File
advertisement

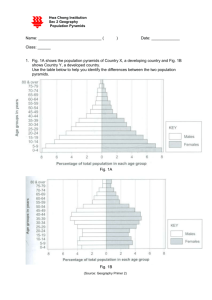
Do Now: Population Pyramids Movie Clip • Answer the following: 1) What is a population pyramid? 2) How do they differ for developed and less developed countries? Aim: Why does population composition matter? Population Composition Population Composition is concerned with: • Gender distribution • Age distribution within a country, region, or place. A Population’s Age Structure Helps Us Make Projections • Age structure categories • Prereproductive ages (0-14) • Reproductive ages (15-44) • Postreproductive ages (45 and older) • Seniors are the fastest-growing age group Population Pyramids – Charts that show the percentages of each age group in the total population, divided by gender. For poorer countries, the chart is shaped like a pyramid. Infant mortality rates are high, life expectancy is shorter. Generalized Population Age-Structure Diagrams Fig. 6-12, p. 136 Population Structure by Age and Sex in Developing and Developed Countries Fig. 6-13, p. 136 Pause…Think…Discuss… • If all the girls under 15 were to have only one child during their lifetimes, how do you think these structures would change over time? In poorer countries, Infant Mortality Rates are usually high, which is reflected in the pyramid shape. In poorer countries, Life Expectancy is usually shorter, which is also reflected in the pyramid shape. Affect of AIDS on population pyramid for South Africa. Predicted population for 2035, without and with AIDS. With AIDS, looks like a population “chimney.” Botswana Age Structure, With and Without AIDS Fig. 6-16, p. 139 Pause…Think…Write • How might this affect Botswana’s economic development? Do you understand how to read an age structure graph? Read A- Loud • Case Study: The American baby boom Population Pyramids – Charts that show the percentages of each age group in the total population, divided by gender. For wealthier countries, the chart is shaped like a lopsided vase. Population is aging, TFRs are declining. Age Structure of a Population • The populations of many countries are aging. - eg. Europe - eg. Japan Bordeaux, France Aging Populations • To replace the population, TFR must be 2.1. - TFR in Bologna, Italy is 0.8 Why are women having fewer children? • What are the impacts of an aging population on a country? • What are the “solutions” to an aging population? Case Study: The American Baby Boom • 79 million people, 36% of adults • Affect politics and economics • Now becoming senior citizens • Graying of America Tracking the Baby-Boom Generation in the United States Fig. 6-14, p. 137 Populations Made Up of Mostly Older People Can Decline Rapidly • Slow decline • Manageable • Rapid decline • Severe economic problems • How pay for services for elderly • Proportionally fewer young people working • Labor shortages • Severe social problems Some Problems with Rapid Population Decline Which three of these Problems do you Think are the most Important and why? Populations Can Decline from a Rising Death Rate: The AIDS Tragedy • 27 million killed: 1981-2009 • Many young adults die: loss of most productive workers • Sharp drop in life expectancy • International community • Reduce the spread of HIV through education and health care • Financial assistance and volunteers Do you understand how an older population negatively impacts a country? Summary: • In terms of TFR and birth and death rates, explain what is happening in each age structure pyramid. Thinking Geographically • In the United States, the national infant mortality rate (IMR) is 7.0. That number represents an average for the country. Think about the differences in IMR in the United States across regions, ethnicities, social classes, and other sectors.