Unit 6 Review Chemistry II ****Bring a scientific calculator
advertisement

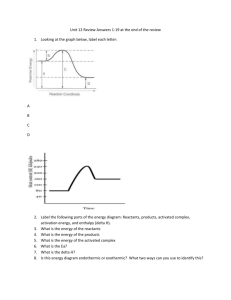
Unit 6 Review Chemistry II ****Bring a scientific calculator Definitions Energy Temperature Heat Exothermic Endothermic Enthalpy Entropy Specific heat Heat of Formation Heat of Combustion Heat of Fusion Heat of Vaporization Thermodynamics Joule Calorimeter Be able to: Calculate Hess’ Law Calculate ∆H given values from table 1st law of thermodynamics 2nd law of thermodynamics Calculate n, q, m, C, ∆T given various values When a spontaneous rxn occurs (decrease in energy, increase in disorder) Example of increasing entropy (dissolving crystals) Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions o Values of H o Where the energy term goes in a thermochemical equation o Energy profile diagram Factors that affect spontaneity Calculate the energy of a phase change Calculate molar heat of fusion and vaporization Calculate molar mass given the molar heat of fusion or heat of fusion Calculate ∆G and determine if a rxn is spontaneous Be able to draw a phase change diagram Formulas and Data given on test: q Cp = -------m x ΔT q = mC∆T Cp = specific heat (J/g · K) q = heat lost or gained (J) m = mass of sample (g) ΔT = change in temperature (K) Tf - Ti q Cp = -------n x ΔT q = nC∆T Cp = specific heat (J/mol · K) q = heat lost or gained (J) n = number of moles (mol) ΔT = change in temperature (K) Tf - Ti ΔH = Hproducts - Hreactants Specific Heat of water 3.77 x 10-2 KJ/mol ▪ ̊C or 2.09 J/g ▪ ̊C Liquid = 7.54 x 10-2 KJ/mol ▪ ̊C or 4.18 J/g ▪ ̊C 3.63 x 10-2 KJ/mol ▪ ̊C or 2.01 J/g ▪ ̊C Solid = Gas = Water = Hv (heat of vaporization) = 40.7 KJ/mol Water = Hf (heat of fusion) = 6.01 KJ/mol ∆G = ∆H - T∆S