2013-04-29
advertisement

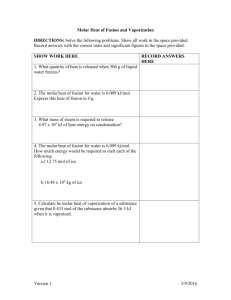
4/29/2013 and 4/30/2013 Standards: 7 (Chemical Thermodynamics) Objectives: ● Students will be able to calculate 2 problem types: a. specific heat problems b. heats of vaporization or fusion DO NOW: 1. Given: 3.70 J and ΔT -21 ---> -41 Find: mass of water 2. Given: 2.25 mol methanol Find: kJ required to vaporize if at -33.3 °C (bp of methanol) HOMEWORK: 1. None =========================================================== BASKET: ● Journal 4/26 (What you learned, or relearned about (for heat of vaporizaiton) specific heat calcs and heats of vaporization and fusion) =========================================================== Please check to see if you accidently put a "W" eraser in your backpack. Who goes with What? Specific Heat J/g°C Heat of fusion kJ/mol Heat of Vap kJ/mol slopes Given Find Given °C Find flat lands g °C J flat lands kJ mol mol J 4.18 Find kJ g J Given g °C kJ 6.02 mol flat lands slopes kJ mol Make up problems for all 3 boxes above and work out in the box provided above. 40.6 kJ mol Name:_______________ Date:_______ Period:__ Direct ions: Pract. Probs. Ch 16.3 - Thermochem. Eqns. Show Specific heat - practice problems ΔT Q# J mass 1 find 2.5 kg 0°C ---> 32°C 2 39.5 J find 100°C ---> 145°C 3 148 J 725 g find 4 2.05 J find -82°C ---> -5°C 5 find 82 g 74°C ---> 30°C Heat of Vaporization/Fusion - practice problems Q# 6 7 8 9 10 mol substance kJ 5.5 find water find 22.5 ammonia (NH3) find 83.1 methanol 1.7 find ethanol find 2.6 NH3 This page was use to make: http://mrwiggersci.com/chem/homework/Ch-16-3-PPs-sp-ht-vap-fusion.htm calcs! Answer questio ns next to each line, or number 1-10 on back and show calcs there with note on front to look at the back. 1. Given: 3.70 J and ΔT -21 ---> -41 deg C Find: mass of water 2.0 J sp ht H2O solid g °C 0.0925 g H2O 2. Given: 2.25 mol methanol Find: kJ required to vaporize if at -33.3 °C (bp of methanol) Specific Heat & Heats of Fusion & Vap «grade» Grade: «subject» Subject: «date» Date: 1 For specific heat problems, if you are given mass and J (joules), what will the find be? A ΔT B mol C J D g For specific heat problems, if you are given mass and ΔT, what will the find be? 2 A ΔT B J C g D mol For Specific Heat problems, if you are asked to find ΔT what information must you be given to be able to solve the problem? (there may be more than one correct answer, choose all that apply, or none) 3 A J B ΔT C g D mol E all of these are needed F none of these are needed 4 For heat of vaporization problems, if you are given grams of He, what will you need to do to solve the problem? A use specific heat and solve for kJ B change grams to moles and use heat of fusion to solve the problem C change grams to moles and use heat of vaporization to solve the problem D you cannot solve this problem 5/1/2013 Standards: 7 (Chemical Thermodynamics) Objectives: ● Students will be able to calculate 2 problem types: a. specific heat problems b. heats of vaporization or fusion DO NOW: 1. Classwork working problems from SmartBoard HOMEWORK: 1. Ch 16.2 p. 498 #12 & 13; Ch 16.3 p. 504 20, 21, 22 (5 pts) Std 7 (students will grade each others homework tomorrow) =========================================================== ● Journal 4/30 (What you learned, or relearned about calcs and heats of vaporization and fusion) specific 10 mi n make trying a habit marriage must be Wife blows forever up at sex husband coming home after work TRY Choose wisely! Always look for what you did wrong first, be the leader! hap py wife hap py life / Who goes with What? Specific Heat J/g°C Heat of fusion kJ/mol flat lands Given Find Given slopes °C J Find mol mol kJ Heat of Vap kJ/mol flat lands Given Find kJ g J 40.6 g °C kJ mol flat lands slopes kJ mol 4.18 J g °C 6.02 kJ mol Make up problems for all 3 boxes above and work out in the box provided above. 40.6 kJ mol Specific Heat & Heats of Fusion & Vap «grade» Grade: «subject» Subject: «date» Date: 1 For specific heat problems, if you are given mass and J (joules), what will the find be? A ΔT B mol C J D g For specific heat problems, if you are given mass and ΔT, what will the find be? 2 A ΔT B J C g D mol For Specific Heat problems, if you are asked to find ΔT what information must you be given to be able to solve the problem? (there may be more than one correct answer, choose all that apply, or none) 3 A J B ΔT C g D mol E all of these are needed F none of these are needed 4 For heat of vaporization problems, if you are given grams of He, what will you need to do to solve the problem? A use specific heat and solve for kJ B change grams to moles and use heat of fusion to solve the problem C change grams to moles and use heat of vaporization to solve the problem D you cannot solve this problem Group practice - work in groups of 4. Copy the questions as given & find, and work out the answers using a series of fractions. Q# J ΔT mass Both are H2O 1 find 4.5 kg 0°C ---> 22°C 2 25.0 J find -60°C ---> -25°C Q# mol substance kJ (Chart p. 502) 3 2.50 find water vaporization 4 find 44.0 ammonia (NH3 fusion ANSWERS 1. 414,000 J 2. 0.356g mol 3. 102 kJ 4. 7.8 5/2/2013 Standards: 7 (Chemical Thermodynamics) Objectives: ● Students will be able to calculate 2 problem types: a. specific heat problems b. heats of vaporization or fusion DO NOW: 1. When HW papers returned, trade papers for grading. HOMEWORK: 1. Zum Heating Curve Questions 13-17 (bottom right) (5 pts) Std 7 2. Help Sheet for Mini Quiz Ch 16.1-16.3 (5pts) Std 7 =========================================================== BASKET: ● Journal 5/1 (What you learned, or relearned about specific heat calcs and heats of vaporization and fusion) 1. Ch 16.2 p. 498 Ch 16.3 #12 & 13; p. 504 20, 21, 22 (5 pts) Std 7 (students will grade each others homework tomorrow)5 Announcement quiz on a. specific heat problems b. heats of vaporization or fusion Tomorrow, Friday (5/3) Homework answers for Th 5/2 for substance X 13. heat of vaporization heat of fusion 14. 15. 16. 17. vaporization = 22 x fusion melt 10.0 g of X = 0.48 kJ vap 27 10.0 g of X = 27 kJ 848 J melts 11.5 g H2O 3,020 J vaporizes 11.5 g H2O fuse 25.og H2O = 8.37 kJ vap 37.5g H2O = 84.4 kJ warm H2O 55.2g 0 ---> 100°C 23.1 kJ cool 10.0g H2O from 200°C ---> 100°C = 2.03 kJ condense 10.0g H2O = 22.50 kJ cool 10.0g H2O from 100°C ------> 0°C = 4.18 kJ freeze 10.0g H2O = 3.34 kJ cool 10.0g H2O from 0°C ------> -5.0°C = 1.03 kJ ------------total energy removed from 10 g H2O going from 200°C --> -5.0°C 32.08 kJ 5/3/2013 Standards: 7 (Chemical Thermodynamics) Objectives: ● Check for understanding of: a. specific heat problems b. heats of vaporization or fusion DO NOW: 1. Prep. for Ch 16 Mini Quiz Ch 16.1, 16.2, 16.3 - polish your Help Sheet HOMEWORK: NONE =========================================================== BASKET: ● Journal 5/2 (What you learned, or relearned about heat calcs and heats of vaporization and fusion) 1. Zum Heating Curve Questions 13-17 (bottom right) (5 pts) Std 7 For this period only, if you didn't do the homework last night, or didn't complete it, you may redo and turn in on Mon for full credit. Put papers into 5 stacks Help Sheets scratch The following in order with smallest # on top: quizzes scantron charts Spread so #'s show ΔH = - 50kJ °C β α Ω Δ ♂ ↓ ↑ ♀ ᵝᵦ