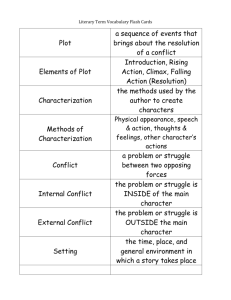
Literary Terms Definitions Review Worksheet
advertisement

Name:________________________________ Period:___________ Date:_________ Literary Terms Review Worksheet 1. Fiction is any ________________ story. 2. Non-fiction is literature which describes only real people or ___________________ such as historical works, ___________________, and autobiographies. 3. A short story is a ___________________ account of events brief enough to be read in ___________________, including plot, ___________________, setting, ___________________ of ___________________, and theme. 4. Conflict is the ___________________ between _________ ___________________ 5. External conflict has three types: ___________________;___________________; and ___________________ 6. Internal conflict is a character’s ___________________ or ___________________. 7. The protagonist is the ___________________ character in the story. 8. The antagonist is the ___________________ or ___________________ which causes the main character conflict. 9. The point of view is the ___________________ from which the story is told. 10. First person point of view is when the story is being told by a ___________________ in the story. Words like _____ or _____ are used throughout the story. 11. Third person point of view is when the story is told by an ___________________. Words like ____________ and _____________ are used throughout the story. 12. A narrator is the ___________________ who ___________________. 13. The setting is the ___________________ and ___________________ in which the story occurs. 14. The theme of the story is the statement about ___________________ of which the author wishes to make. It is also many times the ___________________ of the story. Usually the theme of a story can be expressed in a ___________________ ___________________. 15. The plot of a story tells what happens in a story in the ___________________ in which the ___________________ occur. 16. The exposition of the story is at the beginning and contains the ___________________, ___________________, and ___________________. 17. The rising action of the story tells the ___________________ that occur before the climax or turning point. 18. The climax or turning point of the story is the part where the most ___________________ or major ___________________ occurs in the story. 19. The falling action contains all of the ___________________ of the turning point or climax. 20. The resolution is at the end of the story and is where the ___________________’s conflics are resolved in some way. 21. Characterization is the means by which an ___________________ creates ___________________ people in his writing. 22. An ___________________ and ___________________ character is developed in two ways. 23. Direct characterization is what is said ___________________ by the narrator about a character. For example, “Sally was extremely rude.” Is an example of direct characterization. 24. Indirect characterization is what a character ___________________, what a character ___________________, and what other characters ___________________ about the character. For example, in a story we may read, the character, John, works out every day of the week; never messing a day. (This would indirectly lead the reader to understand that John was in good shape.) 25. Situation irony is an event that turns out the ___________________ of what the reader has been lead to expect of that situation. 26. Dramatic irony is when the ___________________ knows something that the characters in the story ___________________. 27. Foreshadowing uses ___________________ and ___________________ that predict the ___________________ of the story. 28. Flashback is a total ___________________ in the present action of the story to ___________________ a small back story that occurred previously. This many times gives background information. 29. Author’s Purpose is the ___________ that the author had for creating the work. Sometimes the author will state his or her purpose ___________________. Other times the reader will need to make ___________________ (reasonable ___________________) about the author’s purpose. Recognizing an author’s purpose helps the reader get more out of the reading. 30. There are four basic reasons an author might choose to write: a. To ___________________ or inform. b. To ___________________ c. To ___________________ d. To ___________________, or ___________________. 31. Mood is the ___________________ that a literary work gives to the readers. Writers use ___________________, ___________________, and images to create mood. 32. Tone is the ___________________ of the narrator. Tone can be ___________________, sad, ___________________¸sympathetic, or ___________________. 33. A symbol is something concrete, like a person, ___________________, or ___________________ used to represent something else bigger than itself; something abstract, such as a concept or an idea. Writers use symbols to bring meaning and emphasis to their writing. 34. A metaphor is a ___________________ comparison of two things NOT using ___________________ or as. 35. A simile is a ___________________ of two things using ___________________, ___________________, or ___________________. 36. A hyperbole is a comparison using an ___________________ metaphor or simile. 37. Denotation is the literal or “___________” definition of a word. (May also be referred to as a literal meaning.) 38. Connotation is the ___________________ or ___________________ a particular work or phrase may arouse. Words acquire their connotation by the way they’ve been___________________ in the past and by the ___________________ in which they’ve been used. (May also be referred to as an implied meaning.) 39. An allusion is a reference that a writer makes within the story to something in ___________________, ___________________, or ___________________. 40. The premise of a story is the “___________________”of the story. It contains just the ___________________ elements of a story that could apply to many stories like it.