Module 04
advertisement

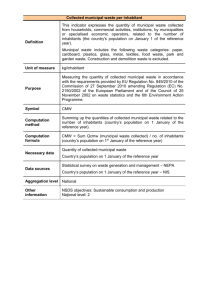
Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM [Module 4] Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM How do you manage a solid waste management system? Can it be framed around technology only? Nowadays we have to ask other important questions – Which ones ? For whom is the waste managed? How can conflicting ideas and claims be dealt with Who is responsible for planning the system and creating it? Who operates it? Who maintains it? Who pays for it? Who uses it? Who owns it? Module 4: Basics 2 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM How do you manage a solid waste management system? Planning Management Using best practice examples to promote solutions Inclusion of stakeholders Compile a personal work plan Financing Prepare a report on the outcomes of the training Institutional framework Module 4: Basics 3 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Strategic planning of integrated MSWM Strategic planning is a systematic process of envisioning a desired future, and translating this vision into broadly defined goals or objectives, and a sequence of steps to achieve them. Module 4: Basics 4 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Strategic planning of integrated MSWM – the process stakeholder - consensus building Governance and institutional framework 2. Define baseline Financial sustainability 3. Establish strategic planning framework Capacity building Awareness generation & behavioural change Integrate strategic aspects Integrate functional elements 4. Identify and evaluate options Technology options 5. Develop strategy 6. Prepare action plan 7. Implement the strategic plan update Delegation / Regional approach Stakeholder participation 1. Mobilise the planning process Module 4: Basics 5 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Planning of integrated MSWM – Understand the context Content of the plan (1) Framework & context (2) Strategy for collection, storage and transportation (3) Strategy for treatment and disposal (4) Strategy for waste reduction (5) Institutional and organizational setup Technical options (6) Strategy for financing and cost recovery Implementation strategy (7) Strategy for building public awareness and education Framework conditions Local conditions Local objectives and Plan http://origin-ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S0956053X13000032-gr2.jpg Module 4: Basics 6 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Planning of integrated MSWM – City Sanitation Task Force as responsible body Who is involved? Repres. from educational and cultural sector Repres. from formal and informal companies Agencies directly responsible City Sanitation Task Force Repres. from Unions NGOs working in relevant sectors Repres. of higher levels of Govt. Agencies indirectly involved Re-pres. from civil society / communities Eminent individuals and practicioners Repres. from private sector Module 4: Basics Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Planning of integrated MSWM – City Sanitation Task Force as responsible body Responsible for e.g. Municipal Corporation Launching MSWM Campaign Recommend permanent responsibilities Overall guidance to implementing agency Communication of progress Generating awareness City Sanitation Task Force Approval of project documents and reports Approving the MSWMPlan Field visits to supervise progress Module 4: Basics Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Exemplary planning issues Waste quantification Regional apporach Planning of transfer stations Module 4: Extras 9 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Quantification of waste Why? Input for assessment of required capacities and services What? Amount of waste generated within the municipality (per type / per day / per year) Spatial distribution of waste generated http://www.iswa2012.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/03/garbage-india.jpg Composition of waste generated How? Rough estimation as per average waste production and composition as a function of city and ward size Identification and location of generators of specific wastes or bulk waste (commerce, institutions, hotels, restaurants, etc.) Application of specific methods as described in MoUD technical manuals Module 4: Extras 10 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Quantification of waste Module 4: Extras 11 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Regional approach What Is Regionalization ? • Regionalization refers to bundling of the waste disposal needs of several towns/cities and tackling the problem of all of them through creation of one regional facility • A partnership between Urban Local Bodies Module 4: Extras 12 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Optimization of waste transfer – best practice example Status quo • • • • 70 square kilometres city area; 1000 tonnes of waste per day; landfill 40km east of the city; severe traffic congestions in the city restricting the hours of collection. • • • • • 125 trucks (plus standby vehicles), 125 drivers and 500 loaders. vehicle costs: 8,750,000 $ total staff: 625 Option 1: Large transfer station Collection system requires: • 63 collection vehicles (plus standby vehicles), • 63 drivers and • 250 loaders. Transfer system requires: • 22 trucks, (plus standby vehicles), • 22 drivers and • 22 drivers’ assistants • vehicle costs: 6,230,000 $ • total staff: 379 Source: Solid Waste Management in the World’s Cities, UN-Habitat (2010), page 90 Module 4: Extras 13 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Optimization of waste transfer – best practice example Option 2: 12 small transfer stations Each SRS requires collection system: • 12 handcarts and tricycles collect 8 tonnes per day within a 0.5km radius of the STS (one crew). • 8 three-wheelers (1.5-cubic-metre Tuctucs) collect 40 tonnes per day within a 1.5km radius (one crew). • 5 3-cubic-metre tipping trucks collect 40 tonnes per day within a 3km radius (two crews) (each of the above vehicles will require backup vehicles to allow for breakdowns) Transfer vehicles for 12 STS requires: • Transfer vehicles: 12 work two shifts with 24 drivers and 24 assistants. • Handcarts and tricycles: 12 X 12 = 144 with 144 loaders. • Three-wheelers: 12 X 8 = 96 with 96 unskilled driver/loaders. • Small tippers: 60 with 60 drivers and 60 loaders. • Total labour requirements: 84 drivers and 324 unskilled workers. Total requirements • vehicle costs: 3,088,000 $ • total staff: 372 Module 4: Extras 14 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Regional approach Why? Municipality A Collection Treatment and disposal exceed technical and financial capacities No land available Municipality B Collection Municipality C Collection Municipality D Collection Joint Transportation Joint Treatment Facility Economy of scale more attractive for private sector Joint Disposal Facility Framework Organisational set-up Delegation of responsibility Lead by State Government Partners ensure efficiency jointly Lead by Authority Reliable and sound cost sharing Competitive biding of Private Partners Sanctity of contracts Each ULB has responsibility for its part Module 4: Extras 15 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Regional approach more efficient use of land Advantages higher efficiency of costs Module 4: Extras 16 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Efficient use of land Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Figure showing landfill area (plan) local landfill 3 Acre local landfill Height of landfill up to bund is 1.5 m above bund is 3 m excavation depth is 1.1 m 11 Acre regional landfill waste going to landfill is 20 tpd landfill is designed for 3 years regional landfill Height of landfill up to bund is 1.5 m above bund is 15 m excavation depth is 1.1 m Waste going to landfill is 200 tpd landfill is designed for 3 years four times the area can dispose 10 times amount of waste ! Module 4: Extras 17 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Cost efficiency in INR per ton of waste Site development local landfill 20 tpd Rs. 39.83 / ton regional landfill 200 tpd Rs. 4.06 / ton Construction Rs. 579.00 /ton Equipment Operation and maintenance Rs. 188.00 / ton Rs. 135.00 / ton Rs. 25.34 / ton 20 tpd landfill is 4.3 times costlier 20 tpd landfill is 7.4 times costlier cost efficiency 20 tpd landfill is 9.8 times costlier 20 tpd landfill is 4.0 times costlier Factors determining O & M cost : • Number of equipments • Utilisation of equipments • Manpower • Consumables • Return of capital Module 4: Extras 18 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Management - General orientation / basic idea The municipal authorities should make concerted efforts to inculcate among their officers and staff a sense of pride in the work they do, and to motivate them to do their best to improve the level of services in the city and the image of the municipal administration. Module 4: Basics 19 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Discuss in group: Management key questions Management principles / tools Leadership involves • establishing a clear vision, • sharing that vision with others so that they will follow willingly, • providing the information, knowledge and methods to realize that vision, and • coordinating and balancing the conflicting interests of all members and stakeholders. • Who or what guides you? • How do you adapt your work to changing conditions? • Do you evaluate the achievements? • Do you communicate achievements and needs to upper and lower levels? • leadership • framework / rules of conduct • communication / information flow • follow-up • adjustment / intervention / decision • Capacity Development / Human Resource Development Module 4: Basics 20 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Management - elements Levels of management The circular model of management Data management Monitoring and improvement of performance Module 4: Basics 21 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Management tasks Mayor, President Commissioners, Chief Officers Upper Management Middle Management Health Officers, Engineers Lower Management Is there something to be added? Sanitary inspectors and supervisors Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM strategy goals, policy decisions framework for MSWM overall annual planning overall monitoring formation city sanitation task force technical supervision, monitoring operations guidance operations quality control operations supervision of strategy & plan implementation specific annual planning responsibility for service contracts stakeholder management working counterpart city sanitation task force implementation and supervision of day-to-day operations / services guidance and human resource development monitoring of contractors complaints redress maintenance infrastructure and equipment reporting Module 4: Basics 22 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Management of Municipal Solid Waste Citizens are responsible for Proper segregation of wastes at source Avoid littering of streets; Delivery of wastes Municipality is responsible for: Waste management from collection to disposal Sensitization of citizens for 3R and overall waste management; : http://www.cmar.csiro.au/research/mse/images/adaptive_cycle.gif What is Management ? The Management Cycle Module 4: Basics 23 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Information and data management There is a common rule in management: ‘If you want to manage, measure’! Why? (1) You have to know what is happening at any time (2) You need to recognize and address deficiencies (3) You need to have an idea on future requirements (4) You must be able to answer questions of stakeholders and supervisors Module 4: Basics 24 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Information and data management - basics Data • • • • clearly define data to be collected regularlaly define basic data to be collected in any case define add on data define data formats Collection • • • • standardized method regular intervals check reliability follow-up and supervise Storage • • • • ensure accessibility ensure standardized storage ensure regular updating consider IT solutions Processing • consider IT solutions • follow-up and supervise Module 4: Basics 25 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Management Information System General Waste infrastructure Management Operation Supervision City Wards Generation Storage Financial aspects Staff positions Collection Base line data Transport Treatment & disposal Storage Transport Treatment & disposal Special services Bulk services Vehicle maintenance Environmental monitoring Complaints Cost recovery Penalties Legal matters Module 4: Extras 26 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Monitoring and improvement of performance - Why SLBs are useful for ULBs? o SLBs help to institutionalise performance management o SLBs help ULBs to proof their performance as principal elected institution for city self-governance o Benchmarking with other cities facilitates competitive environment for continuous improvement o Performance data at sub-ULB level are useful for appropriate decisions o Help local decision-makers identify gaps, plan and prioritise improvement measures o Make it possible to link decision-making on financial allocations to service outcomes o Provide framework that can underlie contracts/agreements with service providers o Enhance accountability to customers for service delivery levels o Enable identification and transfer of best practice Module 4: Basics 27 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM SLBs for MSWM Indicator Benchmark (1) Household level coverage of solid waste management services 100% (2) Efficiency of collection of municipal solid waste 100% (3) Extent of segregation of municipal solid waste 100% (4) Extent of municipal solid waste recovered 80% (5) Extent of scientific disposal of municipal solid waste 100% (6) Efficiency in redressal of customer complaints 80% (7) Extent of cost recovery in SWM services 100% (8) Efficiency in collection of SWM charges 90% Module 4: Basics 28 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Monitoring process Module 4: Extras 29 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Inclusion of stakeholders Participation Gender aspects of MSWM Participaton of informal sector Module 4: Basics Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Inclusion of stakeholders – Why is it important? (1) Solid waste management is a shared responsibility (2) Participation creates ownership and means shared responsibility for the strategy and its joint undertaking (3) Participants bring information for the strategy, ensuring that it is based on a common understanding of purpose, problems and solutions (4) Participation is the most effective way of communicating information on which the strategy is based, its goals and tasks to be undertaken; (5) Participation by stakeholder groups is critical for decision making. The result will be a realistic strategy with a broad base of knowledge, understanding and commitment from the groups involved Module 4: Basics Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Inclusion of stakeholders – Where and when is it important? http://4.bp.blogspot.com/-7IwhuRXM-hI/UN-h-25BjgI/AAAAAAAB0XY/FXbI1neWl6U/s1600/SELFSERVICE-BIN.jpg (1) Implementation of the 3R approach (2) Segregation at source and (secondary) storage of biodegradable / non-biodegradable wastes, recyclables etc. at source (3) Community storage facilities and collection form there in flats, multi-storied buildings, societies, commercial complexes, institutions, etc. (4) Door-to-door collection or collection via community bins, collection of recyclables, HHW, etc. (5) Stop of public littering (6) Introduction of user charges / fees, understanding need to pay for services; Module 4: Basics Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Stakeholder participation Guiding principles (1) Build confidence – take partners serious, ensure two way communication and collaboration, establish rules and respect norms, respect each other, don’t play games, respect other interests, and opinions (2) Ensure to reach the community – ensure that all relevant stakeholders / actors are reached and included; make the project attractive; make added value visible; motivate reluctant parties to participate https://kce.fgov.be/sites/default/files/imagecache/content_page_image_doublec olumn/R_174.jpg (3) Involve stakeholders actively in problem identification and solution - involve partners in problem analysis, visioning, priority setting, solution identification, strategy development, implementation and monitoring; avoid the feeling of only being decoration (4) Include stakeholders in implementation and success stories – make success in pilot projects visible to other areas, let the stakeholders participate in success stories (5) Public Information, Education and Communication – ensure sufficient outreach and visibility, offer various measures to build the required awareness and capacities Module 4: Basics 33 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Extent of participation Passive • spectator • no own initiative Only for incentives • participate only if there is some kind of gain Consultations • engagement only on particular topic • not proactive • answering questions Functional participation • proactive • functional engagement • supportive efforts Interactive participation • ability to influence decisions • suggest / demand for alternate options Self Mobilization • willingness to contribute resources • highly empowered to take up activities • decision making Module 4: Extras Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Tools to organize and manage participation – stakeholder analysis 1) stakeholder landscape 2) analyse interests of stakeholders: are they in line with the project or controversial ? 3) possible impacts of dissonances, differences in interests 4) develop strategy for management of stakeholders according to their role / influence, interest and potential conflicts https://www.wbginvestmentclimate.org/toolkits/public-policy-toolkit/images/sample-stakeholder-matrix_1.JPG Module 4: Extras Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Tools to organize and manage participation – how to deal with conflicts? Options to deal with conflicts: a) ignore b) live c) find options to achieve win-win situation Avoid: http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcQhLbwVzBwBK7oViaKQEHvGNcTP9W39SIHm53RnvZi013JYhMhO a) naivety b) neutral poses when you are not c) underestimating potential for violence d) to be the do-gooder e) to be the megaphone Module 4: Extras Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Tools to organize and manage participation - examples (1) Group meeting After an opening presentation, the group is broken into smaller groups to discuss an issue or complete a specific task. Summaries of small group discussions and an open comment period may follow. Focus group discussion Small discussion group led by a facilitator who draws out in-depth stakeholder input on specific questions. Normally, several focus groups are held, and participants can be chosen randomly or to approximate a subset of the community. Interview Face-to-face or telephone interaction with stakeholders conducted by the agency or by a third-party representative. Field trip Trip to specific location organized so that participants can match their mental images to real, on-the-ground conditions. Participants may be asked to express their reactions verbally or in writing. Module 4: Extras Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Tools to organize and manage participation - examples (2) Open house Event in which the public is invited to drop in at any time during an announced period. Event includes staffed booths or stations on specific topics and may precede a public meeting. Public hearing Formal, single meeting where stakeholders present official statements and positions, and those ideas are recorded into a formal record for delivery to the agency. Poll or survey Written or oral lists of questions to solicit community impressions about issues at a specific moment in time. Polls and surveys can be administered in person, or via the telephone or Internet. Module 4: Extras Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Gender aspects of MSWM (1) Women and men look at waste from different perspectives. (2) Recycling and reusing of wastes have critical gender dimensions: a. on generation side b. on recycling side What are gender related key issues in MSWM? • Women and children are prime handlers of garbage in households • Services and equipment are designed by men, with other priorities in mind • Women and children are often more exposed to SW health hazards than men • Women are key to improving SWM of family and community Module 4: Basics 39 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Gender aspects of MSWM Roles and responsibilities of women in waste management of households • Women decide what is useful and what is waste, and handle the waste • Women know the waste disposal places in their neighborhoods • The boundary between household and community is a gender boundary: Waste collectors, as well as the city leadership, who are generally male, tend not to understand the interests and needs of women in relation to the collection of household waste, e.g.: • They may complain when the waste is not set out properly, not taking into account that the women often cannot really leave their homes to put it in its proper place; • Times for waste collection may not have been set with any attention to the schedules and responsibilities of the women who will bring the waste to be collected. • Containers which are appropriate for storage in the home may not be acceptable to the collectors, etc. • Storage bins may not be easy to handle for women Module 4: Basics 40 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Gender aspects of MSWM Women as workers in waste management • Services and equipment are designed by men • Women workers are usually paid less • Women entrepreneurs and workers are underprivileged, their access to credits is even worse than for men • Lack of interest, political will or weak sense of importance in the community of decision makers to address issues of women workers in any cogent manner Module 4: Basics 41 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Participation of informal sector - Social business door-to-door collection of waste collection, processing and sale of recyclables collection, processing and sale of biodegradable waste collection, processing and recycling of E-waste A Social Business o addresses a social objective o is a non-loss, non-dividend company o is distinct from a non-profit because the business seeks to generate a modest profit o profit will be used to expand the company’s reach, improve the product or service or to subsidize the social goal can help to formalize informal activities improves social security requires entrepreneurs improves income requires investment can be a partner for the ULB requires support Module 4: Basics 42 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Financing Financing Public Private Partnership Module 4: Basics Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Financing – priotization and optimization of costs and income Priority for obligatory services Define minimum level of services Check options for increase of income Review level of existing charges and fees Encourage delegation Review costs Module 4: Basics 44 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Financing - implementation Financing of investments • • • • • government schemes and subisidies international loans and funds Municipal bonds, financing from own sources PPP or other private financing regional MSWM to reduce costs O&M and capital cost recovery • • • • introduction and collection of charges and fees percentage of property tax alternative income sources (products, carbon credits …) private investment in O&M, institutional finance, loans Financial management • controlling of project costs • double entry accrual accounting system • track costs of service provision Module 4: Basics 45 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Public Private Partnership private body provides a public service or project • makes an investment • takes a risk • guarantees a service in a specific quality and quantity • expects revenue Private Partner Public Partner • delegates a task • keeps ultimate responsibility • supports approval process • ensures payment • provides quality control and monitoring Module 4: Basics 46 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM PPP - process Module 4: Basics 47 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM PPP – Lessons learnt 1) Importance of rigorous project preparation and capacity building 2) Structuring focus on outcomes rather than inputs 3) Clarity on land availability and certainty of meeting concessioning authority’s obligations 4) Political commitment and policy continuity 5) Effective communication and engagement with a wider set of stakeholders 6) Need for well-defined transition process/duration 7) Commitments relating to waste quantity and quality Module 4: Basics 48 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Institutional framework Frequent weaknesses 1) Service providers entrusted with parts of MSWM are usually not directly accountable their clients 2) MSWM is usually under the responsibility of municipal departments not having the organisational and technical expertise to handle MSW 3) Performance and efficiency of workforce of the ULB entrusted with MSWM are often far from being satisfactory Module 4: Basics 49 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Institutional framework Required improvements in framework 1) Authorities and service providers should be for the delivery of the services and sustainability of the MSWM 2) Professionalization of MSWM and its workers and of their technical and managerial capabilities 3) Transparent institutional framework with well-defined roles and responsibilities for each task 4) Authorities to facilitate the processes and to build proper institutions to handle SWM Module 4: Basics 50 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Institutional framework Municipality is responsible for waste management from collection to disposal Goals Protection of environmental quality and health conditions Money for service quality – ULB is guardian of public money Accountability for delivery and quality of services Principles Transparent and well defined responsibilities for all tasks Authorities act as service providers to the public Mechanisms Decentralization Delegation • transfer of functions • decision making to external actors close to executing • private sector / actors • division of town into CBOs etc. zones • clear line structure Professionalization • capacity building to workers • equipment • human resource development • well educated staff Supervision • day-to-day supervision of services • data base • SLBs Module 4: Basics 51 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Institutional framework Municipality is responsible for waste management from collection to disposal Goals Protection of environmental quality and health conditions Money for service quality – ULB is guardian of public money Accountability for delivery and quality of services Principles Transparent and well defined responsibilities for all tasks Authorities act as service providers to the public Mechanisms Decentralization Delegation • transfer of functions • decision making to external actors close to executing • private sector / actors • division of town into CBOs etc. zones • clear line structure Professionalization • capacity building to workers • equipment • human resource development • well educated staff Supervision • day-to-day supervision of services • data base • SLBs Module 4: Basics 52 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Module 4: Extras 53 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Group work on possible objectives for MSWM plan The next slide lists possible objectives for a MSWM plan. Reflect the relevance of these objectives for your municipality and formulate and reflect other desirable objectives for a MSWM plan Select three or more of the objectives listed below or formulate other objectives. • increase in coverage of collection, • improvement in transportation, • improved management of specific waste classes, • waste reduction in general, • increase of recycling rate, • segregation of dry and wet waste, • establishment of procedures to prevent hazardous or untreated bio-medical waste from entering municipal waste chain, • ensure scientific controlled disposal, • establishment of procedures to formalize role of informal sector, • achieve financial self-sufficiency, Module 4: Activities 54 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Group work on possible objectives for MSWM plan (II) Discuss the following list of questions for each objective selected (you can indicate specific situation in single towns): • Specific relevance / urgency of the objective for the municipality • Data available to provide sound assessment of the situation? Op-tions to improve the database • Stakeholders to be involved • Analyse realistic options given in your municipality to achieve the objective. Which resources would be required to do so? • Discuss with your colleagues from other towns and compare the situations in the towns represented in your work group. Module 4: Activities 55 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Group work on SLBs in the home towns of the participants SLBs are an important tool for improvement of MSWM. They require a broad database and regular updating of relevant data. Reflect the situation in the home towns of the participants and collect ideas for improvement of the database. • Four working groups discuss 2 out of the 8 SLBs for MSWM each • Each group answers the questions listed in the table on next slide • Discuss with your colleagues from other towns and compare the situations in the towns represented in your work group. Module 4: Activities 56 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Group work on SLBs in the home towns of the participants SLB A SLB B SLB checked? Y/N Mode of data collection / calculation; If not checked regularly, which data would be available? Reliability of data Options to improve reliability of data. What would be required for improvement in terms of resources and working processes/ mechanisms? Conclusions from discussion Module 4: Activities 57 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Group work on using best practice examples to promote solutions in MSWM • Topics: Construction of small transfer stations in / or close to housing areas Promotion of segregation of wet and dry waste and big items at source Delegation - engaging informal sector in collection, segregation and composting Create your own project idea • Develop a concept and find arguments to convince reluctant decision makers and stakeholders to accept the concept for implementation by answering the following questions: What are the benefits of the selected projects for MSWM? What are the concerns of stakeholders and decision makers you expect? How can / will you address these in your project? Who could support you in promoting the project? • Discuss with your colleagues from other towns and analyse the obstacles and concerns in the different towns. Module 4: Activities 58 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Compile a personal work plan - individual and group work • Individual work: Each participant compiles an individual plan for improvement of his / her work within the next 3-6 months: What definite actions will you take within the next months to promote integrated and sustainable MSWM in your municipality? Please consider actions under your direct responsibility, Keep in mind the reasons for non-compliance and options for improvement as analyzed in the working groups during this training. Each participant takes the personal work plan with him / her as a reminder and agrees with a partner to report on progress every 4 weeks within the next 3-6 months. At the end of this period everybody reports to GIZ on the achievements. • Group work: Each group compiles a summary presentation of the individual actions for presentation and discussion. Module 4: Activities 59 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Prepare a report on the outcomes of the training • Individual work: Each participant reflects the training course and prepares an individual report to his ULB considering the following leading questions: Which new insights and best practice knowledge have been provided by the training? Which specific ideas and actions to improve the situation in your home towns have been triggered by the course? Please do not only focus on technology, but also consider governance, participation, management, organisation, and monitoring etc. What would you need to convince the decision makers in your ULB? • Group work: Each group compiles a summary presentation of the individual analyses for presentation and discussion. Module 4: Activities 60 Basic training on Municipal Solid Waste Management for Urban Local Bodies – M4: Key issues and principles of sustainable MSWM Thank you very much Indo-German Environment Programme (IGEP) Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH Sustainable Urban Habitat B-5/2, First Floor, Safdurjung Encalve, New Delhi-110029, Tel: +91-11-49495300/01/02 Module 4: Basics 61