function - Computer Science 101
advertisement
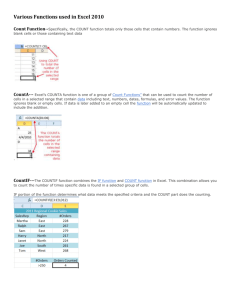
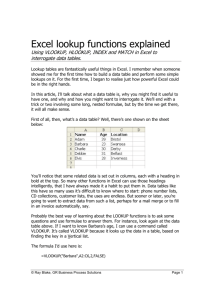
EXCEL CHAPTER 2 OBJECTIVES • Use semi-selection to create a formula • Use relative, absolute, and mixed cell references in formulas • Insert a function • Total values with the SUM function • Insert basic statistical functions • Determine results with the IF function • Use lookup functions • Use range names 2 SEMI SELECTION TO CREATE FORMULA • Semi-selection uses the mouse pointer to build a formula containing cell references or ranges • This technique is also called pointing 3 CELL REFERENCES • Excel offers three types of cell references for use when a formula is copied – Absolute$A$1 – Relative A1 – Mixed $A1 or A$1 • $ indicates that the row number or column letter will not be modified during a copy 4 EXAMPLE • Download Day4-Example.xlsx file to your computer and save it. • Apply cell style to cell A1 and cell range A7 to C7. • Adjust column A width as required. • Wrap text for cell range A7 to C7. 5 EXAMPLE • Format cell range A8 to A12 as Currency with 0(zero) decimal places. • In cell B8 type the formula =A8*$B$5 • Autofill B9 through B12. • In cell C8 type =A8- and click on cell B8 • Autofill C9 through C12. 6 EXAMPLE AFTER WORKING 7 FUNCTIONS • An Excel function is a predefined formula that performs a calculation • Syntax is the set of rules that govern correct formation of a function • An argument is an input, such as a cell or range • A function begins with the equal sign (=) followed by the function name and arguments in parentheses Example: =SUM(A1:A3) 8 FUNCTION CATEGORIES AND DESCRIPTION Category Description Compatibility Contains functions compatible with Excel 2007 and earlier. Cube Returns values based on data in a cube. Database Analyses records stored in a database format in Excel. Date & Time Provides methods for manipulating date and time values. Engineering Calculates values commonly used by engineers. Financial Performs financial calculations. Information Provides information about the contents of a cell. Logical Performs logical tests and returns the value of tests. Lookup & Reference Looks up values, creates links to cells, provides references to cells. Math & Trig Performs standard math and trigonometry functions. Statistical Performs common statistical calculations. Text Manipulates text strings. 9 INSERTING A FUNCTION • When a function is typed, Formula AutoComplete displays a list of functions matching the partial entry 10 INSERTING BASIC FUNCTIONS • A function ScreenTip is a small pop-up description that displays the function arguments • Totaling values with SUM function • =SUM(number 1, [number 2],…..) • Using Average Function • =AVERAGE(number 1,[number2],…..) • Using Median Function • =MEDIAN(number 1,[number2],…..) 11 MORE MATH AND STATISTICAL FUNCTIONS Function Syntax Description =ABS(number) Displays the absolute value of a number =FREQUENCY(data_array,bins_arr Counts how often values appear in given ay) range =INT(number) Rounds a value number down to nearest whole number =MODE.SNGL(number1,[number2] ,…) Displays the most frequently occuring value in list =PI() Returns the value of pi accurate upto 15 digits =PRODUCT(number1,[number2],… Multiplies all values within argument list. ) =RANDBETWEEN(bottom,top) Generates random numbers between two numbers =ROUND(number,num_digits) Rounds value to specific number of digits =RANK.AVG(number,ref,[order]) Returns an average rank for identical values 11 DATE/TIME FUNCTIONS Function Syntax Description =TODAY() Displays today’s date: month, day, year =NOW() Displays today’s date and current military time =DATE(year,month,day) Returns serial number for a date =EDATE(start_date,months) Displays serial number of a date a specified number of months in future or past =DAY(serial_number) Displays the day within a month for a serial number =MONTH(serial_number) Returns the month for a serial number =YEAR(serial_number) Identifies the year for a serial number 13 LOGICAL FUNCTIONS • IF function – IF(logical_test,value_if_true,value_if_false) • The IF function has three arguments: – A logical test or condition that is true or false – The resulting value if the condition is true – The resulting value if the condition is false NESTED FUNCTIONS • A nested function occurs when one function is embedded as an argument to another function; for example: =IF(A1<A2,MIN(B1:B5),MAX(B1:B5)) – Compute the MIN function if A1 is less than A2 – Compute the MAX function if A1 is not less than A2 15 LOOKUP FUNCTIONS • Lookup functions are used to look up values in a table to perform calculations or display results • For example, a teacher may want to look up an average in order to assign a grade • When searching a range, the breakpoint is the lowest value 16 CREATING LOOKUP TABLE • A lookup table typically lists breakpoints in one column and return values in a second column 17 VLOOKUP FUNCTION • The VLOOKUP function searches a lookup table for a value and returns the result from the related column • VLOOKUP has three required arguments: – Lookup value – Table array (range of lookup table) – Column index of return value 18 EXAMPLE • In Day4-Example.xlxs open GradeBook worksheet • In cell F3 type the formula for lookup as =VLOOKUP(E3,$A$3:$B$7,2) • Autofill the remaining cells. 19 20 RANGE NAME • A range name is a word or phrase used to identify a cell or cell range • Range names make formulas easier to read • Create a range name – Click the Formulas tab, click Define Name in the Defined Names group to open the New Name dialog box, type the range name in the Name box, and then click OK – Click in the Name Box, type the range name, and then press Enter. 21


![VLOOKUP ([Score], A5:B10, 2)](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/007008406_1-329b439ee1a3b5923ce08e77bb280c5d-300x300.png)
