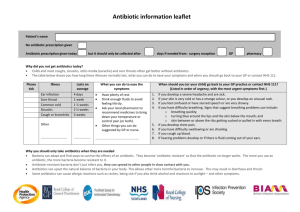
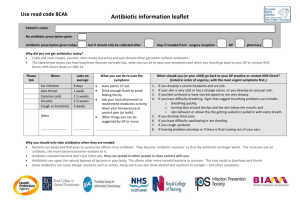
Antibiotic

ANTIBIOTICS
1) How do we usually fight bacteria, naturally?
2) Differentiate between bactericidal and bacteriostatic?
3)What is the single form of bacteria?
4)Why don’t doctors prescribe antibiotics for the common cold?
5) What are anaerobic bacteria?
6) Explain the purpose of a prophylactic antibacterial regimen.
7) What is a major side effect of clindamycin?
8)Why/how do bacteria become resistant?
Mozart-Minuet
December 5, 1791-Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart dies at 35-a mystery!!
Today- a common strep infection killed the maestro at the age of 35
(Annals of Internal Medicine) –HOW DOES THIS MAKE SENSE?
• Strep in the 18 th c = MRSA etc in the 21 st c
• Infections are increasingly difficult to stop—even with a modern arsenal of antibiotics.
• Resistant infections for which we have no effective treatment— putting us in much the same situation as those in the pre-antibiotic era
Maya Sequeria www.kevinmd.com
S. Aureus staph infection
Antibiotic Players
**In 3500 BC the Sumerian doctors would give patients beer soup mixed with snakeskins and turtle shells.
**Babylonian doctors would heal the eyes by using an ointment made of frog bile and sour milk.
**The Greeks used many herbs to heal ailments.
Read article
Modern History-Do Now-make a list!
1) Louis Pasteur-bacteria kill other bacteria
2) Ehrlich’s “Magic Bullets”-synthetic antimicrobial
3) Sir Alexander Fleming-1929-penicillin
4) Domagk-synthetic antimicrobials (sulfonamides)
http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/Antibiotics_Attack/frameset.html
Vocabulary
Antibiotic
Sterilization/disinfection/antisepsis
Selective toxicity
Bactericidal
Bacteriostatic
Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC)
Susceptibility testing
Resistance
ANTIBIOTICS/ANTIMICROBIALS
Bacterial Infections!!!
• Medications to treat bacterial infections
• Ideally, culture of suspect area should be done
BEFORE starting antibiotic
ANTIBIOTICS
• Selectively toxic for bacteria-targets bacterial structures
– bactericidal
– ex: antibiotics that target the cell wall, w/o which, there is no osmotic pressure and the cell bursts
– bacteriostatic
• no harm to patients…..
•Inside the body
•MIC (minimum inhibitory concentration)-next week!
antibiotic attack
What was the point of this game-what does it teach you about the different antibiotics and their activity in the body? Research & write about their targets, side effects and effectiveness.
Antibiotic Sterilization
Disinfection Antisepsis
Sterilization
1) All killed and non-selective
2) Methods:
• autoclaving
– 121 o C (heat/pressure): use heat-resistant materials
• ethylene oxide
– usually equipment
• ultra-violet light
– surfaces (e.g operating rooms)
– not totally effective
Disinfection
substances that kill bacteria on non-living surfaces
(ex. Phenol based)
-too toxic for the skin surfaces
-not as effective as the extreme methods of sterilization
Antisepsis
-Topical (ex. Skin)-on living tissue
-Ex. Iodine or 70% alcohol
-Meant to reduce the bacterial load
Antibiotic Resistance