Chordata, "protochordates"
advertisement

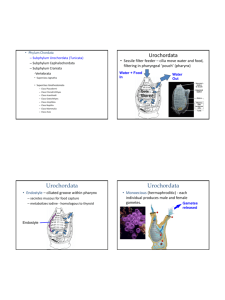
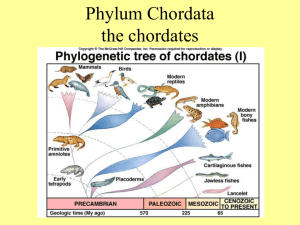
Gastrulation and neurulation (frog) Neurulation animation (human) Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicata) Subphylum Cephalochordata “Craniata” group Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha Superclass Gnathostomata Class Placodermi Class Chondrichthyes Class Acanthodii Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class Reptilia Class Mammalia Class Aves Urochordata Urochordata Sessile filter feeder – cilia move water and food, filtering in pharyngeal ‘pouch’ (pharynx) Water + Food In Gets filtered Water Out Urochordata Endostyle – ciliated groove within pharynx secretes mucous for food capture metabolizes iodine - homologous to thyroid Endostyle Urochordata Monoecious (hermaphroditic) - each individual produces male and female gametes. Gametes released Tunic – polysacchrides w/tunicin secreted by mantle Urochordata Adult lacks most chordate synapomorphies Urochordata larvae Eyespot (ocellus) and statocyst Non-tunicate Urochordates Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicata) Subphylum Cephalochordata “Craniata” group Subphylum Vertebrata -Superclass Agnatha Superclass Gnathostomata Class Placodermi Class Chondrichthyes Class Acanthodii Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class Reptilia Class Mammalia Class Aves Cephalochordata Motile filterfeeders Ciliated wheel organ and pharynx Notochord – “hydroskeleton” Stiffness of notochord under neural control amphioxus Notochord extends into anterior end Cephalochordata Amphioxus Tail musculature and associated nerves & vessels are segmented. myomeres ‘Metamerism” Cephalochordata Amphioxus Circulatory system with dorsal and ventral aorta. Cephalochordata Metapleural fold – stability for swimming In text, Euchordates = Somitichordates What were early chordates like? Pikaia gracilens - 530 million years ago myomeres (muscle blocks) skeletal notochord cephalization Cambrian explosion - ~550 million y.a. Burgess shale It’s a long way from amphioxus Kiss off, you dang annelids! Oh, a fish-like thing appeared among the annelids one day, It hadn't any parapods or setae to display. It hadn't any eyes or jaws or ventral nervous cord. But it had a lot of gill slits and it had a notochord. Chorus: It's a long way from amphioxus, it's a long way to us. It's a long way from amphioxus to the meanest human cuss. It's good-bye to fins and gill slits, and welcome lungs and hair. It's a long, long way from amphioxus, but we all came from there. It wan't much to look at and it scarce knew how to swim. And Nories was very sure it hadn't come from him. The Molluscs wouldn't own it and the Arthropods got sore. So the poor thing had to burrow in the sand along the shore. "My notochord shall change into a chain of vertebrae, And, as fins, my metapleural folds will agitate the sea." "My tiny dorsal nervous cord shall be a mighty brain. And the vertebrates shall dominate the animal domain." Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicata) Subphylum Cephalochordata “Craniata” group Subphylum Vertebrata -Superclass Agnatha -Superclass Gnathostomata Class Placodermi Class Chondrichthyes Class Acanthodii Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class Reptilia Class Mammalia Class Aves Craniata contains hagfish and all vertebrates Chordates with skulls, neural crest cartilagenous, fibrous or bony encases brain & sense organs Hagfish Lamprey Craniata Sensory, digestive and respiratory anatomy Neural crest cells NC cells are found in all craniates and give rise to a variety of structures QuickTime™ and a Animation decompressor are needed to see this picture. It’s nice to have a neural crest…. pigment cells gill arches, jaw ganglia in ANS base of skull induce skin ‘structures’ Craniata vs. ‘protochordates’ Selection for predatory characteristics active feeders muscular gut tube for filtering Pikaia gracilens Haikouella Evolutionary scenarios Craniates were originally linked w/arthropods, annelids, mollusks But essential differences in development Chordate metamerism doesn’t involve coelom as in annelids Linking the subphyla Garstang (p.44) Euchordates (Somitochordates) evolved via paedomorphosis (a type of heterochrony) Paedomorphosis: Adult form of the descendant species retains juvenile features of ancestral species. Adult salamander w/gills Garstang: Mutation caused development of sexual maturity in a non-metamorphosing lineage of Urochordata – better locomotion Early craniates – larger, more mobile than cephalochordata. Driven by predation? Conodonts - 540-230 m.y. ago after Pikaia, the next fossil Chordates microfossils of teeth, probably in pharynx Cool thing about conodonts A new hard substance appears: mineralized tissue – calcium phosphate (hydroxyapatite)