VOC Measurements at Hohenpeissenberg as part of the
advertisement

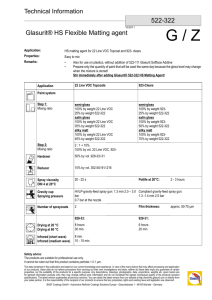
VOC MEASUREMENTS AT HOHENPEISSENBERG AS PART OF THE GAW PROGRAM Christian Plass-Dülmer and Harald Berresheim Meteorologisches Observatorium Hohenpeißenberg, DWD, Germany Meteorologisches Observatorium Hohenpeißenberg VOC Monitoring - Objectives GAW expert meeting Report 111, 1995 • Global distribution, seasonality and trends • understanding the biogeochemical cycling (sources, sinks, chemistry) • impact on ozone, photooxidants, oxidising capacity, aerosol, climate, health EMEP Strategic Plan 2004 • European distribution and trends • Compliance monitoring (compliance with protocols) • understand physical and chemical processes • Support for EMEP model WMO (1995): WMO-BMBF Workshop on VOC - Establishment of a „World Calibration/Instrument Intercomparison Facility for VOC“ to Serve the WMO Global Atmosphere Watch (GAW) Programme, WMO Report, 111. EMEP (2003): The EMEP Monitoring Strategy 2004-2009 Background document with justification and specification of the EMEP monitoring programme 2004-2009, eds. Kjetil Torseth and Oystein Hov, EMEP, CCC-Report 9/2003. GAW-Program VOC: MOHp •Stage 1: C2-C9 hydrocarbons HC •Stage 2: C10-C14 HC (biogenic) •Stage 3: oxygenated VOC (OVOC) •GC-FID •GC-MS/FID •GC-PDHID/FID Measurements at 1:00 and 13:00 CET ca. 80 VOC Detection limits: 1 ppt ... 10 ppt Accuracy: C2-C9 HC 5-25%, Terpenes 20-40% QA and QC Procedures VOC Intercomparisons: NOMHICE, AMOHA, and GAW 0.01 Cis-2-pentene Trans-2-pentene 1,3-Butadiene Cis-2-butene Trans-2-butene Propyne Isoprene Heptane 1-Butene o-Xylene Cyclohexane Hexane Ethylbenzene 2-Methylpentane 2-Methylpropene p,m-Xylene 2+3-Methylpentane Pentane Propene 2-Methylpropane Benzene 2-Methylbutane Toluene Butane Ethyne Ethene Propane Ethane median mixing ratio, ppbv X AMOHA - Task 4.2 - canister sampling at Hohenpeißenberg 04/2000 10 1 0.1 0.1 Cis-2-pentene Trans-2-pentene 1,3-Butadiene Cis-2-butene Trans-2-butene Propyne Isoprene Heptane 1-Butene o-Xylene Cyclohexane Hexane Ethylbenzene 2-Methylpentane 2-Methylpropene p,m-Xylene 2+3-Methylpentane Pentane Propene 2-Methylpropane Benzene 2-Methylbutane Toluene Butane Ethyne Ethene Propane Ethane participant results/ reference X 100 10 1 1 0.1 0.01 median mixing ratio, ppb AMOHA - Task 4.2 - canister sampling at Hohenpeißenberg 04/2000 10 70 % of data fulfil GAW - Quality Objectives VOC - Trends at Hohenpeissenberg Mixing Ratio, pptv X 10000 Ethane -1% /year Acetylene -2% /year Ethene 0% /year 1000 Benzene -1% /year Toluene -5% /year p,m-Xylene -7% /year 100 10 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Biogenic VOC at Hohenpeißenberg monthly means of noon-time concentrations (preliminary data) isoprene a-pinene camphene sabinene myrcene g-terpinene b-pinene terpinolene 3-carene b-phellandrene limonene Mixing ratio, pptv 1000 100 10 1 0.1 7/2002 1/2003 7/2003 1/2004 7/2004 1/2005 7/2005 Annual cycles of noon- and midnight monthly mean concentrations benzene-day toluene-day p,m-xyl-day 1,2,4-triM-B-day benzene-night toluene-night p,m-xyl-night 1,2,4-triM-B-night mixing ratio, pptv 1000 100 10 1 7/2002 1/2003 7/2003 1/2004 7/2004 12/2004 7/2005 Summer ratio day/night: Dt [OH] = 1-4 1010 s molec/cm³ c(day) = c(night) exp(-k[OH]Dt) Turn over-rates due to reactions with OH radicals Jun-Aug Dec-Feb, 10 106 molecules/(cm³s) 3.5 106 molecules/(cm³s) (2004 data at noon time and measured OH) propene other alkenes ethene aromatics alkanes CH4+H2 CH4+H2 MACR+MVK+ isoprene a-pinene b-pinene CO alkanesethene propene other alkenes aromatics CO NO limonene g-terpinene sabinene* NO2 NO other terpenes NO2 MACR+MVK+ isoprene a-pinene b-pinene limonene sabinene* g-terpinene other terpenes Research Topics at Hohenpeißenberg with respect to VOC • trends and distribution • oxidizing capacity • aerosol formation and growth • oxidant formation • source attribution HC, OVOC‘s VOC turn-over, radical precursors semi-volatile prod. VOC turn-over tracer, signature Isoprene, monoterpenes, light alkenes, formaldehyde semi-volatile products of monoterpenes and aromatics various C2-C10 hydrocarbons, OVOC‘s and halogenated VOC Future Requirements (presented at GAW workshop Tutzing 2004) •Stations: report VOC+errors to WDCGG/EMEP •SAG: establish DQO‘s, QA/QC procedures, Pilot stations, SOP‘s, error assessment •WCC: continue audits+intercomp., provide standards, SOP‘s, error assessment, data evaluation •QA/SAC: support SAG, WCC, and stations; motivate and coordinate •scientific user: analyse spatial distributions and temporal evolution, sources and sinks •all: workshops/conferences to communicate Annual Cycles of OVOC‘s at Hohenpeissenberg acetone-day MVK-day MACR-day MEK-day acetone-night MVK-night MACR-night MEK-night mixing ratio, pptv 10000 1000 100 10 1 7/2002 1/2003 7/2003 1/2004 7/2004 1/2005 7/2005 GC-2 Varian 3400CX MS/FID C5-C14 Hydrocarbons Halocarbons Oxygenated VOC GC-2: sample in ozone trap He carrier gas adsorption trap TenaxTA/Carboxen (303 K / 473 K) He carrier gas vent sample volume cryo focus silcosteel line (87 K / 453 K) vent GC column BPX-5 50 m x 0.22 mm FID MS GC-1 Varian 3600CX, FID C2-C8 Hydrocarbons GC-1: sample in ozone trap He carrier gas cold trap dryer (233 K) cryo trap glass beads (85 K / 473 K) vent sample volume GC column Al2O3/KCl 50m x 0.53 mm FID Glass-Sampling Line VOC patterns of boundary-layer and free troposphere air Ethan Propan i-Butan n-Butan i-Pentan n-Pentan Photochemical age: 2-M-Pentan n-Hexan n-Heptan Ethen about 8 days Propen 1,3-Butadien Isopren Acetylen Propin Benzol Toluol Ethylbenzol Boundary-layer p,m-Xylol Free troposphere o-Xylol 1 10 100 Mixing ratios, pptv 1000 T-Winter = MR-Winter T-Summer MR-Summer p,m-Xylol Toluol Benzol Propin Acetylen 1-Buten t-2-Buten Ethen Propen VOC-emissions = const. n-Pentan 1 1,3-Butadien Lifetime Ethan T=1/(K[OH]+k[O3]) Measurement i-Pentan O3 n-Butan OH i-Butan Atmosphere 10 Propan Box: Ratios Winter/Summer X Annual Cycle: Winter-Summer Ratios of selected VOC OH impacts, O3 sources Despite of chemical -³ 32 ppb 0.2E6are cmimportant andNov-Feb meteorology Jun-Aug 1.7E6 cm ³ 51 ppb Ethen gegen Acetylen Propen gegen 1-Buten 10000 1000 1000 100 y = 1.0686x R2 = 0.8298 100 y = 4.5899x R2 = 0.5729 10 10 1 10 100 1000 10000 1 Benzol gegen Acetylen 10 100 1000 p,m-Xylol gegen o-Xylol 1000 1000 100 y = 0.3042x R2 = 0.9493 100 y = 2.071x R2 = 0.8979 10 1 10 10 100 1000 10000 1 10 100 1000 mean mixing ratio 1998, pptv X Mixing Ratios 1998 vs. reactivity with OH 10000 1000 100 Alkanes 10 Alkenes Alkynes Aromatics 1 1E-13 1E-12 1E-11 k(OH), cm³/(s molecule) 1E-10 Biogenic Emissions - mixing ratios versus temperature 1000 Sum of Terpenes Isoprene 800 Mixing Ratio, pptv ---> Emission driven by temperature (meteorology) ---> Ozone-smog 600 ---> Particle-formation ---> climate ! 400 200 0 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 Temperature, °C 20 25 30 Do we see changes in the composition of anthropogenic VOC? Trends are still uncertain due to the short observation periode! linear Trend, %/year x 5% 0% -5% -10% 1E-13 Alkanes Alkenes Alkynes Aromatics 1E-12 1E-11 k(OH), cm³/(s molecule) 1E-10 reaction rate constant with OH, cm^3/molec/s 1.0E-13 1.0E-12 1.0E-11 1.0E-10 Ethan Propan n-Butan C2-C7 n-alkanes n-Pentan n-Hexan n-Heptan i-Butan i-Pentan 2,3-DiM-Butan C4-C7 i-alkanes 2-M-Pentan 3-M-Pentan 3-M-Hexan 2,3-DiM-Pentan Ethen Propen 1-Buten i-Buten C2-C6 alkenes t-2-Buten c-2-Buten t-2-Penten c-2-Penten ?-2-M-Buten-2 1,3-Butadien 1 ppb 100 ppt 10 ppt mixing ratio equivalent (1 ppb ethane) 1 ppt Isopren 40 days Acetylen Benzol Toluol 4 days 10 h life time at OH=2.8 E6 cm^-3 1h C7-C8 aromatics Ethylbenzol p, m-Xylol 10 000 km o-Xylol 1 000 km 100 km distance at 3 m/s wind speed 10 km VOC Monitoring Program NMHC Measurements by GC/FID - canister / on-line GAW • stage 1: C2-C9 hydrocarbons • stage 2: C10-C14 hydrocarbons • stage 3: oxygenated VOC EMEP • level 2: C2-C7 hydrocarbons • level 2: C1-C6 carbonyls • level 3: C6-C12 hydrocarbons • establish 3 pilot stations • level 2 = approx 15 sites • level 3 = research stations GAW/EMEP: 30 target compounds C2-C9 VOC QA / QC GAW • Report 111, ... • Intercomp.+audits by WCC • training (GAWTEC) EMEP • Manual (EMEP/CCC-1/95) • intercomp.+audits by NILU • data screening by NILU and local laboratories VOC Data Quality Objectives accuracy NMHC: 10 - 20 % accuracy NMHC 15-25% no calibration gas standards no QA / QC protocol SOP‘s ? Yearly „Trend“ of anthropogenic VOC: Measurements and Estimates UBA/EMEP Waldhof estimated emissions (UBA ) estimated emissions (UBA ) 1998-2003 1992-2002 1990-2001 2000-2001 -4% -5% Transport Emissions -12% 0% total (without solvents) -10% 0% Measurements DWD Hohenpeißenberg (National Emission-Inventory Germany - 2002, UBA, 31/07/03) Et ha Pr n op an i-B ut an nBu ta i-P n en n- tan Pe nt n- a n H ex n- a n H ep ta n nO kt an Et he Pr n op t-2 en -B ut e 1- n Bu te n i-B ut cen 2Bu t-2 t en -P e 2M nte -B n ut 2en M -B -2 ut c - en21 Pe nt en Be nz ol To Et h y luo l lb en m zol ,p -X yl o o- l Xy lo l mixing ratios, pptvjf Plass-Dülmer und Berresheim, Meteorologisches Observatorium Hohenpeißenberg 10000 measured profile traffic-emissions 1000 100 10 Annual winter (Nov-Feb) median concentrations of hydrocarbons at Waldhof (DE), Kosetice (CZ) and Donon (FR), red letters are results by NILU analysis, blue by national lab. Reference: VOC Measurements 2002 Sverre Solberg, NILU, Kjeller, Norway EMEP / CCC-Report 8/2004 Reference O-92016 mittlere Mischungsverhältnisse 1998, X pptv Mixing ratios 1998 versus reactivity towards OH 10000 1000 100 Alkane 10 Alkene Alkine Aromaten 1 1E-13 1E-12 1E-11 k(OH), cm³/(s Molekül) 1E-10 QC - Recent International Intercomparison Experiments NOMHICE: analytical preformance of participating labs AMOHA: analytical preformance + canisters + sampling procedure GAW-WCC: analytical preformance + on-line / canister NOMHICE - NonMethane Hydrocarbon InterComparison Experiment Tasks 1 - 5 (Apel et al., JGR, 1994, 1999, 2003) AMOHA - Accurate Measurements of Hydrocarbons in the Atmosphere Tasks 1 - 3 (Slemr et al., 2002) Task 4 (Plass-Dülmer et al., in preparation) First GAW - WCC - VOC - Intercomparison 2003 B. Rappenglück et al. First GAW - VOC Intercomparison 2003 Task-1: Synthetic Mixture (73 components, 0.2-10 ppb) Task-2: ambient air - parallel sampling participant / WCC Task-1 • 62 % within Data Quality Objectives (30 Target Compounds) See poster by Rappenglück et al. VOC Monitoring in Europe - EMEP network (since 1992) GAW Global Stations Zeppelin Pallas, since 1992 Birkenes Mace Head, since 2001 ? Izana, no VOC Hohenpeissenberg, since 1998 VOC Distribution (median) in Winter-Months 2002 (EMEP VOC Report, 2004) Lifetime: ca. 60 days EMEP Trend Results no clear trends in Northern Europe (Finnish sites) decreasing concentrations in Central Europe (20-50% / 1992-2000) and a levelling off after 2000 Caution: Trends are uncertain Summary • GAW and EMEP: similar objectives, VOC compounds, and QA /QC •VOC intercomparisons: - Data Quality Objectives are met by 2/3 of results - data quality varies substantially from lab to lab - problem: error assessment (DQO) •European VOC monitoring is mainly provided by EMEP •Results of European monitoring: - higher concentrations in Central and Eastern Europe - trends of anthr. VOC in Central Europe by 0-10% / year