Anatomy of Flowering Plants
advertisement

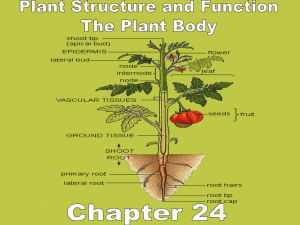
Depending on the region where the meristematic tissues are present, they are classified as apical, lateral and intercalary meristems. Apical meristem Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots and increases the length of the stem and the root. Lateral meristem The thickness of the stem or root increases due to lateral meristem (cambium). Intercalary meristem Intercalary meristem is the meristem at the base of the leaves or internodes (on either side of the node) on twigs. PARENCHYMA They are present in soft parts of the plant. i.e. roots, stems leaves flowers and fruits LOCATION STRUCTURE FUNCTION 1 The cells of this tissue are living. 2 The cell walls are thin and made of cellulose. 3 They are loosely packed. 4 Large intercellular spaces are found in this tissue The parenchyma of stems and roots stores nutrients, waste and water. T.S OF PARENCHYMA COLLENCHYMA They are located below the epidermis in stems and leaves. LOCATION STRUCTURE FUNCTION DIAGRAM 1 The cells of this tissue are living. 2 The cells are elongated. 3 The cell wall is irregularly thickened at the corners due to extra deposition of cellulose and pectin. 4 There is very little intercellular space. It provides elasticity and mechanical support to plants T.S OF COLLENCHYMA SCLERENCHYMA LOCATION STRUCTURE FUNCTION DIAGRAM It is present in the xylem and phloem of root, stem, leaves and the hard coverings of seeds and nuts. 1 The cells of this tissue are dead. 2 They are long and narrow. 3 The cell walls are uniformly thickened due to lignin. 4 There is no internal space inside the cell. It provides rigidity and mechanical support to the plant parts. T.S OF SCLERENCHYMA Dicotyledonous Root Monocotyledonous Root EPIDERMIS It consists of a single layer of compactly arranged cells It bears a number of unicellular root hairs but lacks cuticle. EPIDERMIS It consists of a single layer of compactly arranged cells It bears a number of unicellular root hairs but lacks cuticle. CORTEX It consists of several layers of thin-walled parenchyma cells with intercellular spaces. It stores starch grains. CORTEX It consists of several layers of thin-walled parenchyma cells with intercellular spaces. It stores starch grains. ENDODERMIS The innermost layer of the cortex is called endodermis. It comprises a single layer of barrelshaped cells without any intercellular spaces. ENDODERMIS The innermost layer of the cortex is called endodermis. It comprises a single layer of barrelshaped cells without any intercellular spaces. The tangential as well as radial walls of the endodermal cells have a deposition of water- impermeable, waxy materialsuberin-in the form of casparian strips. The tangential as well as radial walls of the endodermal cells have a deposition of water- impermeable, waxy materialsuberin-in the form of casparian strips. Dicotyledonous Root Monocotyledonous Root PERICYCLE It is made of one or two layers of parenchyma cells. It takes part in the formation of secondary roots and in the formation of cambium for secondary growth. PERICYCLE It is made of one or two layers of parenchyma cells. It does not take part in the formation of secondary roots and in the formation of cambium for secondary growth. VASCULAR BUNDLE Vascular bundles are radial. Xylem patches are 2-6. Diarch to Hexarch Xylem is exarch. VASCULAR BUNDLE Vascular bundles are radial. Xylem patches are many (polyarch). Xylem is exarch. PITH Pith is very small or absent. It is made up of parenchyma cells PITH Pith is large and well developed. It is made up of parenchyma cells All the tissues on the inner side of the endodermis such as pericycle, vascular bundles and pith form the stele. Dicotyledonous Root Monocotyledonous Root DICOT STEM Epidermis Multicellular trichomes present MONOCOT STEM Epidermis Trichomes absent Hypodermis Hypodermis 2 or 3 layers of collenchymatous 2 or 3 layers of sclerenchymatous cells provide mechanical strength to the cells young stem. Cortex Rounded thin walled parenchymatous cells with conspicuous intercellular spaces. Ground Tissue The Ground tissue is not differentiated into cortex and pith. It is parenchymatous. Endodermis The cells of the endodermis are rich in starch grains Endodermis Absent Pericycle Pericycle is present above the phloem in the form of semi-lunar patches of sclerenchyma cells. Pericycle Absent DICOT STEM Vascular bundle Arranged in the form of a ring Conjoint, open, and endarch. MONOCOT STEM Vascular bundle Scattered Conjoint closed and endarch. Peripheral vascular bundles are smaller than the centrally located ones. The phloem parenchyma is absent and water-containing cavities are present within the vascular bundles. Pith Parenchymatous cells with large intercellular spaces. Pith Absent DICOT STEM MONOCOT STEM DICOT LEAF MONOCOT LEAF It is a dorsiventral leaf. It is an Isobilateral leaf. Bulliform cells are absent in epidermis Bulliform cells are present in the epidermis Guard cells are kidney shaped. Guard cells are dumb bell shaped. Stomata are fewer in the upper epidermis, more in the lower epidermis Stomata are equally distributed in the upper epidermis and lower epidermis Mesophyll is differentiated into Palisade and spongy parenchyma Mesophyll is not differentiated into Palisade and spongy parenchyma Bundle sheath cells are parenchymatous Bundle sheath cells are sclerenchymatous DICOT LEAF MONOCOT LEAF