Non-Fiction
advertisement

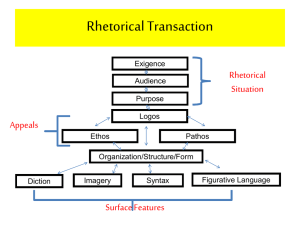
Non-Fiction A Rhetorical Analysis First, start by identifying the piece: Genre: artistic category or style Types of genres we will cover in class: • Speech • Letter • Narrative • Essay • Documentary Author’s purpose: the reason the author writes; what the reader wants to take with him/her from the text. Example: Martin Luther King Jr. wrote his “I Have a Dream” speech to inspire/persuade people to believe in a future with freedom for all. Example: Maya Angelou wrote her memoir I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings to share her story with the world and inspire others who are struggling. Audience: A writer’s readers or listeners. It is important to know the audience of the work to understand authors purpose. The audience determines what rhetorical devices to use. Example: Squealer is able to convince the animals to believe anything he says no matter how unpleasant because he knows that his audience has a need for reassurance and a natural need to believe the voice of authority. Exigence: an issue, problem, or situation that causes or prompts someone to write or speak. (Why now?) Your job is to determine the exigence of each work. Example: Martin Luther King Jr’s “I Have a Dream” is powered by the civil rights movement, which King is a key leader. Tone: the writer’s or speaker’s attitude toward the subject. It is your job to determine the tone the Author creates and why. Example: Orwell adopts a humorous and light hearted tone in the alcohol scene of Animal Farm so that his readers will enjoy his work of satire. When writing your essay, avoid saying: The writer uses tone since ALL writers use a tone of some kind. Instead, say: The writer creates a __________ tone... flippant indignant callous caustic didactic droll incredulous effusive ominous haughty Facetious forthright amiable tactful vexed Quiz dates: Final Exam: Find flashcards on quizlet.com under the username bixbyenglish9 Satire: (this a specific tone we will focus on during this unit) A literary work in which vices, follies, stupidities, abuses, etc., are held up to ridicule and contempt.A pointing out of the difference between how things are and how they ought to be. Your job is to decide what the author is making fun of and how. Example: Vonnegut satires the United States everlasting quest for equality even at the expense of individuality in his short story “Harrison Bergeron.” He mentions the “211th, 212th, and 213th amendments to the constitution” to mock our The next step for analysis is to find the figurative language in the piece and the effect it has on the piece. Figurative Language: any element or the entirety of elements a writer uses in the structure of their work. Types of figurative • Simile language to look for: • Metaphor • Hyperbole • Personification • Imagery Example: In Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream” speech, he contrasts segregation with racial justice by using the contrasting metaphors of dark and desolate valley (of segregation) and sunlit path (of racial justice.) Next you should search for rhetorical devices. Anecdote: a brief story told as an example to illustrate a point. Your job is to find out why the author uses this anecdote. (how does it further prove his/her point?) Novelist, Amy Tan, in her narrative essay, Fish Cheeks, she recounts an embarrassing Christmas Eve dinner when she was 14 years old. Tans purpose is to convey the idea that, at fourteen, she wasn’t able to recognize the love her mother had for her or the sacrifices she made. She adopts a sentimental tone in order to appeal to similar feelings and experiences in her adult readers. Allusion: a reference to a historical or literary person, place, event, or aspect of culture. Your job is to find out why the author makes the allusion. Example: Martin Luther King Jr.s repetition of the phrase “Let freedom ring” is an allusion to the star spangled banner. He is alluding to this document to show how America was founded on this principle, therefore everyone deserved it (King). Diction: the word choice, including the vocabulary used, the appropriateness of the words, and the vividness of the language. It is your job to determine if the author intentionally uses certain diction and what it indicates. Look for specific words or phrases that seem stronger than other. Never write: The author used diction in an rhetorical analysis essay! Examples: *A coat isn’t torn; it is tattered. *The US Army does not want revenge; it is thirsting for revenge. *A door does not shut; it thuds. Denotation: the meaning of the word is strictly literal, as found in the dictionary. “Squealer always spoke of it as a readjustment and never as a reduction” (Orwell 112). Denotation: Literally translated: both “readjustment” and “reduction” meant they had less food. Vs. Connotation: Readjustment makes the animals feel better because it doesn’t imply less food. Connotation: the meaning of a word that carries ideas and feelings. Dialect: a regional variety of language distinguished by features of vocabulary, grammar and diction employed by a specific people as distinguished from other persons geographically or socially. Example: Twain uses dialect in his novel Huck Finn to differentiate between characters, such as when Huck and Finn are discussing Jim’s freedom: Jim: “We’s safe,Huck, we’s safe! Jump up and crack yo’ heels! Dat’s de good ole Cairo at las’. I jis knows it!” Huck: “I’ll take the canoe and go see Jim. It mightn’t be, you know.” Repetition: Repeated words or phrases for effect. Example: The word “comrade” was used throughout Animal Farm to remind the animals that they were a team united for one cause. This made them feel like they were a part of all the decisions made on the farm (Orwell). Anaphora: repetition of beginning phrases of sentences to create a dramatic effect. It is your job to identify the anaphora and determine the effect. Example: In time the savage bull sustains the yoke, In time all haggard hawks will stoop to lure, In time small wedges cleave the hardest oak, In time the flint is pierced with softest shower. — Thomas Kyd, The Spanish Tragedy, I, vi. 3 Parallelism: an arrangement of the parts of a composition so that elements of equal importance are balanced in similar constructions. It is your job to identify what two things the author is saying are of equal importance and the effect of this statement. Ex 1: In Patrick Henry’s historical speech he states, “Give me liberty or give me death” to show that a life without liberty is equal to death (Henry). Ex 2: "The inherent vice of capitalism is the unequal sharing of blessing; the inherent virtue of socialism is the equal sharing of miseries." Aristotle Appeals There are 3 Aristotle appeals: • Ethos • Pathos • Logos Logos: argument based on logic Ethos: Developing trust, ethics, or credibility. Pathos: Emotional words Logical Fallacies: Sometimes authors use arguments that are fallacies. A logical fallacy is an error in reasoning that renders an argument invalid. Bandwagon •Everybody is doing this. •If you want to fit in, you need to “jump on the bandwagon” and do it too. •The implication is that you must JOIN in to FIT in. Clipart-Microsoft Office XP 2002 Ike for President Slippery Slope a relatively small first step leads to a chain of related events culminating in some significant effect, much like an object given a small push over the edge of a slope sliding all the way to the bottom. We’ve all seen how this ends Mud slinging the use of insults and accusations, esp. unjust ones, with the aim of damaging the reputation of an opponent. Not for Tennessee Hasty Generalization reaching an inductive generalization based on insufficient evidence— essentially making a hasty conclusion without considering all of the variables. Sad Cat Diaries Plain-folks appeal This idea, product, or person is associated with normal, everyday people and activities. Real People Transfer •Symbols, quotes, or images of famous people are used to convey a message. •The message may not necessarily be associated with them. Slavery Faulty Dilemma when someone tries to force on you only one answer (either or ) Ex: “Either you have faith or you believe science.” "This is Alabama. We Speak English. If you want to live here, learn it.” Fear Mongering •the use of fear to influence the opinions and actions of others towards some specific end. Peace Little Girl “Daisy” Straw Man: a type of argument and is an informal fallacy based on misrepresentation of an opponent's position Saddam back in power? Card-Stacking only presenting information that is positive to an idea or proposal and omitting information contrary to it. Lesser of Two Evils tries to convince us of an idea or proposal by presenting it as the least offensive option. Repetition Convincing someone to do something by repeating the slogan, song, picture, word to embed it in the brain. – Billboards for attractions – Commercials with repeating phone numbers Head On: apply directly to the forehead