Short Story Lit Terms PowerPoint

Short Story Unit
Literary Terms &
Definitions
Adapted by Scott Victor from Erin Salona
Parts of Plot
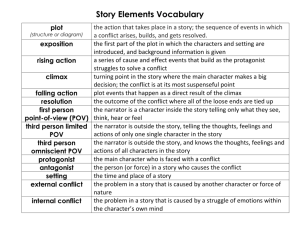
Plot: The sequence of events in a story.
Exposition: The basic situation of a story —this is where the reader learns the background information necessary to understand the story.
Exposition Example
The reader learns Liz lives in an apartment by herself.
Liz is 25-years-old.
Liz is tired from a long day at work as a nurse.
Liz is talking on her cell-phone to her best friend Julie as she walks to the door of her own home.
Parts of Plot
Complication (Rising Action): The part of the story which occurs between the exposition and climax. Here is where conflicts occur which build up the story and make it interesting.
Complication: Rising
Action Example
Liz hears some strange thumping sounds coming from the inside of her apartment as she is about to put her key in the door.
Liz tells Julie she hears something.
Julie suggests she calls the police.
Liz tells Julie that she was probably imagining the sounds but still hears them.
Parts of Plot
Climax: The main conflict is typically resolved at this place. This is also known as the turning point or highest point of action in a story.
Climax Example
Liz opens the door to her apartment and sets her bag by the door.
Her heart jumps when she sees a pair of black shoes peeking out from under her living room curtains.
The curtain moves slightly.
Climax Example
Liz bravely walks up to the curtain and picks up a heavy candlestick on the way.
She strikes the candlestick against the curtain, and at the same time, something grabs her hand from behind the curtain.
Liz drops the candlestick, and a tall man with a black mask emerges from behind the curtain.
Suddenly, her front door is flung open.
Parts of Plot
Resolution (Falling Action): The part of the story which occurs after the climax and continues to the end of the story. Here is where loose ends are tied up toward the end of the story.
Falling Action Example
The police emerge, and the masked man releases Liz from his grasp.
He quickly exits her home through the open window, but is met with the gun from a policeman.
Julie had called the police for Liz.
Liz realizes many of her possessions are knocked over or broken.
Parts of Plot
Resolution: The final outcome of the story.
Resolution Example
The police try to comfort Liz while taking her statement.
Liz packs some possessions to take to
Julie’s house for the night.
She decides to invest in a second lock for her door in the morning and to install a burglar system. She knows it will be difficult to continue living in her home.
Parts of Plot
Rising Action
Climax
Falling Action
Exposition
Basic Situation
Conflict
Resolution
Plot Curve
Time
Conflict
Internal Conflict: A conflict that occurs within a character’s mind. (man vs. himself)
Conflict
External Conflict: A conflict that occurs between a character and an outside force. Man vs. man, man vs. nature, for example.
Characterization
Static Character: A character who
does NOT change throughout the story.
Dynamic Character: A character who changes throughout the story.
Characterization
Round Character: A character with many qualities and personality traits.
Flat Character: A character with only a couple characteristics; is often the stereotypical character in a story.
Characterization
Protagonist: The main character of a story —who pushes the action of the story forward.
Antagonist: The character who frustrates, deceives, or works against the main character.
Methods of
Characterization
Direct Characterization: The narrator makes direct comments about the character. i.e. “She is friendly.”
Indirect Characterization: We learn about the character through her speech, thoughts, feelings, actions, physical appearance and through other characters’ thoughts, feelings, and speech about her.
Setting
Setting: Where and when the story takes place.
Place - geographical location. Where is the action of the story taking place?
Time - When is the story taking place?
(historical period, time of day, year, etc)
Weather conditions - Is it rainy, sunny, stormy, etc?
Describe the Setting
Point of View
Who is telling the story?
1 st Person POV: The narrator is a character in the story and uses “I” or “me” when telling the story.
2 nd Person POV: The narrator brings “you”, the reader, into the story when telling the story.
Point of View
3 rd Person Limited POV: The narrator tells only what one character thinks, feels, and observes, and uses “he,”
“they,” “she,” etc.
3 rd Person Omniscient POV: The narrator sees into the minds of more than one character when telling the story – uses “he,” “she,” “they,” etc.
Point of View
3 rd Person Objective Point of View:
the narrator tells what happens without stating more than can be inferred from the story's action and dialogue.
The narrator never discloses anything about what the characters think or feel, remaining a detached observer.
3 rd person pronouns are used (he, she, etc.)
Point of View
How can the point of view from which the story is told affect the credibility
(believability) of the story?
Consider: “Seventh Grade” is told in 3 rd person omniscient, allowing the reader to access all characters perspective. What if the story was told solely from Victor’s perspective? What would change?
Foreshadowing
The use of hints or clues to indicate events and situations that will occur later in the plot.
Spooky music
Thunder and lightening
A new suspicious character introduced (purpose unknown at the time)
Suspense
The excitement or tension a reader feels when reading.
I wonder what will happen next?
Mood
The feeling or atmosphere that the writer creates for the reader through word choice and imagery.
Types of mood: scary, romantic, violent, hopeful, etc.
Tone
Tone - the manner in which written words might be said (for example, sarcastic, mild, witty, angry)
Genres of Literature
• Different types of writing each genre shapes a theme or topic differently. Genres include…
• Classic literature
• Contemporary lit.
• Historical fiction
• Fantasy
• Science fiction
• Folklore
• Mythology
• Poetry
• Short stories
• Dramas
• Comedy
Theme
A perception about life that the writer conveys to the reader. A theme must be written in a complete sentence, and must apply to the story as well as to life in general.
A good way to find the theme is to ask yourself the question, what does the main character learn in the course of the story?
Theme
“There are some things that can never be fixed or repaired, even if you spend a lifetime trying..”
“The cruelest lies are often told in silence.”
“Money does not guarantee happiness.”
Universal Themes
Recurring themes (such as good versus evil) that appear frequently across traditional and contemporary works.
• Love
• Abuse of power
• Coming of age
• Effects of the past
• Courage
What is the theme of this film?
Symbol
A person, place, thing, or event that stands for itself and for something beyond itself as well.
Examples: the American flag symbolizes freedom, liberty, and love for America.
A wedding band symbolizes_______.
A white flag symbolizes__________.
Symbols in Literature
Dove = Peace
Eagle = freedom, liberty, strength
Spring = new beginning, re-birth, birth
Summer = youth, prime of life
Fall/Autumn = middle age, maturity
Winter = death, dying, old age, the end
Water = birth, re-birth, renewal, purification
Symbols in Literature
Rose = love, beauty
Sunrise = new start, beginning
Sunset = coming to an end
Full moon = danger, bizarre behavior
Sleep = death
Skull = death
Forest = place of testing or challenge
Light = good, hope, freedom
Symbols in Literature
Darkness = evil, magic, fear, unknown
Red = anger, passion
Blue = happiness, peacefulness, sadness, intellect
Green = jealousy, wealth, growth
Black = death, evil
White = purity, innocence