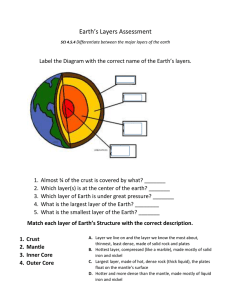
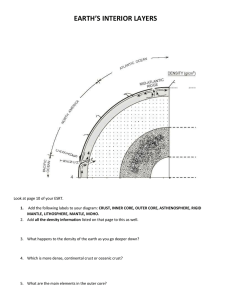
Layers of the Earth
advertisement

1. _____heat from inside the Earth 2. _____type of resource minerals and metals are 3. _____cutting down all of the trees in an area 4._____crops that replenish the nutrients in the soil 5. ___what does the anchoring of plant roots prevent 1._____burning of wood or dung 2. _____type of resource sun, wind, water 3. _____moving of sediment 4._____various methods humans use to save the soil 5. ___what does the anchoring of plant roots prevent • • • • • • • • • • • • • • What are the layers of the Earth? What is the crust? What are the characteristics of the Earth’s Crust? What is the composition of the Earth’s Crust? What is the lithosphere? What is the Moho? What is the mantle? What are the characteristics of the Earth’s Mantle? What is the composition of the Earth’s Mantle? What is the asthenosphere? What is the mesosphere? What is the core? What is the outer core? What is the inner core? • Crust • Mantle • Core • • • • • Thinnest layer Outermost layer Made of rock Covered by water, soil, life Made of oxygen, aluminum, silicon, iron, and magnesium • 2 types continental and oceanic • Crust floats on the mantle. • Two layers – Top layer of granite and a more dense bottom layer of basalt. Both layers are found under continents, only the basalt layer is under the oceans. • Temperatures increase with depth: 20° C at top and 870° C at bottom. • Thickness: 5 to 100 kilometers thick Continental Crust: ~ 30 km Oceanic Crust: ~ 5 km • Oxygen: ~ 50% • Silicon: ~ 30% • Aluminum: ~ 10% • thickest part of the Earth • Made of iron, oxygen, silicon, aluminum, and magnesium • Temperatures: Top of mantle is ~ 870° C and bottom is ~ 2,200° C. • Rock begins to flow like very thick syrup as temperature increases. • Thickness: ~ 2,900 km • Upper and Lower Mantle – they differ in temperature, density, and pressure. These increase as depth increases. • Silicon, Oxygen, Iron, and Magnesium • The deeper the rocks are in the mantle, the more iron they hold. • Innermost layer of the Earth. • Made of iron and nickel • Two layers – Outer Core and Inner Core • Made up of crust and uppermost layer of the mantle. • Broken into pieces (tectonic plates) which move around on the asthenosphere. • Upper part of the mantle. • Soft, weak, hot rock (magma) • Tectonic plates float on • Lower mantle. • Solid and rigid moves slowly • LIQUID iron and nickel • Creates Earth’s magnetic field which protects us from solar radiation • Solid iron and nickel • Highest temperature, pressure, and density • Solid due to extreme pressure bearing down. • Boundary between the crust and the mantle that is more dense than the crust.