Civil Rights Movement Matching
advertisement

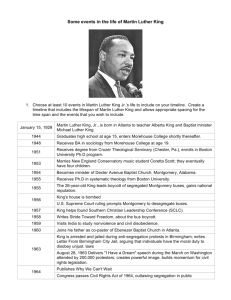
Civil Rights Movement Matching 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. Name __________________________________ ____ The organization that sponsored the Montgomery bus boycott ____ Type of segregation supported by law ____ One of the 9 members of the “Little Rock 9;” first to integrate the public school system ____ Type of segregation based on custom or tradition; a fact of life ____ The man who assassinated Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. in Memphis ____ Leader of the Civil Rights movement ____ Method of civil rights protest in which African Americans would sit at lunch counters until closing time ____ Birmingham’s Public Safety Commissioner who used police dogs and fire hoses on protesters. ____ Organization founded in the 1940’s by James Farmer and others to bring an end to racial injustice ____ Banned literacy tests and empowered the government to oversee voting ____ Strategy of non-violence advocated by Thoreau and Gandhi ____ President who sent troops into Little Rock to enforce the Court’s decision ____ Radical civil rights leader who became a convert to the Nation of Islam and was later killed ____ U.S. President who desegregated the military ____ Event in 1964 where thousands of students went to the South to help register blacks to vote ____ First African American student to enroll in the University of Mississippi ____ Site where blacks were attacked as they marched from to Montgomery to urge passage of voting rights laws ____ Landmark case that ended segregation of public schools ____ Civil rights attorney who represented Linda Brown in Brown v. Board of Education ____ Law that established the U.S. Civil Rights commission ____ U.S. Chief Justice who presided over the Supreme Court during the Brown case ____ City where the governor, Orval Faubus, tried to prevent the integration of the public school system ____ Grassroots movement of young black students that was organized to bring all classes together in the struggle for equality ____ Phrase used by Stokely Charmichael that meant blacks should use their collective economic and political power to achieve equality ____ African American woman who refused to give up her bus seat to a white passenger ____ Economic strategy used by the NAACP following the arrest of Rosa Parks ____ Organization made up of largely African ministers who advocated nonviolent resistance to fight injustice ____ Young, militant civil rights group ____ Co-founder of the SCLC along with MLK, Jr. ____ Banned the poll tax ____ Federal committee that determined that racial discrimination was the most significant cause of social unrest and violence ____ Group headed by Elijah Muhammad and prescribed strict rules of behavior and separation among races ____ One of the most important pieces of civil rights legislation in history; signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson ____ Groups of people civil rights activists rode buses into the south to make sure the federal government was enforcing the law ____ National Association for the Advancement of Colored People ____ Leader who was instrumental in integrating the University of Mississippi and was later murdered ____ Important document written by MLK, Jr. outlining why the civil rights movement was so important ____ Civil rights workers who were killed in Mississippi in the summer of 1964 ____ Enormous rally in front of the Lincoln Memorial where Martin Luther King made his famous “I Have a Dream” speech ____ Organization designed to investigate charges of job discrimination against blacks. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. De jure segregation De facto segregation CORE Civil disobedience Truman Brown v. Board of Education NAACP Thurgood Marshall Earl Warren Little Rock, AR Elizabeth Eckford Eisenhower Civil Rights Act of 1957 Rosa Parks Montgomery Bus Boycott Martin Luther King, Jr. MIA SCLC Ralph Abernathy Sit-in SNCC Freedom Ride James Meredith Medgar Evers Letter From a Birmingham Jail “Bull” Connor March on Washington Civil Rights Act of 1964 EEOC Freedom Summer Schwerner, Chaney, Goodman Selma Voting Rights Act of 1965 24th Amendment Kerner Commission Malcolm X Nation of Islam Black Power Black Panthers James Earl Ray