Rhetorical Transaction: Appeals, Modes, and Analysis
advertisement
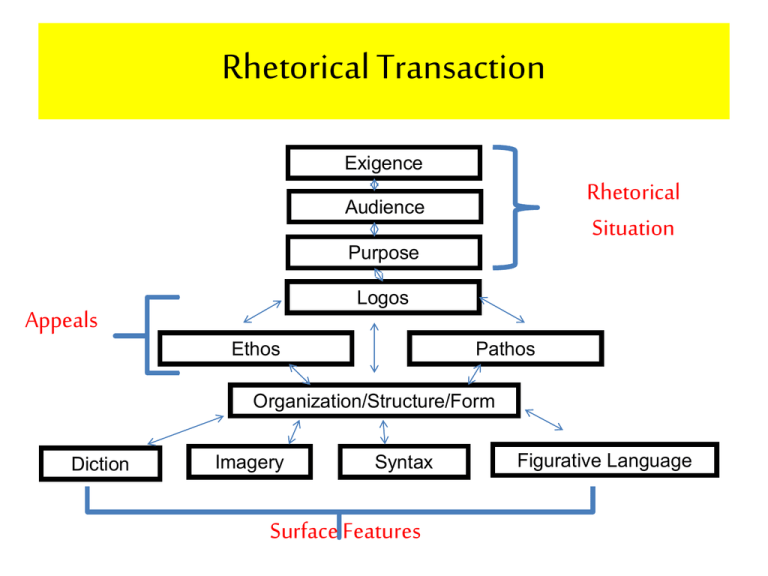
Rhetorical Transaction Exigence Rhetorical Situation Audience Purpose Logos Appeals Ethos Pathos Organization/Structure/Form Diction Imagery Syntax Surface Features Figurative Language Rhetorical Modes: Patterns of Development 8 major patterns Organize individual paragraphs or sections •Narration •Description •Process Analysis •Exemplification •Comparison & Contrast •Classification & Division •Definition •Causal Analysis Author’s Purpose Organize entire text Narration 1) Tells story; recounts events; personal 2) Chronological (detail, pov, dialogue) 3) Craft story to support thesis 4) Often used as a way to enter topics 5) Draws a reader in Description 1) Paints a picture with senses; details 2) Establishes mood/atmosphere 3) Empathy; connection to text Process Analysis 1) Explains how something works 2) Clear and logical 3) Proper transitions 4) Concise verbs Exemplification/Illustration 1) Provides a series of examples 2) “Let me give you an example…” 3) Aristotle = Induction = series of examples lead to general conclusion Comparison & Contrast 1) Analyze information 2) Similarities & differences 3) Subject by subject 4) Point by point Classification & Division 1) What goes together & why 2) Categories….to help readers see relationships between seemingly unrelated things Definition 1) Established common ground 2) Identifies areas of conflict Causal Analysis 1) Cause leads to an effect 2) Effect that results from a cause 3) Needs logic 4) “Why” in the title Rhetorical Transaction Exigence Rhetorical Situation Audience Purpose Logos Appeals Ethos Pathos Organization/Structure/Form Diction Imagery Syntax Surface Features Figurative Language Narration What it does: * Relates events in some climatic sequence * Tells a story When to use: * Fiction * Essays, news releases, case histories, etc. * Anecdotes * Relate an experience; present dramatically Narration How to write: * Have a point * Pace the story * Tell the story from a consistent P.o.V. * Insert appropriate details Tone Definition: a literary technique which encompasses the attitudes toward the subject and toward the audience implied in a literary work Tone For Discussion: What is the difference in TONE between the two parts? “Shooting an Elephant” George Orwell • • • • Read pages 199-205 Do questions 1-5 (The facts) Do questions 1-5 (The Strategies) Due Thursday