Anna M. NewmanEDCI 6304August 6, 2012 Assignment #12
advertisement

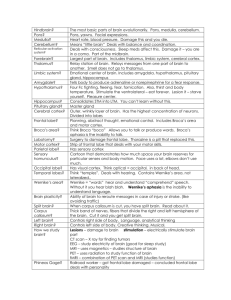
Anna M. Newman EDCI 6304 Assignment #12 August 6, 2012 Phrenology: a now abandoned study of the shape of the skull as indicative of the strengths of different faculties Broca’s area: the motor speech center in the left hemisphere of the brain in most people Broca’s aphasia: aphasia in which expression by speech or writing is severely impaired Aphasia: inability to use or understand language because of a brain lesion Liminal: the threshold of conscious perception Subliminal: below the threshold of conscious perception Absolute threshold: An absolute threshold is the smallest detectable level of a stimulus Difference threshold: is the minimum difference in stimulation that a person can detect 50 percent of the time. Agnosia: inability to recognize objects by use of the senses Apraxia: inability to make purposeful movements Frontal lobe syndrome: dysfunctions of the frontal lobe can give rise to relatively specific clinical syndromes, broca aphasia is an example of a frontal lobe syndrome. Heritability: the extent to which genetic individual differences contribute to individual differences in observed behavior (or phenotypic individual differences). IQ : IQ, or the intelligence quotient, was originally computed as the ratio of a person's mental age to his chronological age, multiplied by 100. Following this method, a child of 10 years old who performed on the test at the level of an average 12 year old (mental age of 12), was assigned an IQ of 12/10 3 100 5 120. More recently, the concept of "mental age" has fallen into disrepute and IQ is computed on the basis of the statistical percentage of people who are expected to have a certain IQ. An IQ of 100 is considered average. An IQ of 70 or below indicates mental retardation, and an IQ of 130 or above indicates gifted abilities. CAT scan: an image produced by scanning PET scan: a unique type of imaging test that helps doctors see how the organs and tissues inside your body are actually functioning. Limbic system: a system of functionally related neural structures in the brain that are involved in emotional behavior Menos or noble anger in 21st century jargon? Noble anger is about protecting one's own good, the good of the community, and even the good of the person who inflicted the injury. In 21st Anna M. Newman EDCI 6304 Assignment #12 August 6, 2012 Century jargon, it is like Clint Eastwood’s anger in the movie, Grand Torino. “Justifiable homicide?” 1. If I had to choose I would choose nurture. I would choose nurture because of the recent developments in brain research. The idea of plasticity of the brain has opened up a whole new realm of possibility for learning. I think that nature gives us some basic equipment to work with but what we end up doing with it is very much determined by the environment. Of course, in real life I don’t have to choose and I can be happy with a co-construction of meaning which includes aspects of both nurture and nature blending to make a whole! 2. “Learning Theories” used to describe conclusions drawn in psychological research in some cases is justified and in others it is not. A theory needs to be testable and tested and either supported with empirical evidence or not. Because of the nature of the topic, it is difficult to have a good clean experiment in which the variables are controlled and definite cause and effect relationships can be discovered. Both Watson and Vygotsky were bothered by this phenomena!