Amines & Amides note guide
advertisement

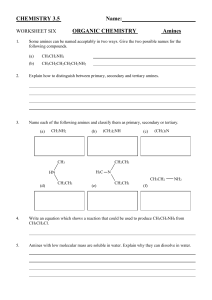
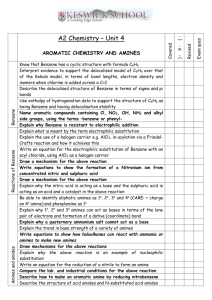
Amines & Amides Nitrogen: • _____________________ most common atom in living systems. • Important component of the structure of ______________________________________ • Essential to the structure and function of proteins – _________________________________ Amine Structure: • Characterized by the presence of an ___________________________________________ • One or more of the ________________________________ can be replaced by an organic group. • Organic derivatives of ___________________________ and, like ammonia, they are __________________. • Amines are classified according to the ___________________________________________ attached to the nitrogen. • Primary (1°) – _______________ hydrogen replaced • Secondary (2°) – ______________ hydrogens replaced • Tertiary (3°) – ___________________ hydrogens replaced Properties: • Because nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen, the N-H bond is _______________. • ____________________________________________ can occur between amines and water. • Primary and secondary amines have higher boiling points than tertiary amines because tertiary amines cannot ___________________________________________________. • Small amines (six or fewer carbons) are ____________________ in water. Naming Amines – IUPAC • Least common system used • Parent chain is longest continuous chain to which the ______________________________. • Use a number to indicate the position of the _________________________. • Add the prefix _________________________________ to the name of the _____________. • If a substituent is present on the nitrogen, it is designated by the prefix _________________. Naming Amines – Common • CA system – Chemical Abstracts system • The final _____ of the parent name is dropped and the suffix ______________________ is added. • For secondary and tertiary amines, the prefix ____________________________ is added to the parent compound. Aromatic Amines: Other Common Name Amines: Amides: • Products formed in a reaction between a _________________________ and an __________. • Contains two portions: the ______________________________ group from a carboxylic acid and the ____________________ group from the amine Properties of Amides: • Most are ________________________ at room temperature • ___________________________________ boiling points – __________________________ bonding between N-H bond of one amide and the C=O group of the second amide • Simpler ones are quite ________________________ in water • Unlike amines, amides are NOT _______________________ Naming Amides – IUPAC • Replace the ____________________________ from the carboxylic acid with the ending ________________________________. • Substituents on the _____________________________ are placed as ___________________ and are indicated by _____________ followed by the name of the substituent.