Lecture 1 - Center for Structural Biology
advertisement
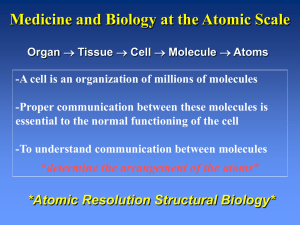
Jan. 10, 2007 Biochemistry 300 Introduction to Structural Biology Walter Chazin 5140 BIOSCI/MRBIII E-mail: Walter.Chazin@vanderbilt.edu http://structbio.vanderbilt.edu/chazin/classnotes/ Biology is Organized into Structures Organ Tissue Cell Molecule Atoms • A cell is an organization of millions of molecules • Proper communication between these molecules is essential to the normal functioning of the cell • To understand communication: *Determine the arrangement of atoms* What is Structural Biology? Sequence 3D structure MESDAMESETMESSRSMYN AMEISWALTERYALLKINCAL LMEWALLYIPREFERDREVIL MYSELFIMACENTERDIRATV ANDYINTENNESSEEILIKENM RANDDYNAMICSRPADNAPRI MASERADCALCYCLINNDRKI NASEMRPCALTRACTINKAR KICIPCDPKIQDENVSDETAVS WILLWINITALL Structural Scales polymerase SSBs Complexes helicase primase Organism Assemblies Cell Structures System Dynamics Cell Atomic Resolution Structural Biology Determine atomic structure to analyze why molecules interact The Reward: UnderstandingControl Anti-tumor activity Duocarmycin SA Atomic interactions Shape Atomic Structure in Context NER RPA BER RR Molecule Pathway Activity Structural Genomics Structural Proteomics Struct. Systems Biol. Current Strategy for Atomic Resolution Structural Biology • Break down complexity so that the system can be understood at a fundamental level • Build up a picture of the whole from the reconstruction of the high resolution pieces • Understanding basic governing principles enables prediction, design, control Pharmaceuticals, biotechnology Build-up Quaternary Structure 14/32D/70C 70AB X-ray Zn P C D 14 32CTD B A RPA70 RPA32 CTD RPA14 NTD quaternary structure? NMR 70NTD Put Structure Into Context MBP-tagged Siah-1 Approaches to Atomic Resolution Structural Biology NMR Spectroscopy X-ray Crystallography Computation Determine experimentally or model 3D structures of biomolecules • ESR/Fluorescence to measure distances when traditional methods fail • EM/Scattering to get snapshots of whole molecular structures (Cryo-EM starts to approach atomic resolution!) Inserting High Resolution Structures Into Low Resolution Envelopes Mesh = DAMMIN Ribbon = 1QUQ Why Structure in silico? • A good guess is better than nothing! – Enables the design of experiments – Potential for high-throughput • Crystallography and NMR don’t always work! – Many important proteins do not crystallize – Size limitations with NMR Computational Approaches Molecular Simulations • Convert experimental data into structures • Predict effects of mutations, changes in environment • Insight into molecular motions • Interpret structures- characterize the chemical properties (e.g. surface) to infer function Computational Approaches Structure Prediction 1 QQYTA KIKGR 11 TFRNE KELRD 21 FIEKF KGR Algorithm • Secondary structure (only sequence) • Homology modeling (using related structure) • Fold recognition • Ab-initio 3D prediction: “The Holy Grail” Complementarity of the Atomic Resolution Methods • X-ray crystallography- highest resolution structures; faster than NMR • NMR- enables widely varying solution conditions; characterization of motions and dynamic, weakly interacting systems • Computation- fundamental understanding of structure, dynamics and interactions (provides the why answers); models without experiment; very fast Representations of 3D Structures C N Both accuracy and precision are important THE STRUCTURE? • To correctly represent 3D structure (not a model), the uncertainty in each atomic coordinate must be represented • Polypeptides are dynamic and therefore occupy more than one conformation Which is the biologically relevant conformer? Does the molecule crystallize in the biologically relevant conformation? Accuracy/Precision Determined Differently for X-ray and NMR X-ray X-rays Diffraction Pattern NMR RF Resonance RF H0 Direct detection of atom positions Crystals Indirect detection of H-H distances In solution Variability: Uncertainty and Flexibility in Experimental Structures X-ray NMR •Uncertainty Avg. Coord. + B factor Ensemble Coord. Avg. •Flexibility Diffuse to 0 density Mix static + dynamic Less information Sharp signals Measure motions Representation of Structure Conformational Ensemble Neither crystal nor solution structures can be properly represented by a single conformation Intrinsic motions Imperfect data Variability reflected in the RMSD of the ensemble Challenges For Understanding The Meaning of Structure • Structures determined by NMR, computation, and X-ray crystallography are static snapshots of highly dynamic molecular systems • Biological process (recognition, interaction, chemistry) require molecular motions (from femto-seconds to minutes) • New methods are needed to comprehend and facilitate thinking about the dynamic structure of molecules: visualization Visualization of Structures Intestinal Ca2+-binding protein! Need to incorporate 3D and motion Center for Structural Biology Dedicated to furthering biomedical research and education involving 3D structures at or near atomic resolution http://structbio.vanderbilt.edu