Chemical Reaction Notes

Chemical Reaction
Notes
Chemical Reaction Notes
Known amounts of elements, polyatomic ions, and/or compounds can break apart , rearrange, and form ionic or covalent bonds in new compounds in order to increase stability and decrease the total amount of chemical potential energy .
Chemical Reaction Notes
These changes are called chemical reactions , and are different from the nuclear reactions we studied, which are when nuclei come together (or split apart) and create new atoms.
Chemical Reaction Notes
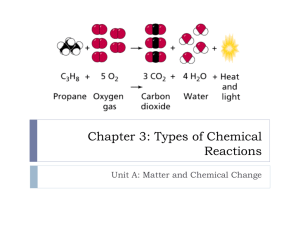
Chemists represent chemical reactions with equations.
There are three types — word , skeleton or chemical .
Chemical Reaction Notes
Chemical equations consist of a list of formulas for all of the reactants (compounds or elements added together to begin a chemical reaction) on the left side and a list of all of the products (compounds or elements which form during a chemical reaction) on the right side.
Chemical Reaction Notes
Reactants and products are separated by an arrow.
Reactants are separated from one another by plus signs (as are products).
Chemical Reaction Notes
Each formula may be followed by a subscript
(solid, liquid, gas, aqueous) to show what state of matter each compound is in.
We may represent energy
(heat, light, energy) as either a product or a reactant by writing it on the appropriate side of the equation.
Chemical Reaction Notes
Law of Conservation of Mass: In a chemical reaction the arrangement of atoms will change , but the total number of each type of atom, and therefore the total mass , will remain constant.
http://nanopedia.case.edu/NWPage.php?page=chemical.reactions
Chemical Reaction Notes
All chemical reactions must obey this law and therefore all chemical equations must obey it also.
Chemical Reaction Notes
In order to ensure that our chemical equations obey the law of cons. of mass, we balance all of our equations.
To do this:
1. You must make sure that all of the individual compound’s formulas are correct.
(Hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and the halogens are all diatomic elements , meaning that whenever they are not found in a compound they form a molecule with themselves and have a formula with a subscript 2 ). Remember
BrINCl HOF !
Chemical Reaction Notes
2. Pick any number and place it as a coefficient in front of any compound.
3. You should then balance one element at a time from one side of the equation to the other by placing coefficients in front of the remaining formulas.
Chemical Reaction Notes
4. Multiply coefficients to get rid of fractions if necessary.
5. Reduce coefficients if necessary.
Chemical Reaction Notes
Special hints:
1. Never change your subscripts .
2. Balance elements that only appear in one formula on each side first .
3. After your first “free choice” of a coefficient, you must only use coefficients that balance the element.
Count polyatomic ions as one unit.
Balance the element oxygen last.
Table Team Practice.
Chemical Reaction Notes
Chemical Reaction Notes
Chemical Reaction Notes
Chemical Reaction Notes
Chemical Reaction Notes
Which of the following is NOT a chemical reaction?
A.
a piece of wood burning
B.
a car rusting
C.
an ice cube melting into water
D.
red litmus paper turning blue
Chemical Reaction Notes
What is the coefficient of bromine in the equation 2Al(s) + 3Br
2
(l) → 2AlBr
3
(s)?
A.
1
B.
2
C.
3
D.
6