America the Beautiful
advertisement

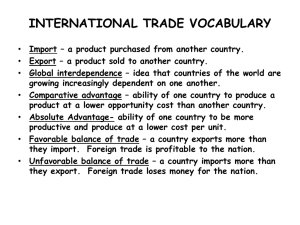
Unit Four International Trade Foundations Objectives Get the students to be familiar with the concepts of international trade. Cultivate the students’ ability of problem solving. Help the students overcome the vocabulary barrier in reading. Section A Introduction International trade is the activity that one country and region exchange goods,technologies and services with other countries and regions. It includes not only international trade and foreign manufacturing, but also comprises the growing services industry in areas such as transportations, tourism, banking, advertising, construction, retailing, wholesaling and mass communications. It includes all business transactions that involve two or more countries. Pre-reading Before reading the following passage, answer these questions: 1. What do you think are the characteristics of international trade? 2. Have you known any forms of international trade? Text Birdview of International Trade International trade is just like any other trade except that it crosses international boundary lines. To be more exact, it is the exchange of goods and services across national borders. In most countries, it represents a significant part of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). While international trade has been present throughout much of history, its economic, social, and political importance have increased in recent centuries, mainly because of industrialization, advanced transportation, globalization, transnational corporations. In fact, it is probably the increasing prevalence of international trade that is usually meant by the term “globalization”. Although there are usually few trade restrictions within countries, international trade is usually regulated by governmental quotas and restrictions, and often taxed by tariffs. Tariffs are usually on imports, but sometimes countries may impose export tariffs or subsidies. All of these are called trade barriers. If a government removes all trade barriers, a condition of free trade exists. A government that implements a protectionist policy establishes trade barriers. In general,import and export transactions may be carried out in various ways and forms according to the international trade requirements. First, trade can be carried out according to Trade Agreement, Trade and Payment Agreement, Exchange of Goods and Payment Agreement, etc., signed between the governments concerned. Then, the export and import trade may be made according to the terms and conditions of the sales contract concluded between the parties concerned. A lot of export/import trade transactions are carried out in this way in China today. Besides, there are some other ways of dealing in international trade. Barter Trade All imports are to be made against a corresponding value of exports. Compensation Trade Payment of imports (chiefly machinery and equipment for a factory) is to be made by products of the particular factory during certain years of its production according to the agreement. Processing Trade Imports of raw materials, packing materials, etc. are to be re-exported after processing or manufacture according to the agreement. Consignment Trade An exporter exported goods (the consignor) to an import abroad (the consignee) and the latter made payment only after the goods have been sold. A certain percentage of commission for the importer and other agreed expenses are deducted from the sale proceeds according to the agreement. This mode is chiefly used to start exports of goods of new designs, new production or invention, new brands, etc. Exclusive Sales Agreement The exporter may sign an exclusive sales agreement with an importer abroad. He may also set up his own branch office and employ his own sales organization abroad. He may act through a subsidiary company which is established under the laws of the foreign country in question. Or, he may combine with other traders in a joint selling organization (or joint venture), a consortium or an export group. Agency Arrangements The exporter enters into direct relations with the customers abroad, by means of a contract procured and conducted on behalf of the exporter by a representative who resides abroad and is not his employee. The remuneration of the representative or independent agent is usually based upon a commission on the purchase price of the exports. Invitation for Bid or Tender When enterprises, utilities as well as governments are in need of certain materials, products or planning to build a project, they often invite people to bid. With the development of foreign trade, more and more kinds of business are involved in this type of trading, ranging from contracting a big project to importing a kind of commodities. Trade Fairs Export / import trade may be possible through commodity exchange at international fairs. e.g., Guangzhou Fair: The Chinese Export Commodities Fair is held twice a year in the City of Guangzhou. The spring session of the fair lasts from April 15 to May 5 and the autumn session from October 15 to November 5. When it comes to the international trade, there are two important principles we must pay attention to --absolute advantage and comparative advantage. The principle of absolute advantage states that one nation is more efficient than another in the production of one commodity but is less efficient than the other nation in producing a second commodity, then both nations can gain benefits by each engaging in the production of the commodity of its absolute advantage and exchange part of its output with the other nation for the commodity of its absolute disadvantage. By this way, resources are used in the most efficient way and output of both commodities will rise. According to the law of comparative advantage, there is still a basis for mutually beneficial trade even if one nation is less efficient than the other nations in the production of both commodities. The first nation should concentrate on producing and export those commodities in which its absolute disadvantage is smallest (the commodity of its comparative advantage) and import the commodities in which its absolute disadvantage is greatest (the commodity of its comparative disadvantage). Finally,let's clarify some important terms about international trade: Import vs. export Normally, every nation’s foreign trade comprises both imports and exports, classified by the directions of the movement of commodity traded. Buy in commodity from another country is import and sell out commodities to another country is export. Favorable balance trade vs. unfavorable balance of trade when nations export more than they import, they have a favorable balance of trade. When they import more than they export, an unfavorable balance of trade exists. Visible trade vs. invisible trade Visible trade involves the import and export of goods and merchandise, while invisible one involves the exchange of services between nations. Direct trade vs. indirect trade Direct trade means that the producing country sells the goods directly to the consuming country. However, the goods may be shipped directly or indirectly from the producing country to the consuming country. If the goods are shipped through a third country, the third country is referred to as a transit country. To the transit country, such a transaction is transit trade and may be imposed a transit duty. Indirect trade means that the producing country sells the goods to a third country first and then the third country resells them to the consuming country. To the third country, this is entrepot trade. Entrepot trade is usually carried out by a middleman in the third country but the goods are shipped directly from the producing country to the consuming country in normal cases. Post-reading Answer the questions on the text. 1. What is international trade? 2. What accounts for the increasing prevalence of international trade ? 3. What are trade barriers? In what case does a government establish trade barriers? 4. What are the ways of dealing in international trade mentioned in the text? 5. When are people invited to bid as a type of trading? 6. Is it popular to carry out export/import trade transactions through commodity exchange at international fairs in China today? 7. What are two important principles in the international trade? 8. What is favorable balance trade? 9. Do you think invisible trade plays an important role in international trade? Why? 10. What are the differences between direct trade and indirect trade? Section B Reading Skills Strategies to identify unknown words Recognizing Words through Prefixes Recognizing Words through Suffixes Speed Reading Task Let’s have a glimpse of terms in international trade. Use techniques for speed reading to find out the answers to Exercise 1 as quickly as possible. True or false KEY: TFFT TFFT 1. _____ International Commercial Terms (INCOTERMS) are a set of internationally agreed trade terms, which are the short terms or abbreviations used to explain the price composition and determine the responsibilities, expenses and risks borne by two parties as well as their rights and obligations accordingly. 2. _____ Among others, today Incoterms 1936 is most widely used since it was first published in 1936 by the International Chamber of Commerce. 3._____ Among the 13 terms in Incoterms 2000, six terms, FOB, CFR, CIF, FCA, CPT, and DAF are commonly used in practice. 4. _____ It would be best for importers to refrain from dealing in the term EXW. 5. _____ According to FCA, buyer is responsible for the main carriage/freight, cargo insurance and other costs and risks. 6. _____ According to FOB, seller is responsible for the main carriage/freight, cargo insurance and other costs and risks. 7. _____ According to CFR, buyer is responsible for the delivery of goods to the named port of destination. 8. _____ According to CIF, the seller is responsible for the cargo insurance and delivery of goods to the named port of destination (discharge) . Section C Case Study Task Apply the theory of the two important principles in international trade, absolute advantage and comparative advantage, to the following cases. First, a numerical example of absolute advantage is shown in the table below: Table 1 Output per Man-hour of Labor Country Textiles Perfume France 10 yards 30 bottles Australia 30 yards 15bottles The table shows that France per man-hour of labor time produces 30 bottles of perfume, while Australia only 15 bottles. On the other hand, Australia produces 30 yards of textiles, but France 10 yards.Thus, France has an absolute advantage over Australia in the production of perfume, whereas Australia has an absolute advantage over France in the production of textiles. Discuss in groups:In this case, what is your suggestions on the trade between the two nations? Then, let’s focus on the illustration of comparative advantage. Assume that France can produce both textiles and perfume more efficiently than Australia. Table 2 Output per Man-hour of Labor Country Textiles Perfume France 30 yards 60 bottles Australia 15 yards 20 bottles In table 2, France has an absolute advantage in the production of both textiles and perfume over Australia. A man-hour of French labor is more efficient in the production of textiles and perfume than that in Australia. On the other hand, Australia has an absolute disadvantage in the production of both textiles and perfume with respect to France, but since its absolute disadvantage is smaller in textiles (2:1) than perfume (3:1), Australia has a comparative advantage in textiles. Discuss in groups:In what way can tradehe be mutually beneficial to the two nations ? Notes 1. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) 国内生产总值 2. Barter Trade 易货贸易 3. Compensation Trade 补偿贸易 4. Processing Trade 加工贸易 5. Consignment Trade 寄售贸易 6. Exclusive Sales Agreement 包销协议 7. Agency Arrangements 代理协议 8. Invitation for Bid or Tender 招标 9. Trade Fairs 贸易交易会 10. absolute advantage and comparative advantage 绝对优势和比较优 势 11. Favorable balance trade vs. unfavorable balance of trade 贸易顺差 和贸易逆差 12. Visible trade vs. invisible trade 有形贸易和无形贸易 13. Direct trade vs. indirect trade 直接贸易和间接贸易 14. transit country过境国;transit trade 过境贸易; transit duty 过境税 15. entrepot trade 转口贸易