Speech and Music
advertisement

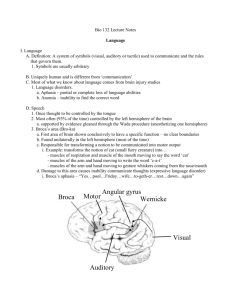
Language Humankind’s greatest achievement Language Defined Any set of symbols Ex: sounds, pictures, music Arranged according to rules Ex: grammar, sentence structure Convey an infinite number of meanings From one user to another Language takes two One person to produce the language by speaking or writing. Another to comprehend the language by hearing or reading “Language is something that goes in the ear and comes out of the mouth.” Norman Geschwind Language Skills Two basic, inherited Speaking and hearing Two developed and taught Writing and reading Language skills Two are primarily motor (movement) Speaking and writing Speech production Two are primarily sensory Hearing and reading Audition and vision Language is a whole brain task KW 9-19 Auditory Cortex KW 9-12 Speech comprehension KW 9-17 Penfield’s Surgery KW 9-18 PET Scanner KW 9-20 PET Scans KW 9-21 Cortex Activated in Sounds KW 9-23 Wernicke’s area Next to auditory cortex Attends to the sound and determines if the sound is a phoneme Connects phonemes to produce words Meaning of words Brain Dictionary Asymmetry in Language Broca Location of Broca’s Area Geschwind’s Model Geschwind’s Model in Action Producing speech KW 9-17 Effects of Brain Damage on Language Broca’s Aphasia Difficulty speaking and writing Prepositions, conjunction and other grammatical connectives are especially difficult Fail to understand speech when its meaning is dependent on connectives, sentence structure, or word order Wernicke’s Aphasia Trouble understanding speech and recalling names of objects Wernicke’s Wernicke’s Aphasia Music and the cortex Hearing and appreciating music is right hemisphere task Comprehend music with right hemisphere Production of music requires the left hemisphere as well Trained musicians: music is language Processing Music KW 9-24 Ravel’s Aphasia Composer of Bolero Left hemi stroke Loss of language Maintained some music abilities Could comprehend music Could not produce it The music’s over. End of slide show