Phylum Chordata
advertisement

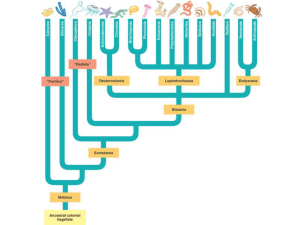
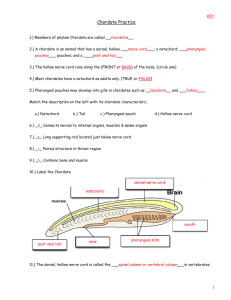
Phylum Chordata The chordates Five Chordate Hallmarks Notochord – flexible rodlike structure; extending length of body Five Chordate Hallmarks Dorsal tubular nerve cord Five Chordate Hallmarks Pharyngeal pouches and gill slits Five Chordate Hallmarks Endostyle or thyroid gland – secretes mucous that traps food particles in pharyngeal cavity Five Chordate Hallmarks Postanal tail – tail extends beyond anus Sixth Chordate Feature Ventral Heart – heart located ventrally Higher Classification of Chordata Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata – tunicates, sea squirts Subphylum Cephalachordata – lancelets Subphlum Vertebrata- vertebrates Subphylum Urochordata Sea Squirts or Tunicates Urochordate Characteristics Have a non-living tunic Most chordate features found in the free living acidian larva Adults sessile filter feeders Acidean Larva and Metamorphosis Adult Urochordate Subphylum Cephalochordata Lancelets Cephalochordate Characteristics Notochord and nerve cord found along entire length of body, persists throughout life Fish-like in form Includes the lancelets (amphioxus) Amphioxus Subphylum Vertebrata The Vertebrates Vertebrate Characteristics Bony or cartilaginous vertebrae surrounding spinal cord Notochord only in embryonic stages, persisting in some fishes Two superclasses according to presence of jaws Vertebrate Higher Classification Superclass Agnatha - without jaws Class Myxini – hagfishes Class Cephalaspidomorphi – lampreys Superclass Gnathostomata – with jaws Class Chondrichthyes – sharks, rays, chimaeras Class Actinopterygii – ray-finned fishes Class Sarcopterygii – lobe-fin fishes Class Amphibia – frogs, salamanders Class Reptilia – snakes, lizards, crocodiles Class Aves - birds Class Mammalia - mammals