) 3rd Person ________: A narrator tells the story from an all knowing point of view, revealing the inner life of ___ character they choose. The protagonist is referred to as he or she. Multiple ___ characters…epic size story. (i.e. The DaVinci Code…The Chronicles of Narnia.) Questions for analysis of Point of View Why did the author choose this ________ point of view? What does the ______ of point of view reveal about the author’s overall _______? Plot: The way the author _______ the events in a story. Function: Creates the cause/effect ____ that allows the story to ____ together. Controls the ____ of the story. Gives the right hints at the right times to ______ the reader in the story. Introduces, develops, and ________ the key conflicts that make the story worth telling. Beginning, Middle and End…Duh But it is not that simple. Plot _______ the most important aspects of life. Here are __ ways to look at it. Exposition…_____ Action…Climax…Resolution. Traditional view. Stories come full circle. W…W…W…end. (Should I stay or should I go?) Confusion and ______ of emotion. 3 Acts: Act I: Define characters, ______, and goals. Act II: Create _______ for characters and bring them to the brink of _______. Act III: Create the _______ moment where the character rises or _____, and then wrap up the story. Questions for analysis of plot Why did the author choose to ______ the details the way they did? Where are the key ________ points in the story? i.e. exposition to rising action…rising action to climax Is there anything significant about what the author chooses to _____ ___? What does the author do to create _______? Jumps in time or place. Foreshadowing, back story, etc. Changes in point of view. Are there any recognizable ______ in the action? What events in the story ______ the theme? Key Terms related to plot Foreshadowing: Use of an event or plot detail to help the reader _____ at what is coming in the story. Back Story: The part of a character’s story/past that is ___ ____ directly in the story. “In Medias Res”: The technique of starting a story in the _____ of an event/conflict, _______ the reader to catch up. Flashback: A ____ in ____ back to an event that occurred previously to the story’s plot. Setting: The ____ and place in which the events of a story occur. Function: Creates the mood and ____ of the overall story. Establishes the cultural/social ____ of the story. Transports reader into ____ world. Reader experiences “_______ of disbelief.” SIFT your way through the setting. Pay attention to places where the author has _______ the setting in ______ detail. Pay attention to _____, shape, and _____ of things in the setting. Pay attention to objects that have inherent symbolic characteristics: bridges, animals or flowers, ______, natural _____, sexual, religious, or _____ symbols, etc. Questions for analysis of setting? What characterizes the author’s ____ as he describes the setting? -or in other words- What ____ is established? What ______ concepts can be best associated with the time and place of the story? What _____ conflicts are created by the time and place of the story? Key Terms related to setting Hyperbole- use of ____ exaggeration to create a ______ effect. Local Color- use of details that provide _________ to a particular area or _____. Allegorical- A story where all aspects of the setting take on ______ meanings. Setting allusion: When the description of a setting _____ a setting from a famous story. (i.e. Duloc = ______, an ideal setting = garden of eden) Characterization: The methods an author uses to reveal a character’s personality Function: Reveals the traits, _____, and character ______ that are relevant to the story. Creates _______ or ______ in the reader to make the story more interesting. Generates the theme through the character’s ______ and reactions to events in the story. Gives meaning to ______ in the story. Methods of Characterization: Direct description: The author describes the ______ and sometimes ______ traits of the character. Action: The character is revealed through their _______ and responses to situations. Reaction of other characters: The character is revealed by the way _____ see them. Dialogue: The character is revealed by the way they ____. Internal monologue: The character is revealed through description of their ____ thought life. Questions for analysis of Characterization? What does the character ____? How does the character _____ to conflict in the story? What ____ has the author revealed? What kind of character are we dealing with? Round or ____, _______ or static? How does the character’s actions create the theme of the story? (i.e. a story about ________ will have a character who struggles to _____.) Key Terms related to characterization Protagonist or ______: The main character playing the role of the “good guy” or the main character ____ the role of the “bad guy.” Pro = we are ____ for them. Anti = we are _____ against them. Flat or Round: Flat ______ reveal only ___ personality trait. Round characters reveal ___ dimensions (sometimes ______ traits). Static or _____: Static characters do not change. Dynamic characters change and _____. Key terms related to characterization, con’t: Foil: When two characters _____ so strongly they create a thematic connection. Minor character: Characters who are not at the center of the story, but who ______ the plot by their relationship to the major characters. Allusion: References to meaningful images ______ the realm of the story. Function: To add an extra _______ to the story. To make the meaning of the story more ______. To make the ______ reader feel smarter. Types of allusions: Biblical Mythological Literary Popular Culture Questions for analysis of allusion? What does the allusion add to the story? How does the allusion ___ into the ______ of the story? Is the allusion ______ to be _____? Irony: A contrast between _______ and _______. Function: To create ______. To intensify the _____ of any given scene. To ______ the emotional tone. Types of Irony: Situational: When the ____ of a situation is the _____ of what one would expect. Verbal Irony: When one person says something, but ____ something else entirely. Dramatic Irony: When the ____ knows something that the _______ do not. Questions for analysis of Irony? What ____ of irony is on ____ here? Is the author’s use of irony _______? What does the irony ___ to the ____ of the piece?