Chemical Reactions
advertisement

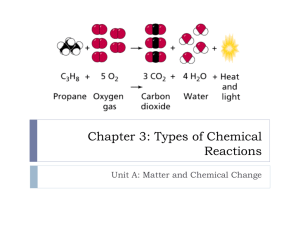
Chemical Reactions Chemical Equations Reactants are the substances entering a reaction Written on left Products are the result Written on right A chemical equation uses symbols and formulas to represent identities and amounts of products and reactants in a chemical equation Indicators of Chemical Reaction Change in temperature Change in color Smell Formation of a precipitate Formation of bubbles Diatomic Molecules Always occur in 2’s when alone Br I N Cl H O F Equations Word equations: use words and symbols to describe a reaction Formula equations: use formulas and symbols to describe a reaction Write a word & formula equation for the following: during electrolysis, water decomposes into hydrogen and oxygen gas Symbols Description Symbol Yields Reversible reaction Solid (s) Liquid (l) Gas (g) Aqueous-dissolved in water (aq) Reactants are heated Pressure is 2 atm Pressure is higher than normal Temp is 25 degrees C Catalyst MnO2 was used 25 C Balancing Equations Law of Conservation of Mass must be satisfied Equal # of atoms on both sides Balance by adjusting coefficients Do not alter subscripts Balance O’s and H’s last Counting Atoms Distribute coefficient to every atom 2 H2O - 4 H’s and 2 O’s 3 Ca (NO3)2 – 3 Ca’s, 6 N’s, 18 O’s Example __ Al2O3 ___ Al + ___ O2 1. Count atoms- 2 Al’s on left and 1 on right 2. Balance by placing 2 in front of Al on right __ Al2O3 2 Al + ___ O2 3. Count atoms- 3 O’s on left and 2 O’s on right 4. Balance by placing 2 in front of compound on left and 3 in front of the O’s on the right to make 6 O’s on each side Example 2 Al2O3 2 Al + 3 O2 5. Now Al’s are not balanced. Make the one on right a 4 2 Al2O3 4 Al + 3 O2 Equation is now balanced! Reaction Energy 1. A catalyst is used to speed up or slow down a reaction, but it does not react 2. Activation energy is the amount of energy needed for a reaction to start 3. ∆H is the symbol used to represent a change in energy + ∆ = exothermic (heat is released) - ∆ = endothermic (heat is absorbed) Energy Diagrams Exothermic- energy is released and is lower than starting *catalyst lowers the hump (activation energy) Endothermic- energy is absorbed and is higher than starting Reaction Types: Single Replacement One element replaces another Reactants: element + compound A + BX AX + B Reaction Types: Decomposition One compound splits into 2 pieces Can be elements or simpler compounds AB A + B Reaction Types: Synthesis Reverse of decomposition reaction 2 pieces join together to produce one, more complex compound Pieces can be elements or simpler compounds A + B AB Reaction Types: Double Replacement Cations and anions of 2 different compounds switch places AB + XY AY + XB A, X= cations Y, B= anions Reaction Types: Combustion Reaction of O2 gas with anything, normally a hydrocarbon (compound with H + C) CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O