Subject: Economics with Financial Literacy
advertisement

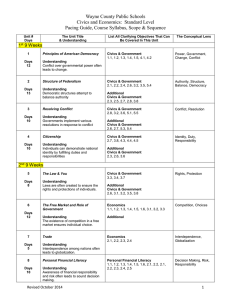
Lesson Plans Subject: Economics with Financial Literacy Week of: Teacher: Mr. J. Ruggiero November 3 - 7, 2014 Organizing Principle: Understand the fundamental concepts relevant to the development of a market economy. Measurement Topic Benchmark(s) Learning Target Monday Tuesday Financial Literacy Financial Literacy Financial Literacy Financial Literacy Financial Literacy SS.912.E.2.10 SS.912.FL.3.5 SS.912.FL.5.12 SS.912.E.1.14 SS.912.FL.4.1 SS.912.FL.4.2 SS.912.FL.4.9 SS.912.FL.4.12 SS.912.FL.4.3 SS.912.FL.4.5 SS.912.FL.4.6 SS.912.FL.4.7 SS.912.FL.4.8 SS.912.FL.4.13 SS.912.FL.1.1 SS.912.FL.1.2 SS.912.FL.1.3 SS.912.FL.2.1 SS.912.FL.2.3 SS.912.FL.2.4 SS.912.FL.3.4 SS.912.FL.4.4 SS.912.FL.4.11 SS.912.FL.5.8 SS.912.FL.6.4 Describe the organization and functions of the Federal Reserve System. Compare credit, savings, and investment services available to the consumer from financial institutions. Loans can be either secured or unsecured with collateral. Non-income factors can influence which jobs/careers people choose. Consumer decisions are influenced by prices, prices of alternatives/substitutes, income and other preferences. The possible benefits of education/training must be weighed against the immediate costs. Before purchasing a good, consumers should consider its features, durability and maintenance costs. People make more informed education, job, or career decisions when they evaluate the costs and benefits of different choices. Consumers can be influenced by a good or services pricing. Government agencies supervise and regulate financial institutions to help protect the safety, soundness, and legal compliance of the nation’s banking and financial system. The Security and Exchange Commission (SEC), the Federal Reserve, and other government agencies regulate financial markets. Consumers should compare the cost of credit by considering annual percentage rate (APR), initial fees, late payment fees, annual fees, and missed payment charges. Financial institutions sometime compete by offering low introductory credit rates that increase at a set date or after a late/missed payment. Consumers who have difficulty repaying debt Wednesday Lenders determine eligibility and interest rates largely based upon the payment history of loan applicants which can be obtained via credit reports. Credit Bureaus ae businesses that calculate/compile ratings of loan applicants-called a credit score-and provide them to lenders. An applicant’s credit score can also be used by prospective employers, landlords, insurance companies, Thursday Friday Describe ways that money received (or paid) in the future can be compared to money held today by discounting the future value based on the rate of interest. Down payments on a loan give borrowers an equity stake in the transaction which reduces not only the principal being borrowed can seek assistance through credit counseling services and/or by negotiating directly with their leaders. There are laws in place to protect those who use credit. but also the risk to the lender which can result in a lower interest rate. and even utility companies. Failure to repay a loan has significant consequences for borrowers such as negative entries on their credit report, repossession of property (collateral), garnishment of wages, and the inability to obtain future loans. Mortgages are a popular type of loan for people buying homes or other types of real estate. Discuss ways that the prices of financial assets are affected by interest rates and explain that the prices of financial assets are also affected by changes in domestic and international economic conditions, monetary policy, and fiscal policy. Consumers are entitled to an annual free copy of their credit report. People may be required by governments or by certain types of contracts (e.g., home mortgages) to purchase some types of insurance. Lesson Assessment (D,F,S) Work through EverFi Financial Literacy modules. Obs/Dis (D) Work through EverFi Financial Literacy modules. Obs/Dis (D) Work through EverFi Financial Literacy modules. Obs/Dis (D) Work through EverFi Financial Literacy modules. Obs/Dis (D) Work through EverFi Financial Literacy modules. Obs/Dis (D) EverFi Module 2: Banking Quiz (F) EverFi Module 3: Payment Types Quiz (F) EverFi Module 4: Credit Scores Quiz (F) EverFi Module 5: Higher Education Quiz (F) EverFi Module 6: Renting vs. Owning Quiz (F) Accommodations: Visuals; Cooperative Learning; Repeat, clarify, summarize directions; Allow extra time for assignments/tests