Civil War Overview Part II
advertisement
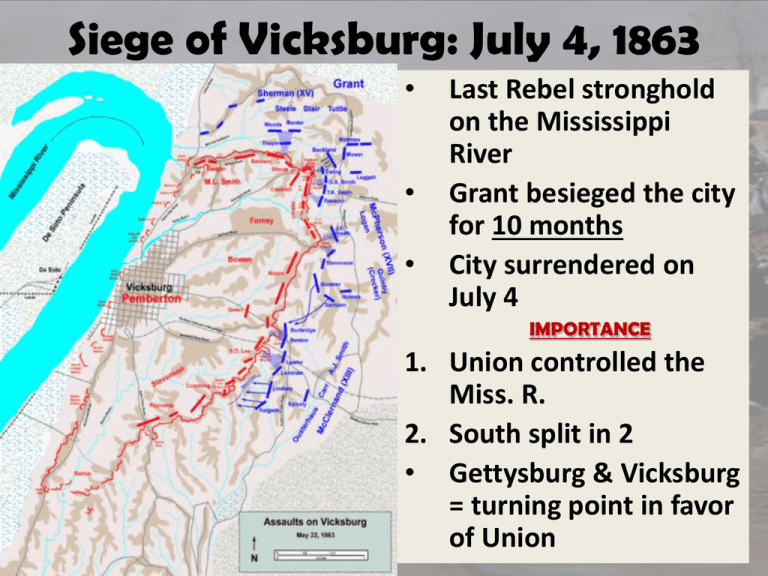
Siege of Vicksburg: July 4, 1863 • • • Last Rebel stronghold on the Mississippi River Grant besieged the city for 10 months City surrendered on July 4 IMPORTANCE 1. Union controlled the Miss. R. 2. South split in 2 • Gettysburg & Vicksburg = turning point in favor of Union Bell Ringer What were some problems on the home front during the Civil War? Disagreements on the War • Desertion, riots (N.Y. and Richmond) • Copperheads: Northern Democrats who supported the South • Lincoln suspended the writ of habeas corpus and jailed demonstrators Draft Laws • North and South pass conscription laws • Exceptions: – Southern planters owning 20 + slaves / no service to keep economy strong – Northerners could hire “subs” for $6000 – Northern Bounties: cash to volunteers • N.Y. riots “Gangs of New York” Economic Effects of the War • Inflation in the South • Industry replacing Agriculture as main money maker • 1861: 1st Income Tax – Tax on all earnings • 1862: Green Backs – Paper Money Civil War Overview Part II Battle of Gettysburg: July 1-3 1863 • 90,000 Union troops under Gen. George Meade vs. • 75,000 Rebels under Gen. Lee Gettysburg: Turning Point, Day 3 • Pickett’s Charge: 13,000 men –50 min. / 10,000 Casualties • Lee retreated to VA., Meade did not follow DEATHS • North: 23,000 • South: 28,000 Exit Ticket Now that you have read the Gettysburg Address, why do you think this is considered one of the most famous speeches in history? Explain! Bell Ringer What was the Gettysburg Address? What impact does this speech have today? Gettysburg Address • Lincoln came to Gettysburg to honor the fallen soldiers with the dedication of the new memorial and cemetery. • It is recognized today as an enduring statement of Americas values and goals. Four score and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent, a new nation, conceived in Liberty, and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal. Now we are engaged in a great civil war, testing whether that nation, or any nation so conceived and so dedicated, can long endure. We are met on a great battlefield of that war. We have come to dedicate a portion of that field, as a final resting place for those who here gave their lives that that nation might live. It is altogether fitting and proper that we should do this. But, in a larger sense, we can not dedicate—we can not consecrate —we can not hallow—this ground. The brave men, living and dead, who struggled here, have consecrated it, far above our poor power to add or detract. The world will little note, nor long remember what we say here, but it can never forget what they did here. It is for us the living, rather, to be dedicated here to the unfinished work which they who fought here have thus far so nobly advanced. It is rather for us to be here dedicated to the great task remaining before us—that from these honored dead we take increased devotion to that cause for which they gave the last full measure of devotion—that we here highly resolve that these dead shall not have died in vain—that this nation, under God, shall have a new birth of freedom—and that government of the people, by the people, for the people, shall not perish from the earth. Grant’s Plan • Grant given command of the Union Army in March 1864 when Lincoln fired Meade after Gettysburg • Grant’s Plan: 1. Pursue Lee in Virginia 2. Sherman would push through the South to Atlanta Grant in Virginia •His goal was to inflict more losses on the Confederates than they could withstand. • Battle of the Wilderness, May ’64 – Grant lost 17,000 • Spotsylvania & Cold Harbor – Grant lost 7,000 • June ’64, Grant arrived in Petersburg, outside of Richmond. Sherman’s Total War • Total War = war against the military and the people – Destroy way of life in the South • Sherman’s success helped Lincoln’s re-election. • Atlanta to Savannah- 300 miles of destruction Fall of Richmond • Battle of Petersburg * Lee vs. Grant = 10 month stand off in the 1st trench warfare battle • Lee could not hold – Pulled out and left Richmond open to Grant. • April 1865, Union Army arrived in the Confederate capital Lee Surrenders • April 9, 1865, Lee met Grant at Appomattox Courthouse in VA. • Grant’s terms: –Turnover arms –Keep belongings –Return to their farms –Feed the Rebels Exit Ticket • Why was Vicksburg and Gettysburg the turning point of the Civil War? • How does the Union win at the end?











