Chemical Reactions
advertisement

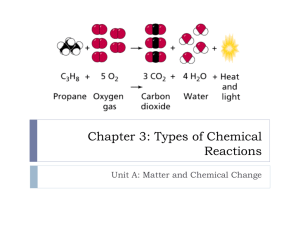
Chemical Reactions Hope Dubbs Chemical Reactions and Equations • Chemical reactions occur when a substance undergoes a chemical change • Reactions take place so there is a stable element • A chemical equation is a representation of a chemical reaction in which the reactants and products are expressed as formulas Chemical Reactions and Equations • We use chemical equations to summarize the process of the reactions • Chemical equations should be balanced in order to show that mass is conserved during a reaction • The principle that during chemical reactions, the mass of the products is always equal to the mass of the reactants, is known as the law of conservation of mass Reactants and Products • In a chemical reaction, the substances that undergo change are called reactants • The new substances formed as a result of that change are called products • The arrow in the equation means that the reaction of the reactants yields to the product Synthesis Reactions • A synthesis reaction is a reaction in which two or more substances react to form a single substance • The reactants may be either elements or compounds • The product synthesized is always a compound Synthesis Reactions • The way this looks in symbol form is A+B AB • An example of this equation is 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl • An analogy to remember this reaction is chocolate chips + cookie dough chocolate chip cookie dough Decomposition Reactions • A decomposition reaction is a reaction in which a compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances • The reactant in a decomposition reaction must be a compound • The products may be elements or compounds Decomposition Reactions • The symbol form for decomposition reactions is AB A + B • An example of this type of equation is 2H2O 2H2 + O2 • An analogy to remember this reaction is Peanut Butter & Jelly Peanut Butter + Jelly Single Replacement • A single-replacement reaction is a reaction in which one element takes the place of another element in a compound • Single-replacement reactions look this way in symbol form: A + BC B + AC Single Replacement • An example of this type of equation is Cu + 2AgNO3 2Ag + Cu(NO3)2 • An analogy to remember this reaction is blue + greenpurple green + bluepurple Double Replacement • A double-replacement reaction is one in which two different compounds exchange positive ions and form two new compounds • The symbol form for this reaction is AB + CD AD + CB Double Replacement • An example of this type of equation is Pb(NO3)2 + 2KI PbI2 + 2KNO3 • An analogy to remember this reaction is bluegreen + redpurple bluepurple + redgreen