Opportunity Cost
advertisement

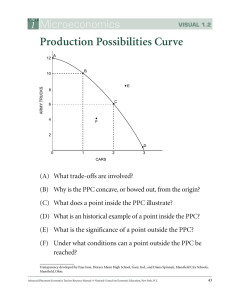
Unit 1 Basic Economic Problems * MicroEconomics - deals with individual units or groups * MacroEconomics - deals with nation or economy as a whole This is a need! A Want This is a need! A Want!!! This is a need! A Want!!! Our wants are UNLIMITED but resources are LIMITED……… So there is SCARCITY Hence we have to make CHOICES So we say, Resources are FINITE but Wants are INFINITE Economics is the Science of CHOICE (decisions made by YOU and ME, FIRMS, GOVERNMENT ) Hence scarcity forces us to make CHOICE After the CHOICE has been made……… You will use different resources to FULFILL THE CHOICE ALLOCATION OF RESOURCES Decision on ALLOCATION OF RESOURCES, Leads to 3 major economic problem/ questions: •What to produce •How to produce •Whom to produce Basic Economic Problem- 3 decisions • WHAT TO PRODUCE • Food or Clothes • Cars or hospitals • ipods or Cosmetics or military strength Basic Economic Problem- 3 decisions HOW TO PRODUCE techniques used. least cost method of production labour intensive or capital intensive Basic Economic Problem- 3 decisions for WHOM TO PRODUCE Will everyone get an equal share of what is produced ? Would the income be distributed equally? • Production: Creating goods and services • Consumption: Using the goods and services to satisfy want Economic Problem Factors of Basic Production (FOP) Labor The Enterpreneur: - Organizes the 3 factors and production process - Takes the risk (Profit and Loss) Goods produced Economic Goods Free Good Made by using resources/ FOP FOP not needed. Eg: They have a price Eg: Air, water Opportunity Cost If I ask you, what will you choose?? Schools Or libraries Roads Or Hospitals • What you DO NOT CHOOSE is your Opportunity Cost • Opportunity Cost is the highest cost forgone when making the decision Who has to face this problem of Opportunity Cost? • You and me (Individuals) • Firms (Business) • Government Production Possibility Curve (PPC) • Every decision/choice we make has an Opportunity Cost • This idea of Opportunity Cost can be illustrated using a PPC A Typical PPF …………. Unattainable Opportunity cost of is increasing… Inefficient • Production Possibility curve (PPC) shows the maximum combinations of goods and services that can be produced by an economy in a given time period with its limited resources • A point outside the graph is unachievable and a point inside the graph is inefficient PPC is also tells you: • What you can and cannot produce • What is the cost of producing the other good Depending on our choices of Production, the opportunity cost may Remain Constant Increase Decrease Production Possibilities/ Trade Off A = 24 lbs of coffee B = 16 lbs of cofee & 4 units of computers C = 8 lbs of cofee and 8 Computers D = 12 units of Computer Coffee (lb/day) A 24 B 16 C 8 D 0 4 8 12 Computers (unit/day) Cost of 4 computers= ? Another 4 Computers= ? Another 4 Computers = ? Hence Opportunity cost is same Slide 36 Constant O.C Decreasing O.C Increasing O.C Unit 1 : Macroeconomics National Council on Economic Education • Consumer Goods Products purchased by consumers for personal or household use. • Capital Goods Producers’ goods or means of production (Eg: Machines) Creating Capital goods Investment Shift in PPC Economic Growth Shift in PPC Butter C B Economic Growth due to…… 0 A Guns Availibility of resources (Quantity and Quality) Increased Labour force Improved Technology Shift in PPC Butter C A 0 Economic Decline due to ….. B D Guns Decline in resources Working population falls