Tissues
advertisement
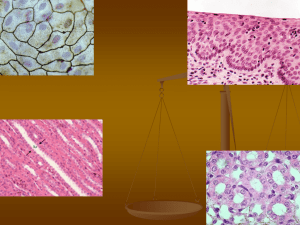
Tissues of the Body Key Terms Histology: the study of tissues. Tissues: groups of cells which are similar in structure and which perform common or related functions. Four Basic Kinds of Tissues Epithelial Tissue Connective Tissue Muscle Tissue Nervous Tissue Epithelial Tissue Epithelial Tissue Locations: Covers the body Lines the cavities, tubes, ducts and blood vessels inside the body Covers the organs inside body cavities Epithelial Tissue Functions: Protection from physical & chemical injury, Protection against microbial invasion, Contains receptors which respond to stimuli, Filters, secretes & reabsorbs materials and Secretes serous fluids to lubricate structures. Connective Tissue Connective Tissue: Most abundant & widely distributed tissue Connective Tissue Functions: Connects, binds and supports structures, Tendons, ligaments, etc. Protects & cushions organs and tissues, Insulates (fat) and Transports substances (blood). Muscle Tissue Muscle Tissue location: Associated with the bones of the skeleton, the heart and in the walls of the hollow organs of the body. Muscle Tissue Functions: Movement Locomotion Maintains posture Produces heat Facial expressions Pumps blood Peristalsis( wave- like motion ) Nervous Tissue Nervous Tissue location: Main component of the nervous system, ie., brain, spinal cord & nerves. Nervous Tissue Functions: Regulates & controls body functions Generates & transmits nerve impulses Supports, insulates and protects impulse generating neurons. Different types of Epithelium Squamous Epithelium Simple – one cell thick Lines blood vessels, body cavities & cover organs in body cavities Stratified – multiple layers Forms epidermis Cuboidal Epithelium Cuboid Cells Duct Cuboid Cells Duct Simple – one cell thick Roughly cube shaped Line ducts in kidneys, etc, where reabsorption and secretory activities take place. Columnar Epithelium Simple – one cell thick Column shaped (long & narrow) Line digestive tract where reabsorption & secretion occurs. Pseudostratified – gives the appearance of more than one layer of columnar epithelial cells Specific Connective Tissue Types: Adipose Bone Hyalaine cartilage Connective - Adipose Stores energy (fat) Insulates Supports & protects organs Connective - Bone Supports & protects Mineral storage Fat storage Blood cell production Connective – Hyaline Cartilage Supports while providing flexibility Absorbs compression between bones in joints (articular cartilage) Holds open respiratory passages Most abundant type of cartilage in body Muscle Tissue Types: • • Consists of specialized cells that contract when stimulated The body has three types of muscle tissue: • Skeletal (voluntary) • Cardiac (involuntary) • Smooth muscle (involuntary) Muscle - Skeletal Muscle fibers (cells) long, parallel & cylindrical With many nuclei (multinucleate) Striations (cross stripes run perpendicular to the cells Produce voluntary movement Locomotion Heat Specific Nervous Tissue Types Nervous – Neuron • Conducting cells, called neurons, transmit impulses from one region of the body to another. • Nonconducting cells, neuroglia, are a type of nervous system connective tissue. Membranes Sheets of tissue that cover or line surfaces or that separate organs, or parts of organs from one another. Mucous – line cavities or passages of the body that open to the exterior such as mouth, esophagus, digestive tract, respiratory passages Function in protection, secretion of mucus, and absorption Cutaneous MembraneCovers the body •Are continuous with mucous membranes Serous line closed cavities of the body such as thoracic cavity (pleura), Abdominal cavity (peritoneum), and sac in which heart lies (pericardium) Also cover organs lying in those closed cavities Has two layers Visceral – covers organs Parietal – lines the cavity Potential space between the two layers is kept moist by the secretion of a small amount of serous fluid which prevents friction when the two layers rub together Synovial MembranesLine joints, tendons, and bursa(A sac containing synovial fluid at sites of friction) • Secrete synovial fluid which prevents friction on the smooth, moist surfaces