Reading Writing Maths combined workshop

Reading, Writing and Maths
Reception and Key Stage One
Laura Kirkham – Year Two
Danielle Keightley – Year One
Gillian Messenger - Reception
New Age-Related Expectations for the end of Key Stage 1 - Reading
Fluency:
• Secure with year group phonic expectations.
• Recognise simple recurring literary language.
• Read ahead to help with fluency and expression.
• Use commas, question marks and exclamation marks to vary expression.
• Read aloud with expression and intonation.
• Recognise:
– commas in lists
– apostrophe of omission and possession (singular noun)
Comprehension:
• Identify past/present tense and why the writer has used a tense.
• Comment on plot, setting & characters in familiar & unfamiliar stories.
• Recount main themes and events.
• Comment on structure of the text.
• Use content and index to locate information.
How we teach phonics
• Letters and Sounds – the phases:
• Phase 1 (ongoing) – hearing rhyme and non-phonic sounds
• Phase 2 – mostly single letter sounds (some consonant digraphs)
• Phase 3 – mostly vowel digraphs (e.g. ee, oa, oo)
• Phase 4 – adjacent consonants (in words such as ‘crash’)
• Phase 5 – alternative spellings for phonemes
• Phase 6 – spelling rules
Phonics screening check
• In June, all Year 1 children will undertake the phonics screening check to assess what they can and cannot decode
• Those children in Year 2 who did not meet the expected level in phonic decoding will also undertake the check
• The check involves reading phonically decodable real words and non-words
Words you can’t sound out!
• We call these ‘tricky words’
• Many are included in the New Curriculum list of common exception words
• They are taught alongside phonics
• For example:
• he is a tricky word because the ‘e’ is not making its usual short sound
• could is a tricky word because the letters ‘oul’ are making an ‘oo’ sound (as in book)
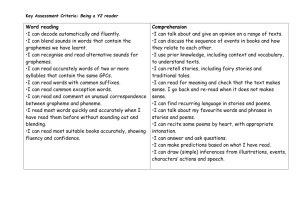
How we teach reading
• Guided reading
• Strategies
– Use phonics, but not if you know the word!
– Does it make sense? What would make sense?
– Look for clues in the picture or context of the book
– Have you seen this word on another page?
– Are there any bits of the words you recognise?
– Read ahead, miss out the word, and work out what it could be when you’ve finished the sentence
– Backtrack and read again for fluency
• Fluency (including use of punctuation)
• Comprehension
Reading at home
• Little and often
• Reading with and reading to children
• Reading for purpose
• Comprehension – and discussion of vocabulary and synonyms (link to writing)
• Using book marks
How we assess reading
• Before moving a child onto the next book band colour, a trained adult hears them read a specially selected book and asks the child questions
• If the child achieves 95% accuracy in reading and has a good understanding of what has been read, they move onto this colour
New Age-Related Expectations for the end of
Key Stage 1 - Writing
• Write different kinds of sentence: statement, question, exclamation, command.
• Use expanded noun phrases to add description and specification.
• Write using subordination (when, if, that, because) and co-ordination (or, and, but).
• Correct and consistent use of present tense & past tense.
• Correct use of verb tenses.
• Write with correct and consistent use of:
– capital letters
– full stops
– question marks
– exclamation marks
• Use commas in a list.
• Use apostrophe to mark omission and singular possession in nouns.
• Write under headings.
• Write lower case letters correct size relative to one another.
• Show evidence of diagonal and horizontal strokes to join handwriting.
• Spell the Y2 common exception words and words containing a range of Y2 phonemes
How we teach writing
• Talk for writing/story making
• Link to video
• Reading for writing – vocabulary/punctuation/sentence structure/story composition
• Sentence construction/oral rehearsal
• Separate grammar/punctuation sessions in preparation for new testing at the end of year 2
• Spelling focus
Spelling games and strategies to try at home
Building vocabulary – how can you do it?
Grammar and Punctuation – some games and resources
Maths: Non-negotiables for each year
• These are provided in your pack – they set out the key learning objectives for each year.
• They have a specific role in helping pupils meet the year group expectations. At
Rodborough we believe that if pupils are not confident in these areas then they will find the rest of the curriculum difficult to access.
• The maths curriculum is much broader than this!
Reception:
Count to 20
Counting
Year 1:
Count forwards and backwards to 100 in ones and from any starting point
Count in multiples of 2, 5 and 10
Year 2:
Count in multiples of 2, 3, 5 and
10 to 100
Count in tens from a 2-digit number
• Songs and books
• Everyday objects
• Numicon
• Hundred square
• Number lines
Reception:
Place numbers to 20 in order and say which number is one more or one less than a given number
Place value
Year 1:
Read and write numbers to 20 in digits and words
Read and write numbers to 100 in digits.
Say ‘1 more’ and ‘1 less’ to 100.
Year 2:
Compare and order numbers up to 100
Read and write all numbers to
100 in digits and words
Recognise place value of any 2digit number
• Arrow cards
• Numicon
• Tens and units resources (or bundles of straws!)
Reception:
Say which number is one more and one less than a given number
Number facts
Year 1:
Know bonds to 10 by heart
Use bonds and subtraction facts to 20
Year 2:
Recall and use addition and subtraction facts to 20
Derive and use related facts to
100
• Numicon
• Flip flops
• Games – ping pong
• songs
Addition and subtraction
Reception:
Using quantities and objects, add and subtract two single-digit numbers and count on or back to find the answer
Year 1:
Add and subtract 1 digit and 2 digit numbers to 20, including zero
Add any three 1-digit numbers with a total up to 20
Year 2:
Add and subtract:
2-digit numbers and ones
2-digit numbers and tens
Two 2-digit numbers
Three 1-digit numbers
Recognise and use inverse for addition and subtraction
• Calculations progression document
• Numicon,real objects, hundred square
• Mental strategies – use of facts
• Progress to COLUMN METHOD
Multiplication and division
Reception:
Solve problems, including doubling, halving and sharing
Year 1:
Solve simple multiplication and division with apparatus and arrays
Year 2:
Calculate and write multiplication and division calculations using multiplication tables
Recognise and use inverse for multiplication and division
• Counting in groups
• Arrays – egg boxes etc
• Sharing and grouping for division
• How many left over? Remainders
Maths Detectives!
Problem Solving and Reading
• Application through real life problems as opportunities arise
• Word problems/application tasks for each objective
• 7 strands of reasoning – Our New Programme
Reception:
Use everyday language to talk about time
Everyday maths
Year 1:
Use language of day, week, month and year
Tell time to hour and half past
Year 2:
Tell time to five minutes, including quarter past and to the hour
• Daily and weekly routines
• Telling the time
• Important dates and calendars
• Money – recognising coins and an opportunity to count in multiples
Thank you for coming!
If you have any further questions, please come and ask one of us after the session.