Cell Respiration Teacher Notes
advertisement

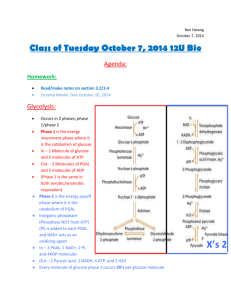
Metabolic Pathways and Enzymes • Cellular reactions are usually part of a metabolic pathway, a series of linked reactions • Illustrated as follows: E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6 A → B → C → D → E →F → G • Letters A-F are reactants or substrates, B-G are the products in the various reactions, and E1-E6 are enzymes. http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter8/animations.html • Enzymes – speed up the rate of chemical reactions • Substrates – molecules which react with enzymes • Only one small part of an enzyme, called the active site, reacts with the substrate(s). • Active site may undergo a slight change in shape in order to fit with the substrate • The enzyme is not changed by the reaction (active site returns to its original state), and it is free to act again. E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6 A → B → C → D → E →F → G Induced Fit Model •Because the enzyme must undergo a slight change in shape to fit with the substrate, this is known as the induced fit model. Activation Energy • Energy of activation (Ea) - the energy that must be added to cause molecules to react with one another • Enzyme lowers the amount of energy required for reaction to occur • Enzymes allow reactions to take place at lower temperatures – otherwise, reactions would not be able to occur at normal body temperatures Energy of activation (Ea) When no enzyme is present – more energy required When an enzyme is added – less energy required Enzymatic Reaction Substrate is broken down into smaller products Substrates are combined into a larger product Enzyme Names • Every reaction in a cell requires a specific enzyme. • Enzymes are named for their substrates: Substrate Lipid Enzyme Lipase Ureas Urease Maltose Maltase Ribonucleic acid Ribonuclease http://www.lewport.wnyric.org/JWANAMAKER/animations/Enzyme activity.html Factors Affecting Enzymatic Speed • Temperature and pH • Substrate concentration • Enzyme concentration • Temperature and pH: • As the temperature rises, enzyme activity increases. • If the temperature is too high, enzyme activity declines rapidly because the enzyme is denatured. • When enzyme is denatured, its shape changes and it can no longer attach to the substrate. • Each enzyme has an ideal temperature and pH at which the rate of reaction is highest. • Change in pH can alter the structure of the enzyme, and can eventually cause enzyme to denature. Rate of an enzymatic reaction as a function of temperature and pH •Rates and concentration: •Reaction rate depends on the number of enzyme-substrate complexes that can be formed. •When all available enzymes and active sites are filled, the rate of activity cannot increase further. •Substrate concentration •Enzyme activity increases as substrate concentration increases because there are more collisions between substrate molecules and the enzyme. •Enzyme concentration •Enzyme activity increases as enzyme concentration increases because there are more collisions between substrate molecules and the enzyme. Overview of Cellular Respiration • Makes ATP (potential energy) from glucose (chemical energy) • Releases energy in 4 reactions • Glycolysis, Transition reaction, Citric acid cycle (Kreb’s cycle), and Electron transport system • An aerobic process that requires O2 • If oxygen is not available (anaerobic), glycolysis is followed by fermentation Coupled Reaction The four phases of complete glucose breakdown Where does each step occur? •Outside the mitochondria •Step 1 - Glycolysis •Inside the mitochondria •Step 2 - Transition reaction (matrix) •Step 3 – Citric acid cycle (matrix) •Step 4 – Electron transport system (cristae) Structure of mitochondria: •Has a double membrane, with an intermembrane space between the two layers. •Cristae are folds of inner membrane •The matrix, the innermost compartment, which is filled with a gel-like fluid. Reaction that Occurs in Cellular Respiration •It is an oxidation-reduction reaction, or redox reaction for short. •Oxidation is the loss of electrons; hydrogen atoms are removed from glucose. •Reduction is the gain of electrons; oxygen atoms gain electrons. •Remember OIL RIG (oxidation is loss, reduction is gain) Enzymes involved: • NAD+ • Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide • Accepts H+ to become NADH • FAD • Flavin adenine dinucleotide (sometimes used instead of NAD+) • Accepts 2H+ to become FADH2 The NAD+ cycle • • • • • Step 1. Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasm (outside the mitochondria) Glucose 2 pyruvate molecules. Universally found in all organisms Does not require oxygen (anaerobic). Main energy source for prokaryotes http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/gly colysis.html Glycolysis Summary • Inputs: • • • • Glucose 2 NAD+ 2 ATP 4 ADP + 2 P • Outputs: • • • • 2 pyruvate 2 NADH 2 ADP 2 ATP (net gain) •When oxygen is available, pyruvate enters the mitochondria, where it is further broken down •If oxygen is not available, fermentation occurs Step 2 - Transition Reaction • Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria • Is the transition between glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. • Pyruvate (made during glycolysis) is converted to acetyl CoA, and CO2 is released • NAD+ is converted to NADH + H+ • The transition reaction occurs twice per glucose molecule. Transition reaction inputs and outputs per glucose molecule • Inputs: • 2 pyruvate • 2 NAD+ • Outputs: • 2 acetyl groups • 2 CO2 • 2 NADH http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/krebs.ht ml Step 3 - Citric Acid Cycle (aka Kreb’s Cycle) • • • • • • Occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria. C2 acetyl group is converted to a C6 citrate. Each acetyl group gives off 2 CO2 molecules. NAD+ accepts electrons 3 times FAD accepts electrons once. Results in a gain of one ATP per every turn of the cycle; there are two cycles per glucose, so a net of 2 ATP are produced. • The citric acid cycle produces four CO2 per molecule of glucose. Citric acid cycle Citric acid cycle inputs and outputs per glucose molecule • Inputs: • 2 acetyl groups • 6 NAD+ • 2 FAD • 2 ADP + 2 P • Outputs: • 4 CO2 • 6 NADH • 2 FADH2 • 2 ATP • • • • Step 4 - Electron Transport System (ETS) Requires oxygen (aerobic) Located in the cristae of mitochondria NADH and FADH2 carry electrons picked up during glycolysis, transition reaction, & citric acid cycle and enter the ETS. The ETS consists of: – protein complexes that pump H+ – mobile carriers that transport electrons – ATP synthase complex - H+ flow through it, making ATP • H+ flow through from high to low concentration • For every 3 H+ that flow through, one ATP is made Overview of the electron transport system http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/atpgradient/movie.htm http://www.sp.uconn.edu/%7Eterry/images/movs/synthase.mov http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/etc.html http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter9/animations.ht ml Energy Yield from Electron Transport Chain • Per glucose molecule: – 10 NADH take electrons to the ETS 3 ATP from each – 2 FADH2 take electrons to the ETS 2 ATP from each • Electrons carried by NADH produced during glycolysis are shuttled to the electron transport chain by an organic molecule (mechanism of delivery may vary # of ATP produced by ETS). Accounting of energy yield per glucose molecule breakdown Fermentation • Occurs when oxygen is not available. • During fermentation, the pyruvate formed by glycolysis is reduced to lactic acid . • Fermentation uses NADH and regenerates NAD+. • Occurs in anaerobic bacteria, fungus, & human muscle cells. http://instruct1.cit.cornell.edu/Courses/biomi290/MOVIES/GLYCO LYSIS.HTML Advantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation • Fermentation can provide a rapid burst of ATP in muscle cells, even when oxygen is in limited supply. • Lactate, however, is toxic to cells. • Initially, blood carries away lactate as it forms; eventually lactate builds up, lowering cell pH, and causing muscles to fatigue. • Oxygen debt occurs, and the liver must reconvert lactate to pyruvate. Fermentation inputs and outputs per glucose molecule • Inputs: • Glucose • 2 ATP • 4 ADP + 2 P • Outputs: • 2 lactate or • 2 alcohol & 2 CO2 • 2 ADP • 2 ATP (net gain)