Nutrition and Diet Therapy
advertisement

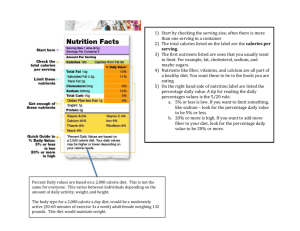
Nutrition and Diet Therapy • Nutrition= digestion, metabolism, circulation and elimination • Nutritional Status= refers to the state of one’s nutrition • Wellness= state of good health with optimal body function (requires good nutrition • Nutrition plays a large role in determining: • Height • Weight • Strength • Skeletal and muscle development • Physical agility • Resistance to disease • Appetite • Posture • Complexion • Mental ability • Emotional and psychological health Immediate effects of good nutrition includes: • Healthy appearance • Good attitude • Proper sleep and bowel habits • High energy level • Enthusiasm • Freedom from anxiety Good Nutrition may delay or prevent the following: • Hypertension • Atherosclerosis • Osteoporosis: prevented by good nutrition • Malnutrition • Obesity • Anemia If your neighbor tells you her MD has placed her on a high protein diet with iron supplements based on her diet which of the above illness is her medical problem? Essential Nutrients • Composed of chemical elements found in food. • Used by the body to perform body functions • Nutrients in foods replace those used by the body • Essential nutrients are divided into six groups. Carbohydrates • Major source of human energy • Starches or sugars • Easily digested, grow well in most climates, keep well without refrigeration • Main sources: bread, cereals, pasta, crackers, potatoes, corn peas, fruits, sugars and syrups Cellulose = indigestible carbohydrate, provides bulk (bran, whole-grain cereal, fibrous fruits, & veggies Aid in absorption of fat-soluble vitamins Fats • Lipids • Concentrated form of energy • Help maintain body temperature by providing insulation • Help cushion organs and bones • Provide flavor to meals Fats Continued • Main sources: butter, margarine, oils, creams, fatty meats, cheeses, and egg yolk • Classified as saturated or poly unsaturated Cholesterol: fatty substance found in body cells and animal fats – eggs, meat, shellfish, butter cream, cheese, milk, organ meats Excess cholesterol is believed to contribute to atherosclerosis Proteins • Build and repair body tissue • Provide heat and energy • Help makes antibodies • Make up to 22 amino acids (9are essential) • Main sources complete protein: meat, fish, milk, cheese, eggs, • Incomplete proteins: cereal, soybeans, dry beans, peas and peanuts • Organic compounds that are essential to life • Regulate body functions • Repair body tissues • Only a small amount required –well balanced diet provides required vitamins • Excess or deficiency can cause poor health • Water soluble or fat soluble Vitamins Someone who eats fat free diet could become deficient in fat-soluble vitamins Minerals • Inorganic (nonliving) elements found in all body tissues • Regulate body functions • Build and repair body tissues • They include: calcium, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, iron, iodine, fluorine and others. • Found in all body tissues • Essential for digestion • Makes up most of blood plasma • Helps body tissues absorb nutrient • Helps move waste material through body Average person should drink 6-8 glasses of water a day. Water Utilization of Nutrients • Digestion- breaks down the foods we eat by 1. Mechanical or chemical 2. Peristalsis • Absorption – process of taking in nutrients by the body 1. Most absorption occurs in the small intestine 2. Water, salts and some vitamins in large intestine Utilization. • Metabolism – use of nutrients by the body – 1. Basal Metabolic rate (BMR) • Measuring Food Energy – 1. Calorie- the amount of heat produced during metabolism – 2. Most people use an average of 3,500 calories/day – 3. To lose wt. a person must take in fewer calories then are burned – 4. To gain weight, a person must take in more calories than the body uses. Write questions and use the web site to find answers…. What is a lowresidue diet? What is not allowed on a low residue diet? Can you have 7up on a clear liquid diet? If someone just had surgery the next day what diet would they likely be on? Someone with chronic esophageal reflux would be placed on what kind of diet? Someone with hyperthyroidism would be on what type of diet? A client wakes up during the night and asks for something to eat. The nurse aide should : To prevent dehydration of the client, the nurse aide should: Could a diabetic have chicken broth? What diet would be appropriate for someone with dentures? If a person was retaining fluid what diet would be ordered? A pt. With a healing wound would most likely be put on what type of diet? Therapeutic Diets • http://www.dietsite.com/dt/diets/hearthealth y/lowsalt.asp • Regular Liquid Soft • Diabetic Low Calorie • High Calorie Low Cholesterol • Fat-restricted Sodium-restricted • Protein Bland Low-residue