IB History Year 2: 20th Century World History Ms. Makarczuk and Ms
advertisement
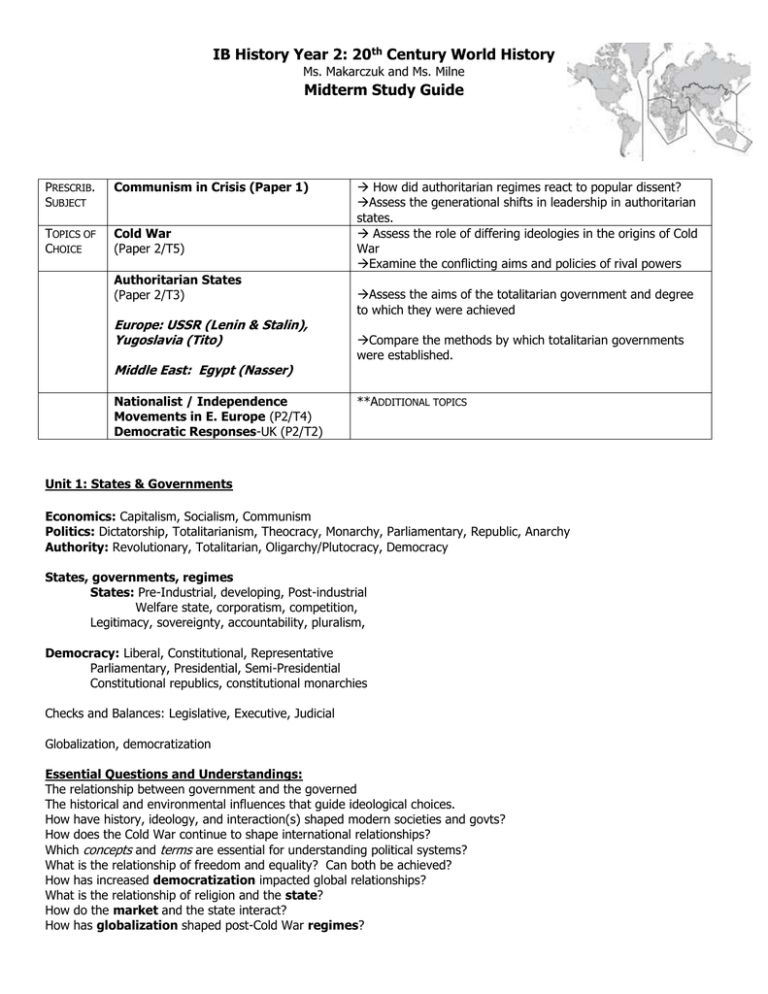
IB History Year 2: 20th Century World History Ms. Makarczuk and Ms. Milne Midterm Study Guide PRESCRIB. SUBJECT Communism in Crisis (Paper 1) TOPICS OF CHOICE Cold War (Paper 2/T5) Authoritarian States (Paper 2/T3) Europe: USSR (Lenin & Stalin), Yugoslavia (Tito) Middle East: Egypt (Nasser) Nationalist / Independence Movements in E. Europe (P2/T4) Democratic Responses-UK (P2/T2) How did authoritarian regimes react to popular dissent? Assess the generational shifts in leadership in authoritarian states. Assess the role of differing ideologies in the origins of Cold War Examine the conflicting aims and policies of rival powers Assess the aims of the totalitarian government and degree to which they were achieved Compare the methods by which totalitarian governments were established. **ADDITIONAL TOPICS Unit 1: States & Governments Economics: Capitalism, Socialism, Communism Politics: Dictatorship, Totalitarianism, Theocracy, Monarchy, Parliamentary, Republic, Anarchy Authority: Revolutionary, Totalitarian, Oligarchy/Plutocracy, Democracy States, governments, regimes States: Pre-Industrial, developing, Post-industrial Welfare state, corporatism, competition, Legitimacy, sovereignty, accountability, pluralism, Democracy: Liberal, Constitutional, Representative Parliamentary, Presidential, Semi-Presidential Constitutional republics, constitutional monarchies Checks and Balances: Legislative, Executive, Judicial Globalization, democratization Essential Questions and Understandings: The relationship between government and the governed The historical and environmental influences that guide ideological choices. How have history, ideology, and interaction(s) shaped modern societies and govts? How does the Cold War continue to shape international relationships? Which concepts and terms are essential for understanding political systems? What is the relationship of freedom and equality? Can both be achieved? How has increased democratization impacted global relationships? What is the relationship of religion and the state? How do the market and the state interact? How has globalization shaped post-Cold War regimes? Unit 2: 20th Century Chronology & Cold War Origins How does historiography impact interpretations of the Cold War? Chronological development of rivalries, new states, phases of Cold War Development of international institutions and organizations Rise of Russia Creation of the USSR: Russia becomes Soviet Union under Lenin: 1905: Industrialization (Witte), Bloody Sunday, October Manifesto, State Duma (Legislature) Political Parties: Anarchists, Social Revolutionaries, Social Democrats (Marxists) Bolsheviks vs. Mensheviks, Kadets, Octoberists, Union of the Russian People, Czarists 1917: February Revolution, Provisional government Alexander Kerensky, Strikes (Women too), Collapse of 2nd Gov’t 1917/1918: Lenin’s Return, Bolsheviks, “Bread, Land & Peace,” October Revolution, Arrest of Tsar /Execution, Treaty of BrestLitovsk, Formation USSR, multiparty Civil War (1918-1922), War Communism 1921: Kronstadt Revolt, Drought & Famine, NEP, Lenin’s 1st strokes 1920s: NEP, Scissors crisis (’23 currency), labor laws, literacy, Death of Lenin (1924), Last testimony (Stalin=unfit ruler), Stalin and Trotsky split 1924: Constitution, authoritarian Politburo Trotsky Menshevik, leader of the red army during the civil war, (Jewish anarchist devil or St. George the dragon slayer?), believed in global communist revolution, exile, Mexico, assassination (1940) Stalin Georgian, Commissar of Nationalities (17-23), “Revolution in one country,” General Secretary of Central Committee (1922-1953) USSR under Stalin: Totalitarian Government: 1 leader, 1 political party, spies, propaganda, paranoia, elimination of enemies, cult of personality, promote nationalism, state control of all aspects of life: government, economy, military, family, education (young pioneers), media (censorship, Pravda)… Everyday Stalinism: 5 Year plans (1928-1991), industrialization, collectivization, nomenklatura system, forced labor camps (Siberian gulags), cult of Lenin, “Dizzy with success,” “The Vanishing Commissar” 1932-1933: Holodomor (Ukrainian forced famine) punish/ purge Kulak class, genocide, 7-10 million people ** Commonly oppressed groups Ethnic minorities (numbering in the millions), Jews, Kulaks, Religious leaders 1936: New Stalin Constitution, year of the stakhanovites (record setting shock workers), roll back in rights of women (duel burden of worker & homemaker, hero mothers, abortion made illegal again) *Stalin’s Henchmen: Beria (Cheka, NKVD), Molotov (Nazi-Soviet Pact), Malenkov (missile program) 1936-1938: Purges/show trials, Trial of 21 (Bukharin, Trotsky, Rykov) Beria has to go, Malenkov is a no, Khrushchev runs the show Paper 2 Topic 3 Theme 1: Origins and nature of authoritarian and single-party states Conditions that produced authoritarian and single-party states Totalitarianism: the aim and the extent to which it was achieved Emergence of leaders: aims, ideology, support Theme 2: Establishment of authoritarian and single party states Methods: force, legal Form of government, (left-and right-wing) ideology Nature, extent and treatment of opposition Theme 3: Domestic policies and impact Structure and organization of government and administration Political, economic, social and religious policies Role of education, the arts, the media, propaganda Statues of women, treatment of religious groups and minorities Unit 3: The Cold War (Paper 2-Topic 5) Assess the role of differing ideologies in the origins of Cold War Examine the conflicting aims and policies of rival powers. - The Struggle for Europe – USSR, Berlin, - Globalization of the Cold War – Asia, Latin America, Middle East - Competition and Co-Existence Cold War Steps: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Wartime Conferences: Tehran 1943, Yalta 1945, Potsdam 1945 Kennan’s Long Telegram, February 1946 Churchill’s Iron Curtain Speech, March 1946 (and Stalin’s reply) Truman Doctrine, March 1947 and Cominform, October 1947 Marshall Plan, June 1947 Red Army occupation of Eastern Europe, 1945-1947 Czech Coup, February 1948 Berlin Crisis: Blockade, June 1948 & Airlift until May 1949 NATO established, 1949, East and West Germany split, 1949 COMECON Founded 1949 NSC-68, April 1950 East German Worker’s Strike Potential Paper 2 Questions: ** Examine the conflicting aims and policies of rival powers which caused the Cold War **"An unnatural alliance that was bound to fall apart after the defeat of the common enemy." To what extent does this statement explain the origin of the Cold War? To what extent does this statement explain the origin of the Cold War? ** “The Cold War was caused by fear, not aggression.” To what extent does this view explain how the Cold War developed between 1945 and 1949? **How, and to what extent, did the conferences at Yalta and Potsdam (1945) contribute to the origin of the Cold War? ** To what extent did events in the final year of the Second World War turn wartime allies into Cold War enemies? ** Assess the part played by differing ideologies in the origin of the Cold War. **Analyse the origin of East-West rivalry and explain why it developed into the Cold War. **For what reasons, and with what results, did the Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan effect Cold War development? ** For what reasons, and with what results, were there disagreements between participants at the conferences of Yalta and Potsdam in 1945? HISTORIOGRAPHY: Marxist: Western Liberal / Western Traditional: Soviet Orthodox: Revisionist: Post-Revisionist: Post Cold War: Unit 4: Authoritarian States (PAPER 2-Topic 3) Assess the aims of the totalitarian government and degree to which they were achieved. Compare the methods by which totalitarian governments were established. Compare authoritarian states – left vs. right wing ideologies Europe: USSR (Lenin & Stalin), Yugoslavia (Tito) Middle East: Egypt (Nasser) Theme 1: Origins and nature of authoritarian and single-party states Conditions that produced authoritarian and single-party states Totalitarianism: the aim and the extent to which it was achieved Emergence of leaders: aims, ideology, support Theme 2: Establishment of authoritarian and single party states Methods: force, legal Form of government, (left-and right-wing) ideology Nature, extent and treatment of opposition Theme 3: Domestic policies and impact Structure and organization of government and administration Political, economic, social and religious policies Role of education, the arts, the media, propaganda Statues of women, treatment of religious groups and minorities Tito Background: Balkans Ottoman and Austro Hungarian control Origins of WWI (Assassination of Franz Ferdinand) Rise of Tito: WWII: Partisans resistance group led by Josip Broz (aka Tito) Defeat Germans, Establish communist government, Yugoslavian Federation Nasser Background: Egypt 1800s: Independent, but under Ottoman control 18050s & 1860s: French company builds Suez Canal 1880s: British but controlling stake in canal Post WWI: British Protectorate 1936-1952: Reign of King Farouk (tool of the British) Authoritarianism: Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY) Prime Minister 1943-1963, President 1953-1980 Rise to Power: Military, fought in 1948 Arab-Israeli border clashes Free Officers Movement 1952 coup (VP) 1954 President Suppressed nationalist insurrections (accusations of systematic elimination of ethnic Germans) Key Terms: Arab Nationalism, Pan Arabism, Arab Socialism, Nasserism Break with Stalin (Tito-Stalin split 1948-1951) -The first (and only successful) Cominform member to defy Soviet hegemony Authoritarianism & Domestic Policies: -1956 Constitution (single party state) -Suppression of opposition (Communists and Muslim Brotherhood) *authoritarian dictatorship* Non-Aligned Movement (1961+) 1956: Aswan Dam Project and Suez Crisis Titoism: Marxist-Leninist socialism, but independent from USSR 1961: Non-Aligned Movement, United Arab Republic Death: 1980 1967: Six Day War Non-Aligned Movement: • 1955: Bandung Conference (Asian-African Conference) • Five founding members: India, Yugoslavia, Indonesia, Egypt, Ghana • Goals of NAM: National independence, sovereignty, Territorial integrity, Security of non-aligned countries in their struggle against imperialism, colonialism, racism, foreign aggression, occupation, domination Potential Paper 2 and 3 Questions: SL: 20th Century World (Paper 2) HL: HOA (Paper 3) Compare and contrast the rise to power of two rulers of single-party states, each chosen from a different country. To what extent were the wars of independence in Latin America due to the grievances of the Creoles against the peninsular Spaniards? Support your answer with reference to one independence movement. Assess the role of economic and social policies as factors explaining the consolidation and maintenance of power of two of the following: Lenin, Stalin, Tito, Nasser. Compare and contrast the foreign policies of two rulers of single-party states, each chosen from a different country. Assess the methods used by either Nasser or Stalin to remain in power Examine the global impact of one ruler of a single-party state. Evaluate the relative impact of economic measures and political ideas, in promoting independence in two colonies of the region. With reference to two countries of the region, to what extent did the civil rights of Native Americans change from the 1960s to the 1980s? Why was the African American Civil Rights Movement in the United States more effective in the years 1954 to 1964 than in the late 1960s? Explain how and why the position of African Americans improved in United States society between 1877 and 1945. HOA Review: Unit 1: Colonization to Independence movements 17th- and 18th-century Enlightenment thought Key events Native American Indians Slave trade Varieties of immigrant motivation, ethnicities, and experiences Colonial experience: political Colonial charters and selfgovernment Colonial slavery Freedom of the press: the Zenger case Salutary neglect, rights of citizens in America The forces that contributed to the rise of the independence movements The paths the movements followed Characteristics of independence processes Immediate effects of the independence movements Unit 4 - US Civil War: causes, course and effects 1840-77 Economic and social conditions leading up to the war Origins of the Civil War The course of the war Reconstruction African Americans in the Civil War and in the New South Unit 8 - The Great Depression and the America’s 1865-1929 Causes of the Great Depression Nature and Efficacy of Solutions of the Great Depression Impact of the Great Depression Unit 11 - Civil Rights Movement The Beginning of the Movement The Kennedy years: Civil rights actions Johnson and the Great Society: continued demands for equality: civil rights movement The modern women’s movement Rising consciousness of Hispanic-Americans Demands for equality: American Indian Movement (AIM) and other protests Rights of the accused







