Prin. of Macro
advertisement

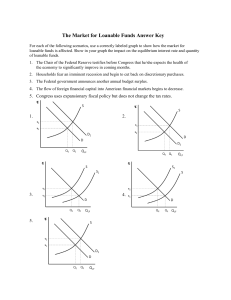
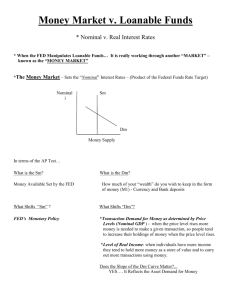
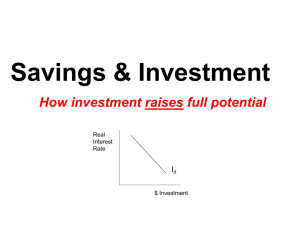
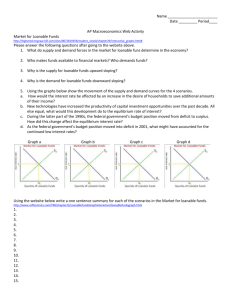
Prin. of Macro – Quiz 4 Name: ______________________ Multiple Choice: Select the BEST answer to the following questions 1. An increase in a nation’s capital stock (amount of capital employed by firms) b. makes labor more productive and hence firm’s demand more labor. 2. Which characteristics tends to be negatively effected by improved economic freedoms b. infant mortality 3. Based on the relationship of economic freedom and economic growth there are no examples of countries that have: b. low economic freedom and high economic growth 4. The catch-up effect says that countries with low income can grow faster than countries with higher income. c. evidence supports this theory for countries with similar institutional infrastructure. 5. From our basic model, an increase in labor demand leads to a. an increase in the wage rates, the number of people, and GDP. 6. A secondary effect of an increase in labor demand is a. a decrease in the price level and interest rate 7. Long run economic growth is likely caused by d. all of the above 8. Which of the following factors, if present, would act to impede the progress of a developing country? b. economic freedom 9. The short run impact of a change in consumer patience is felt d. only in the loanable funds market 10. Why is private ownership an important source of economic prosperity? d. It provides owners with a strong incentive to develop and use assets in ways that others value highly. 11. The loanable funds market is the market where b. equilibrium interest rates are determined by the actions of borrowers and lenders 12. One means of achieving economic growth is through improvements in the capital to labor ratio, however a. is sustainable only with continual dedication for private investment in capital. 13. Thomas Malthus, an 18th century writer-philosopher, believed man-kind was doomed to cycles of prosperity then death and dying that would then repeat. He believed this because d. resources grow at a slower rate than human population and thus become overly strained. 14. Other things constant, an increase in production technology in an economy a. makes labor more productive 15. In order to achieve a high economic freedom rating, a country must d. protect property rights, enforce contracts even-handedly, and rely extensively on markets to allocate goods and services. 16. Which of the following is not directly represented in our basic model? a. foreign exchange rates The People’s Republic of France is in the process of mandating the 32-hour workweek. If people are now working 40 hours a week and the mandatory 32-hour week becomes standard (the labor supply curve becomes independent of wages, i.e. vertical, at 32 hours of work per person), what will be the economic consequences? Completely, trace the effects through our basic model. Show and briefly describe the consequences on wage rates, GDP, employment (man hours), interest rates, investment, and the price level. (7 points) Labor market – increase in wages, decrease in employment Production function – decrease in employment – decrease in Real GDP Equation of exchange – increase in real gdp – decrease in inflation Loanable funds mkt – unclear (wages go up but less hours worked)