14_-_nato_eu_ppt
advertisement

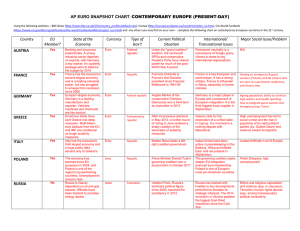
Europe and Russia Tying in Putin, NATO, & EU Debt Crisis We don't appreciate what we have until it's gone. Freedom is like that. It's like air. When you have it, you don't notice it. Boris Yeltsin, 1995 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= wklk123BIa0 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= 7Y49WSc_swo http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/eur ope-july-dec13-ukraine2_12-17/ http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/wh y-russia-is-flexing-muscle-crimea/ Putin’s Rise to Power KGB from the mid 1970 to 1991 Leningrad city council from 1991-1994, then mayor’s aide 1996-1998: Yeltsin advisor 1998: named head of federal security agency 1999: appointed Russian prime minister by Yeltsin Rise to Power continued… Elected President March 2000 Re-elected 2004 Highlights of presidency • Butted heads with powerful oligarchs and media tycoons • 2002 Dubrovka theatre and 2004 Beslan school hostage situations • Chechnyan war • Growing economy thanks to rising oil prices Tandemocracy Russian constitution bars a third term so… • Putin supported Dmitry Medvedev in the 2008 election • Medvedev easily won, nominated Putin his Prime Minister Medvedev stepped down in 2012, Putin ran again and won US-Russian Tensions 2008: Georgia was pushing to join NATO • parts of Georgia (Abkhazia and South Ossetia) wanted independence, • Russia recognized and sent troops to “keep peace” 2013: US wanted to strike Syria, • Putin (ally of Bashir) refused to let UN strike, • brokered a weapons surrender instead Human rights: • • • • banned US adoption of Russian kids, jailed Pussy Riot, banned gay couples from adopting kids, cracked down on homosexuality in general 2013: granted Edward Snowden asylum Western European Cooperation 1948: Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg form the Benelux trade union 1957: West Germany, France, Italy join Benelux to form European Economic Community 1968: Denmark, UK, Ireland, Spain, Portugal, Greece join EEC Maastricht Treaty: January 1992 • Economic union • Single currency (Euro) • Coordination of foreign and defense policy European Union There are currently 28 members in the EU List of members 500 million citizens Largest and wealthiest trading block 30% of the world’s economy 17 countries use the Euro (not the UK) The monetary union (Eurozone) did not include a fiscal union with central financial planning authority • This worked fine from 1999 to 2009 • Lack of central authority allowed countries to grow large debts, made it difficult to resolve the cirisis EU Constitution Proposed in June 2004 Purpose: Centralize decision making, unify treaties and agreements that governed the EU France and Netherlands said no, it would take away national sovereignty • Common thread throughout history of EU Treaty of Lisbon was passed in 2009 as a compromise – streamlined EU institutions, less central authority Debt Crisis Fall 2009: The EU begins to realize that Greece (2001) had been hiding the true size of their debt • Ireland, Portugal, Italy and Spain too The EU, European Central Bank and the IMF put together a $171b emergency loan package to Greece, Ireland, Portugal to avoid bankruptcy To get the loans, the countries needed to adopt fiscal austerity measures: slash social programs and wages, raise retirement age and taxes, etc Greek citizens were not happy Debt Crisis continued Debt crisis caused a rift: • stronger economies like Germany are resentful • economic progress put in danger by the weaker members December 2011: France and Germany lead negotiations for an EU-wide fiscal agreement • All members would have to strictly limit debts and deficits relative to the size of their economy Turning Point Economic growth stayed stagnant or even contracted through 2012 Unemployment in Greece and Spain rose to 20+% In response • voters in many countries tossed out incumbents • electing radicals that promised to move from austerity to stimulus If Greece could not pay its bills, it would have to abandon the Euro and go back to its own currency – this could collapse other weaker Eurozone countries Current State of Crisis If the debt crisis spreads beyond Europe, could lead to a worldwide recession More critics of austerity have emerged (Obama) • US stimulus package in 2009 helped pull the US out of recession • Austerity measures were failing to pull Europe out of debt Pro-austerity leaders (Merkel) are still unwilling to negotiate • European social programs have overspent for decades, it’s time to scale them back