UNIT 1: CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS
advertisement

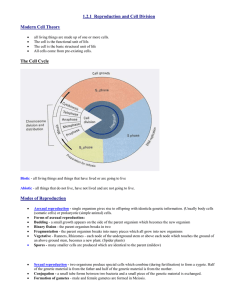
Lab Safety Rules 0 See handout from yesterday 0 Check out this rap What is Biology? 0 Biology is the science that seeks to understand the living world. How can we define “life”? Characteristics of Living Things 0 Made up of units called cells 0 Can reproduce 0 Are based upon a universal genetic code 0 Can grow and develop 0 Obtain and use nutrients and energy 0 Respond to their environment 0 Maintain a stable internal environment 0 Change over time (as a group) Made of Cells 0 Cell: collection of matter enclosed by a barrier that separates the cell from its surroundings 0 Unicellular: made of one cell 0 Multicellular: made of more than one cell Reproduction 0 Produce new organisms 0 Sexual reproduction: cells from 2 different parents unite to form offspring (meiosis) 0 Asexual reproduction: offspring has as single parent (mitosis) Universal Genetic Code 0 Asexual reproduction—offspring and parent have same traits 0 Sexual reproduction—offspring differ from parents in some ways 0 Genetic code=DNA 0 All living organisms follow this code 0 Determines your inherited traits Growth and Development 0 Can lead to an increase in size, a change in form, or an increase in # Obtain Nutrients and Energy 0 Metabolism: (sum of an organism’s life processes) 0 The combination of chemical reactions through which an organism builds up or breaks down materials as it carries out its life processes 0 Autotrophs: obtain energy directly from sunlight 0 photosynthesis 0 Heterotrophs: obtain energy by consuming other organisms 0 respiration Respond to Environment 0 Detect and respond to stimuli from their environment 0 Stimuli: a signal to which an organism responds 0 i.e. switching classes when the bell rings, 0 pulling hand off a hot stove, 0 asking for a mint when you hear a computer restart 0 Stimuli may be internal or external 0 Internal—regulating blood sugar 0 External—seeds germinating when soil is moist Maintain a stable internal environment 0 Homeostasis: process by which organisms maintain a stable internal environment 0 Usually involves feedback mechanisms 0 Such as the blood sugar example 0 sweating 0 Think of a thermostat Maintain a stable internal environment 0 This is the Regulation in RRREGENTS 0 Body systems included: 0 Endocrine system—hormones 0 Nervous system—uses nerve cells Concept Map 0 Work in groups to connect the words into a web that all stems from “Biology” Quick Lab 0 Materials: hand lens, unknown objects (dry), same objects soaked in water 0 Procedure: 0 1. Examine the dry unknown object in jar A. Record your observations. 0 2. Predict what you expect to see when the same object is soaked in water 0 3. Examine the object that has been soaking in water for a period of time in jar C. Record your observations. Wash your hands. 0 Conclusion: Which of these objects were alive? 15 minutes Levels of Organization Viruses, Bacteria, Prions, Ribosomes, and Cells 0 Read the brief passage about each of these, and characterize each as living or non-living. (15-20 minutes)