Slide 1 - Help for MYP 4 and 5 Students
advertisement

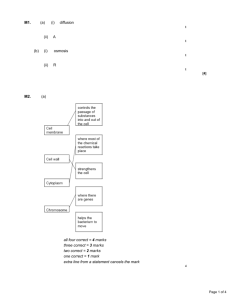
Movement of substances in and out of the cell. • Substances move in and out of the cell across the cell membrane. This movement can take place by: • 1. diffusion • 2. osmosis • 3. active transport. Cell membrane vs. cell wall Cell membranes are selectively permeable barriers. This means that some molecules are able to pass through while others cannot. On the other hand cell walls are non living, fully permeable barriers that allow all substances to pass through. Diffusion: Is the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. There is no energy input into the system . Osmosis: is simply a special type of diffusion, it is the net movement of water from a high water potential to a low water potential solution, through a partially permeable membrane. In both ,diffusion and osmosis, substances move down a concentration gradient. i.e. from high to low concentration. Osmosis in plant cells • Osmosis plays an important role in plants, especially non- woody ones. a) A plant cell is immersed in distilled water, the following diagrams show what happens. The following changes take place: 1. Water moves into the cell through the cell membrane 2. Cytoplasm & cell vacuole increase in volume. 3.Increase in cell volume increases internal cell pressure, which forces the cytoplasm to push against the cell membrane. 4.Cell membrane pushes against the cell wall. Cell becomes TURGID The cell becomes firm, we say it is turgid. As a result, The plant’s stem is upright and stiff. Why is turgidity important for: • a plant, in general? 1. Holds plant stems upright 2. Important in the functioning of the stomata b)Plant cell is placed in a concentrated solution. Gaps between cell wall & cell membrane fill with solution •Water moves out of cell via osmosis •Cell membrane shrinks away from cell wall The following changes take place: • 1 Excess water moves out of the cell • 2 Excess loss of water shrinks cell vacuole & cytoplasm, which radically reduces internal cell volume • 3 cell membrane pulls & cytoplasm away from cell wall The cell become plasmolysed because excess water has been lost through the cell membrane. C) Plant cell is placed in a low concentrated solution. The following changes take place: 1. Water moves out through cell membrane 2. Loss of water from inside the cell reduces the internal volume of the cell. 3. Cytoplasm no longer pushes against cell wall. 4. Reduced internal volume of cell leads to a reduced internal pressure. Cell becomes FLACCID. The cell has become flaccid. Leaves droop and collapse. Osmosis in animal cells • a) in distilled water, an animal cell bursts: Why is this different from plant cells? • b) In a concentrated sugar or salt solution, the animal cell shrinks and shrivels. Osmosis in red blood cells. a) Red blood cells in distilled water. b) Red blood cells in equilibrium. c) Red blood cells in a concentrated solution. The Visking tubing experiment. Set up the following apparatus: 1. Fill the visking tubing half way with colored sugar solution. 2. Place the capillary tube inside the visking tubing and tie with rubber band. 3. Mark the level of liquid in capillary tube. 4. Place the whole set in a boiling tube filled with distilled water. 5. Leave for 20 minutes. Record observations. Active transport • Is the movement of particles from low concentration to high concentration across a partially permeable membrane, against the concentration gradient. • This movement requires energy input from respiration. Examples of active transport 1. in animals: during digestion, the concentration of food molecules inside the small intestine increases as a result of absorption. So simple sugars, amino acids, minerals and vitamins are actively absorbed into the villi, from an area of lower to an area of higher concentration. 2. In plants: Plants need mineral salts (e.g. nitrates) for making proteins and growth. Minerals are at a higher concentration inside the root cells than in the soil particles. So energy is used by the root cells to actively transport minerals across the cell membrane into the root cells, against the concentration gradient. Where will particles diffuse faster? A or B? • 1. Explanation: A or B? • 2. Explanation: A or B? Pure water cells Explanation: Find the area, the volume and the area/volume ratio for A and B. A Side = 1 cm B side = 2cm. Area: Area: Volume: Area/volume: Volume: Area/volume: What factors affect the rate of diffusion? • 1. Temperature: The higher the temperature, the larger the kinetic energy and the faster the diffusion rate. • 2. concentration gradient: the steeper the gradient, the faster the diffusion rate. • 3. the size of particles: the larger the area/volume ratio, the faster the diffusion rate.