S&T Sec. 3. Revision Questions Final Theory Exam
advertisement

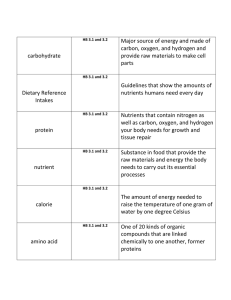
S&T Sec. 3. Revision Questions Final Theory Exam June 17, 2014 1. Describe the nutrients. What are they and what is their function? How much energy is derived from the breakdown in grams for the principal nutrients? Give the corresponding simplified version of the nutrients (once broken down by digestion). Give an example of the foods that contain these nutrients. 2. Give an example of a portion for each food group of the Canadian Food Guide (CFG). 3. In which types of food do you find dietary fibre? What purpose does fibre provide? 4. Draw all the components of the digestive tract. Identify the structures and include their function. 5. In a table, include all the glands of the digestive system. Give the function of each. 6. The liver produces bile. What does bile do? The action of bile corresponds to what type of transformation? 7. Two membranes are active during deglutition (swallowing). Name them and what role do they play. 8. What is the difference between mechanical and chemical transformation? Give 2 examples of each transformation. 9. Draw the respiratory system and identify all its parts. 10. Explain the term diffusion as it relates to gas exchange. Make a drawing and identify the structures and where this exchange of gases takes place. 11. Give the path taken by air during expiration. 12. Make a table comparing the 2 phases of respiration. Include the action of the intercostal muscles, diaphragm and what happens to the volume and pressure in the thoracic cavity where air is going to the lungs. See Fig 6.23 page 175. 13. In a table give the 4 blood constituents. Include a description of each and their function. Page 178. 14. Define agglutinogens, agglutinins, and agglutination. 15. Maggie is AB+, can she donate blood to Ziggy who is B+? Explain. 16. The blood type of Petunia is unknown. How would you go about identifying it? 17. Give some characteristics of each of the 3 types of blood vessels. 18. Draw the heart and identify its components. Include the 4 cavities, blood vessels, the direction of the oxygenated blood (in red), the direction of deoxygenated blood (in blue) and the structure that separates the heart. 19. Where do you find the valves in the heart and what function do they serve? 20. White blood cells defend the body by what 2 methods? 21. An antibody and a blood antibody are not the same thing. Explain. 22. In the urinary system, the oxygenated blood and ______________________ enter the kidney via _______________________ and the ___________________blood and filtrate leave the kidney by the ____________________. 23. Draw the urinary system. Identify all the structures and give the functions of the 4 main parts. 24. What substances is urine composed of? 25. Give examples of situations that increase and those that decrease urine production. 26. The body excretes wastes through 4 ways. What are they? 27. What are the 4 functions of the nervous system? 28. Draw a neuron and name all its parts. Also include the direction the nerve impulse. 29. The peripheral nervous system is composed of __________________. 30. Give the difference between motor and sensory nerves. 31. The two parts of the Central Nervous System are:________________________. 32. What is the difference between the cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem and the spinal cord (function and location)? 33. Give the pathway taken by a nerve impulse during a reflex (reflex arc). 34. Make a drawing of the eye, identifying the key parts and give their function. 35. What is myopia, hyperopia, and presbyopia? Give the type of corrective lens needed in each case. 36. Explain how we hear. 37. What 2 structures of the ear are linked to balance? What is the difference between the two? 38. Put the following words in decreasing order of complexity: cell, system, organ, tissue, and organism. 39. Name the 3 types of muscle tissue. State where one finds each type and whether the muscle is voluntary or involuntary. 40. Give the pathway the blood takes in the pulmonary and systemic circulations. 41. Name the formed elements of blood and give their function. 42. What is the difference between a mixture and a pure substance? 43. Define heterogeneous mixture, homogeneous mixture (solution) and colloid. 44. Define the terms solute and solvent. 45. Define concentration and give its various concentration units (i.e. g/ml or % m/V) 46. Knowing that a substance has a mass of 977mg and a volume of 0.75L, what is the concentration in g/ml? In % m/V? 47. What does solubility mean? How does the solubility of a solid and that of a gas change with decreasing temperature? 48. Define the terms saturated, non-saturated and supersaturated solutions. 49. In which type of solution will a precipitate be visible? 50. Give the following conversion: 3.25 kg/L = ? % m/v 51. A concentrated solution has a volume of 2ml with a concentration de 3.5g/L. If 10ml of water is added in order to dilute , what will be the new concentration of this solution? 52. If a substance has a concentration of 3% m/v and a mass of 0.55 kg , what is it’s volume (L)? 53. Name 6 separation methods and give an example of where each method would be employed. 54. What is the difference between a compound and an element? 55.a) Define and give 4 examples of physical properties and 6 examples of chemical properties. b) What are the properties that help us identify a substance? Explain. 56. Define thermal energy, radiant energy, chemical energy and mechanical energy. Give 2 examples of each. 57. What is the difference between the transfer and transformation of energy? 58. Explain the role of energy in phase changes. 59. Explain the role of energy in dissolution. 60. A deformation is a physical or chemical change? Why? 61. Give an example of a physical change and an example of a chemical change that takes place in the human body. 62. Give 4 types of chemical changes and include their formulas. 63. Draw a closed bottle that contains gas particles. Draw the same bottle but containing fewer particles. Is there a change in pressure? Explain. 64. What is the particle model? 65. Draw the image formation in the eye due to light rays arising from outside. 66. Calculate the density of a gold ring if the volume is 5 cm3 and the mass is 94.5 g. 67. Name all the mechanical constraints, their symbols, the symbols of the forces, and the mechanical properties. 68. Give the types of guides, the types of links and their principal characteristics. 69. Give the complex mechanical functions, transmission of motion (function, components & operation, advantages, disadvantages, examples). 70. What is a Wave? What are its characteristics? (pg. 37, 92-93, long vs. short wave) 71. What is the difference between a compressible and incompressible fluid? 72. What is the difference between an elastic deformation, plastic deformation, and a fracture? 73. There is a small wheel and a larger wheel in a gear train system. Which wheel (gear) turns faster? THE END YIPPEE!!!!