File - BATCE SIXTH FORM UNIT 2 MOB
advertisement

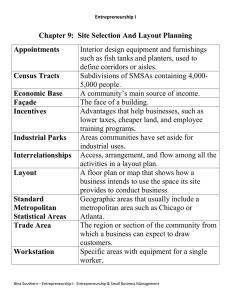
UNIT 2 MANAGEMENT OF BUSINESS Crystal Cassie WEBSITE: http://batcemob.weebly.com/ REFERENCE TEXTS: CAPE Management of Business: Kathleen Singh, Peter Stimpson Business Studies: Bruce R Jewell Business Studies: Dave Hall, Rob Jones, Carlo Raffo, Alain Anderton MODULE 1: Production and Operations Management Week Objectives Content Teaching/learning strategy TERM 1 1 Describe the major decisions involved in the nature of the production process Nature of production Input (FOP) throughout (production process) output (finished goods and services) Production methods: job, batch, flow and cell production Location of production: quantitative factors (site cost, transport cost, labour cost, revenue cost), qualitative factors (infrastructure, environmental and planning consideration, management preferences) Discussion 2 Explain techniques involved in forecasting 3 Discuss the strategies involved in product design 4 Explain the concept of capacity planning Forecasting techniques Sales force composite Delphi method Consumer surveys Jury of experts Moving average Least squares regression Product design strategies Modularization Miniaturization Integration Value analysis Computer aided design (CAD), computer aided manufacturing (basic principles) Capacity Planning Definition of capacity Importance of capacity utilitization Design capacity Efficiency capacity Calculation of capacity utilization(simple calculations) Methods of improving capacity utilization Economies and diseconomies of scale Brainstorming location factors: setting up a NightClub in Trincity Mall Student presentations in groups for each technique (posters) Assessment 2004Q2A 2JUNE2008Q1 2012Q2C 2013Q2B 2014Q1 2009Q2A 2006Q1 2004Q2 2002Q2 PPTS: Pictures of design strategies Discussion of value analysis with examples Discussion 2014Q2 5 6 Examine various strategies used in production layout process Assess the importance of costing in production 7 Examine the concept of inventory management 8 Explain the concept of lean production and quality management 9 Explain methods of measuring and improving productivity Layout Strategies Process layout Production layout Fixed position layout Costing Cost of production (direct/indirect variable/fixed) Approaches to costing (simple calculations): absorption, contribution/marginal. Application of marginal costing: break-even point (definition, uses, advantages and disadvantages, simple calculation of the following: BEP for output and sales, contribution margin sales for a desired profit, output for a desired profit and margin of safety). Draw break even charts Make or buy decisions Inventory Management Importance of inventory (stock) Inventory (stock) control management: EOQ (Simple calculations), Just in Time Lean Production and Quality Management Importance of quality Dimension of quality: performance, features, reliability, conformance, durability, serviceability, aesthetics, perceived quality. Techniques for improving quality including difference between quality control and quality assurance, benchmarking, ISO quality standards, outsourcing, quality circles, TQM (Kaizen or continuous improvement) Lean production (link between inventory management, quality and capacity and employee roles) Productivity Definition (express productivity as an equation) Factors that impact on productivity including technology, training, market demand, competition, quality of labour supply, level of pricing PPT Discussion Accounting students present to class Specimen Paper Question Use of examples to illustrate Discussion 2011Q1B1,11 2010 Q1 Comparison of two goods/services on dimensions of quality 2013Q1 2012Q2A,B 2011 Q1A1,11 2009Q1 30JUNE 2008Q2 2007Q1 2005Q2 2003Q1 Video Discussion Case study 2011Q2 2010Q2 2JUNE2008Q2 2006Q2 2005Q1 2003Q2 10 Assess the importance of project management Project Management: prepare and interpret diagrams of models Critical Path Method Decision trees Use of examples to illustrate 2013Q2A 2012Q1 2009Q2B 30JUNE 2008Q1 2007Q2 2004Q2B 2002Q1 Teaching/learning strategy Assessment MODULE 2: Fundamentals of Marketing Week Objectives 11 Define the term marketing and relate it to the concepts of market, exchange and value added Assess the implications of the marketing concepts The Concept of Marketing Definitions of marketing Related concepts: markets, value added, exchange transactions Distinguish between the micro and macro environments in which a firm operates and their effects on the marketing strategy of the firm The marketing environment Composition of the marketing environment: micro and macro environment Forces in the micro environment: company suppliers, competitors, marketing intermediaries, customers Forces in the macro environment: demographic, economic, natural, political, cultural factors 12 13 Content Implications of different marketing concepts The product concept and implications The production concept and implications The selling concept and implications The societal marketing concept and implications Discussion Students brainstorm and present posters in class on each concept in groups (COMICS) 30JUNE 2008Q3 SUBWAY: the micro and macro factors that impact the marketing strategy 2003Q3 14 15 TERM 2 1 2 Describe the elements of the marketing research process Explain the principles of market segmentation Explain the principles of product management Evaluate various pricing strategies Marketing research Role and importance of market research Importance of developing a research plan Describe the stages of market research: management problem identification, research objectives, sources of data( primary and secondary), sampling (probability and non-probability), research techniques (focus groups, surveys, in depth interviews, observation), analysis and presentation of results Limitations of market research Market research project to conduct in school population Principles of market segmentation Importance of segmentation Niche, target, mass marketing Bases of segmentation: demographic, geographic, behavioural Consumer buying behavior: the buying process, factors influencing buying behaviour Students choose a good/service to market to segments Product Management the concept of product: core, formal/actual, augmented dimensions of the product mix: product line and product extension Boston matrix new product development process product life cycle branding and packaging characteristics of services compared to goods Pricing decision Introduction to pricing: definition, role and importance Factors influencing pricing decisions (elasticity of demand, demand, income, consumer preference) Pricing strategies: cost plus, competition, perceived value, going rate, penetration pricing and price skimming PPT Consumer buying behavior illustrated while purchasing a new PC Students create a product to illustrate concept, dimension Videos Group presentations Case study Discussion Presentation by Economics students 2013Q4 2011Q3,Q4A 2010Q3 30JUNE 2008Q4A 2JUNE2008Q4 2007Q4 2006Q4 2003Q4 2002Q3A 2014Q3A 2011Q4B,C 2010Q4 30JUNE2008Q4B,C 2006Q3 2014Q3B 2005Q4 2002Q3B 3 Discuss the major principles of distribution Distribution management Role of distribution in an organisation Factors influencing distribution decisions Types of distribution channels (direct, indirect) Introduction to logistics strategy Types of distribution strategies (intensive, selective, exclusive) Discussion 2014Q4A 2012Q4 2009Q4 2004Q4 4 Examine the major tools of promotion and their implications Promotion strategy Objectives of promotion Tools of promotion and their relative advantages: advertising, personal selling, sales promotion, publicity Students role play tools of promotion 2014Q4B 2013Q3 2012Q3 2009Q3 2JUNE2008Q3 2007Q3 2005Q3 2004Q3 2002Q4 5 Discuss the importance of internet marketing decisions Internet Marketing Development of internet marketing Opportunities created by internet marketing Challenges posed by internet marketing Importance of ecommerce to business organisations Student written research project MODULE 3: Small Business Management Week Objectives 6 Explain the nature and characteristics of entrepreneurship Content The nature and characteristics of entrepreneurship Definitions of entrepreneurship Intrapreneurship Corporate entrepreneurship Social entrepreneurship Characteristics of successful entrepreneurs Teaching/learning strategy Assessment Nina Programme PPTs Brainstorming Past papers 2002-2014 Q5,6 7 Explain the relationship between business organisations and the economic system in which they operate Assess the criteria for measuring size and growth of business Business and economic systems Economic systems in which businesses operate (free economy, mixed economy, planned economy) The impact of the economic system on business decision making Economics students in class present on economic systems Video Discussion Size and growth of business Criteria for measuring size and growth: output, labour force, market share, capital structure Advantages and disadvantages of small vs large firms: size and financial requirements, economies of scale, strategies for growth, management and control, lack of record keeping, working capital deficiencies, poor management skills, regulation and legislation Comparison of a small and large firm 9 Assess the challenges and opportunities faced by small businesses Major challenges and opportunities faced by small businesses Identifying successful business opportunities Sourcing capital (finance) Selection of business types (sole trader, partnership, company) Determining a location Globalization and trade liberalization Ecommerce Intellectual property Interviewing a small business owner in their community (reporting) 10 Describe the types of assistance agencies offer to small businesses Types and nature of assistance available to small firms Agencies that assist small businesses: government, nongovernment, financial institutions Types of assistance offered to small businesses: financial, technical, education and training Leaflets and information booklets from existing organisations 8 11 Develop a business plan TESTS EVERY THREE TOPICS Preparation of a business plan for a small business Executive summary Business description: legal establishment, start up plans Business environment analysis: target market, customer needs, location Industry background Competitor analysis: who are your competitors Market analysis: customer needs, where they are, how to reach them Marketing plan: pricing strategy, promotion strategy, distribution strategy Operations plan: cost of production, machinery Managerial summary: management personnel, staffing Financial plan: profit and loss, cash flows, break even analysis, source of funds, business ratios, assumptions Preparation of a business plan by each student