Craniata, Vertebrata
advertisement

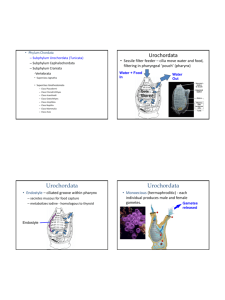
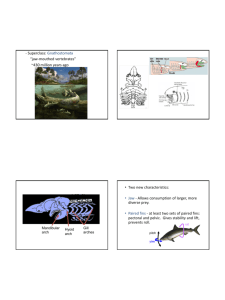
page 5 in lab manual anterior posterior Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicata) Subphylum Cephalochordata “Craniata” group Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha Superclass Gnathostomata Class Placodermi Class Chondrichthyes Class Acanthodii Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class Reptilia Class Mammalia Class Aves Hagfish Scavenge dead, dying fish and invertebrates. Have funnel-like mouths - tongue rasps off food. Where are hagfish classified? Asian aphrodisiac Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicata) Subphylum Cephalochordata “Craniata” group Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha Superclass Gnathostomata Class Placodermi Class Chondrichthyes Class Acanthodii Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class Reptilia Class Mammalia Class Aves Vertebrates Metameric skeletal elements flanking the nerve cord. Neural arch was first element to evolve Hagfish Lamprey Shark Hagfish vertebral elements?? June, 2011 “Ostracoderms” – 430-370 million years ago - early jawless fish head shields w/mineralized bone small bottom-dwelling Calcium phosphate mineralized tissue makes head shield and is related to teeth and scales enamel and dentine developmental interaction of epidermis and dermis Ancestral jawless fish Usually no paired fins Notochord mostly remains Single nostril Main groups of modern jawless fish: Hagfish (Myxiniformes) Lamprey (Petromyzontiformes) Similarities in these two groups are probably due to evolutionary convergence (homoplasy) Lamprey Lamprey respiration Water flows in mouth, through respiratory tube and out gills Respiratory tube internally connects gill pores Specialized flap - velum can close off anterior end of respiratory tube !! Respiratory tube internally connects gill pores Specialized flap - velum can close off anterior end of respiratory tube !! Branchial muscles squeeze water in and out of respiratory tube and over gills “Tidal ventilation” !! Ammocetes - larval form of lamprey up to 7 years Uses muscular movements to make feeding current. Crassus - Roman general Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicata) Subphylum Cephalochordata “Craniata” group Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha Superclass Gnathostomata Class Placodermi Class Chondrichthyes Class Acanthodii Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class Reptilia Class Mammalia Class Aves - Superclass: Gnathostomata “jaw-mouthed vertebrates” ~430 million years ago Two new characteristics: A jaw - Allows consumption of larger, more diverse prey. Mandibular arch Hyoid arch Gill arches Two new characteristics: Jaw - Allows consumption of larger, more diverse prey. Paired fins - at least two sets of paired fins: pectoral and pelvic. Gives stability and lift, prevents roll. roll pitch yaw Big evolutionary radiation after advent of first jawed fish... Acanthodians Placoderms Chondrichthyes Sarcopterygii Actinopterygii Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata (Tunicata) Subphylum Cephalochordata Craniata group Subphylum Vertebrata Superclass Agnatha Superclass Gnathostomata Class Placodermi Class Chondrichthyes Class Acanthodii Class Osteichthyes Class Amphibia Class Reptilia Class Mammalia Class Aves Acanthodians Body armor like ostracoderms, fins w/spines Skeleton had some bone (p.63) Placoderms - “plate-skinned” fish Bony plates are in smaller pieces compared to ostracoderms Mostly fed on bottom, some mid-level predators (p.59) 1 fossil shows live birth placoderm skull Dunkleosteus Bite could exert 22,000lbs of force per sq inch First vertebrate “giants” Placoderm - up to 20 ft, 1 ton