adjectives - TeacherWeb

Take notes on the pages titled “notes” and follow the directions on the pages titled
“practice”.
Lesson 1
• An adjective is a word that modifies, or describes, a noun or pronoun and tells what
kind, or which one.
Examples: The adjectives are the bold words.
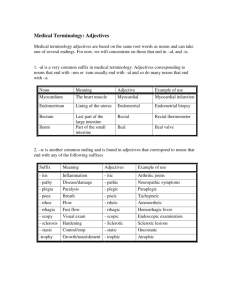
Adjectives
What kind?
Which one or ones?
How many or how much?
sunny day, cool evening
nearest umbrella, next day
many waves, 90 degrees
Directions: Write the adjectives. The sentence can have more than one adjective.
1. Francisco had a difficult time writing English.
2. His teacher had a round face, a small nose, and blue eyes.
3. Francisco worked hard on his homework assignments.
4. He memorized long poems that he kept in his shirt pocket.
5. Francisco was a slow reader.
Lesson 2
• A predicate adjective follows a linking verb and describes the verb’s subject. The linking verb connects the predicate adjective with the subject.
Examples:
V
1. The flood in spring was horrible. (horrible describes flood)
V
2. Such a calamity seemed nearly impossible. (impossible describes calamity)
Directions: Write the predicate adjectives. The sentence can have more than one adjective. If the sentence has no predicate adjective, write NONE.
1. The novel, The Grapes of Wrath, seemed long and difficult to Francisco.
2. Miss Bell looked upset.
3. Francisco was nervous.
4. Miss Bell’s smile seemed friendly.
5. Like Francisco’s family, the Joad family was poor.
6. To Mr. Bell, the rooms appeared old and uninhabited.
7. The first edition of the novel was expensive.
Lesson 3
• A demonstrative adjective points out something and tells
which one or which ones.
• Use this and that with singular nouns. Use these and those with plural nouns.
• This and these refer to nouns that are nearby; that and those refer to nouns that are farther away.
this, that these, those
Demonstrative Adjectives
this dog here, that horse
these dogs over there, those horses
Directions: Study the demonstrative adjectives in parentheses. Write the demonstrative adjective that correctly completes each sentence on the line provided.
1. __________ essay is mine. (These, This)
2. The students must read ________ books for English class. (these, this)
3. ________ book is about a traveling family. (These, That)
4. Will you hand me _______ theater tickets? (those, that)
5. __________ essay got the highest grade in the class. (This, Those)
• A proper adjective is formed from a proper noun.
• A proper noun begins with a capital letter.
• A proper adjective begins with a capital letter.
Asia
Mexico
Proper Nouns Proper Adjectives
Asian
Mexican
Lesson 4
Directions: Rewrite each sentence below., using capitals for any proper adjective.
1. She enjoys novels by italian authors.
2. It took a herculean effort to finish that novel.
3. Italy is a country located on the mediterranean coast.
4. Many american museums contain works of art by italian painters.
5. A popular renaissance painter from Italy is Michelangelo.
6. His paintings and sculptures are found in many european museums.
Lesson 5
• The most commonly used adjectives are the articles a, an, and
the.
• Use a and an with singular nouns.
• Use a if the next word starts with a constant sound.
• Use an if the next word starts with a vowel sound.
• Use the before all plural nouns and before some singular nouns.
a (with a consonant) an the a solution a case a one (sounds like it starts with
“w” an idea an apple an honor (sounds like it starts with
“o” the idea the apple the kids
Directions: Study the pair of articles in each sentence. Write the article that correctly completes the sentence.
1. Matthew and Andrew have (a, an) problem.
2. (A, The) time in the afternoon goes by too quickly.
3. What (a, an) annoying situation!
4. (A, An) owl flew past the window.
5. Make sure to get the doctor to take (a, an) x-ray.
6. Ah! I made (a, an) “F” on the test!
Directions: Tell which words are adjectives. Then tell which noun each of them modifies.
1 . The stormy weather forced the four players to delay the game.
2. We thought that the clumsy puppy would make a fun addition to the family.
3. The new boy in our class is tall.
4. His family comes from a small town in the northern mountains.
5. His older sister sings in a jazz band.
6. I asked the hair stylist for that haircut, and she gave me this one.
7. How will I explain these red spikes to my parents?
8. The helpful librarian recommended that I read this autobiography for my report.
9. I was going to read that novel because it is short and illustrated.
10. After I read the hefty autobiography I wanted to learn more about
Amelia, the main character.
Directions: Complete the sentences with the best possible adjectives to fill in the blanks.
11 . Three students from Paris visited our class and told us about ________ customs.
12. They also showed us how to make ________ crepes and croissants.
13. Last year, two girls from Tokyo came and played us some traditional
___________ music.
Directions: Tell which of the articles in parentheses should be used to complete the following sentences.
14. I was voted (the, a, an) best speaker there!
15. This would be the first time I spoke in front of (the, a, an) audience.
16. I would be telling them about (the, a, an) days when I lived in Costa Rica.
17. My family lived near (the, a, an) large banana plantation.
18. My father was (the, a, an) employee on the plantation.
Directions: Tell which words are adjectives. Then tell which noun each of them modifies.
19 . He plays the electric guitar and sings backup vocals.
20. They played three songs at our annual fundraiser.
21. Marsha finished the toughest calculations with a stubby pencil.
22. Amelia was a brave and fearless pioneer who lived through dangerous times.
23. She had two brothers who disappeared one stormy evening in Montana.
Directions: Proofread and re-write the sentences, paying special attention to the proper use of adjectives.
24. Erik spent last summer hiking, in the amazing new zealand forests.
25. This has been a dream of him since he were a young, boy.
26. He went with a lively group, of twelve International students.
Directions: Tell which of the articles in parentheses should be used to complete the following sentences.
27. My mother worked in (the, a, an) only grocery store in town.
28. On holidays we would visit our relatives on (the, a, an) coast.
29. Sometimes it would take (the, a, an) hour to get there.
30. In the next few years, my family will take (the, a, an) vacation down there.
Lesson 6
• Adjectives are words that describe nouns.
• The comparative form of an adjective compares two nouns.
• The superlative form of an adjective compares more than two nouns.
• Add –er to most one-syllable and some two-syllable adjectives to form the comparative.
• Add –est to most one-syllable and some two-syllable adjectives to form the superlative.
“older” compares two coins
“largest” compares her collection to any other he’s already seen
Lesson 6
• The comparative form of an adjective compares two nouns.
• The superlative form of an adjective compares more than two nouns.
• Add –er and –est to most one-syllable and some two-syllable adjectives to form the comparative and superlative.
• For adjectives ending in e, drop the e before adding –er or –est
• For adjectives ending in a consonant and y, change the y to i and add –er and –est.
• For one-syllable adjectives that have a single vowel before a final consonant, double the final consonant before adding –er or –est.
Lesson 6
Examples of the rules on the previous slide.
1. She is the nicest person I’ve ever met! (nice)
2. He is angrier than I am. (angry)
3. Shady is the laziest cat I know. (lazy)
4. August is the hottest month we have. (hot)
5. Slidell Junior High is bigger than Florida Avenue Elementary.
Lesson 6
Directions: Complete each sentence with the correct comparative or superlative form of the adjective in parentheses.
1. Theo is the (young) member of the group.
2. It was the (busy) group he had ever joined.
3. Their leader was the (happy) woman Theo knew.
4. She was also the (wise) person he had ever met.
5. It was (hot) today than it was yesterday.
6. This building is (tall) than that one.
Lesson 7
• For most adjectives with two or more syllables, use more to form the comparative.
• For most adjectives with two or more syllables, use most to form the superlative.
• Never use more or most with the –er or –est form of an adjective.
Examples:
1. extensive (3 syllables) = more extensive, most extensive NOT extensiver
2. difficult (3 syllables) = more difficult, most difficult NOT difficultest
3. intense (2 syllables) = more intense, most intense NOT intenser
4. fun (1 syllable) = more fun, most fun NOT funnest
5. near (1 syllable) = nearer, nearest NOT more near
Lesson 7
Directions: Write the word or words in parentheses that form a correct comparative adjective.
1. Mr. Smythe was (patienter, more patient) than usual when we were looking for new cards in his shop.
2. Justin thinks a Babe Ruth card is (more expensive, expensiver) than his parents’ car.
3. Of the two collections, Justin’s was the (more fun, funner).
4. Which card shop is (nearer, more near) to my house?
5. Who is (more friendly, friendlier), the pitcher or the goalie?
6. Diana is (more eager, eagerer) than Tasha to start a bell collection.
7. Diana probably will get her first bell (more soon, sooner) than
Tasha.
Lesson 8
Comparing with good
• The comparative form of good is better.
• The superlative form of good is best.
Comparing with bad
• The comparative form of bad is worse.
• The superlative form of bad is worst.
Examples:
1. Sometimes the (goodest, best) thing to do is to stand up for what is right.
2. Juan’s father, Jacob, wanted to get a (gooder, better) job.
3. Juan decided that the food in the school cafeteria was (badder, worse) than ever.
4. Juan stated that it was the (baddest, worst) in the country.
Lesson 7
Directions: Write the word or words in parentheses that form a correct comparative or superlative adjective.
1. Jacob chose the (goodest, best) time to state his case.
2. He also wanted a (gooder, better) working condition for the people on his crew.
3. He knew there was a (better, gooder) way to manage the business.
4. Stevi said that their food was no (worser, worse) than any other school’s food.
5. Which is (badder, worse), eating bad food or having to pay extra for it?
6. For Juan, the (baddest, worst) thing was having no fresh food at all.
7. “This is the (worst, baddest) example of nutrition I have ever seen,” said Juan.
8. French fries every day are a (badder, worse) choice than a baked potato.