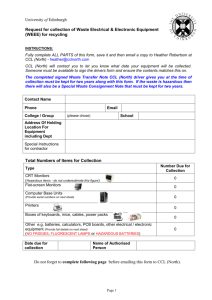
Excel Chapter 2
advertisement
DAY 5: EXCEL CHAPTER 2 Sravanthi Lakkimsetty salakkimsetty@mix.wvu.edu Aug 31,2015 ANNOUNCEMENTS • Any Questions regarding MyITLab registration? There are students who are yet to register in it. (Student ID Update) • There is also Open Lab Online Proctor Sallyanne Fuentes will be available Mondays and Wednesdays from 7:00pm-9:00pm ET. Proctor Eva Llera will be online Sundays 7:00p-9:00pm ET. Students can go to http://cs101.wvu.edu/resources/help/open-lab-online/ and get help using Skype's call or chat features. OVERVIEW • • • • • • • Relative, absolute and mixed cell references Functions Statistical Functions Date Functions Logical Functions IF Function Nested IF Function CELL REFERENCES • Used in formulas so that they can be copied and reused easily. • In some cases, we want the references to cells to move down, or over as we copy the formula. • In other cases, we do not want the reference to change even if we do move. RELATIVE VS ABSOLUTE ADDRESSING • Relative cell references indicate a cell’s relative location from the cell containing the formula; the cell reference changes when the formula is copied • Absolute cell references indicates a cell’s specific location; the cell reference does not change when you copy the formula - Indicated by dollar ($) signs in front of the column letter and row number - Most often used when the value need not change • Mixed cell references contains both an absolute and relative cell references in a formula CELL REFERENCES(CONTD) Relative reference Column absolute mixed reference A1 $A1 Row absolute mixed reference Absolute reference A$1 $A$1 AVOIDING CIRCULAR REFERENCES • A circular reference error occurs if a formula refers to itself FUNCTION • Function is a predefined formula that performs a calculation. • Syntax is a set of rules that govern the structure and components for properly entering a function. • An Argument is an input, such as cell reference or value, needed to complete a function. • A function begins with the equal sign (=) followed by the function name and arguments in parentheses Example: =SUM(A1:A3) INSERTING A FUNCTION • When a function is typed, Formula AutoComplete displays a list of functions matching the partial entry • Use the Insert Function dialog box to search for a function or select one from a list. FUNCTION CATEGORIES AND DESCRIPTION Category Description Compatibility Contains functions compatible with Excel 2007 and earlier. Cube Returns values based on data in a cube. Database Analyses records stored in a database format in Excel. Date & Time Provides methods for manipulating date and time values. Engineering Calculates values commonly used by engineers. Financial Performs financial calculations. Information Provides information about the contents of a cell. Logical Performs logical tests and returns the value of tests. Lookup & Reference Looks up values, creates links to cells, provides references to cells. Math & Trig Performs standard math and trigonometry functions. Statistical Performs common statistical calculations. Text Manipulates text strings. SUM • SUM is the most commonly used function – represented by a sigma () – Adds values within a specified range • Syntax refers to the grammatical structure of a formula – Must adhere to stated structure of formula • Arguments are values ─ used as input and returned as output Function Name • Example: = Sum (B1:B10) Arguments AUTOSUM • • • • • Automates the SUM function Click the cell where you want the result Click AutoSum button Select the range of cells you want to sum Press Enter to complete BASIC STATISTICAL FUNCTIONS • Perform a variety of calculations to aid in decision making process – – – – – AVERAGE calculates the average of a range of numbers MEDIAN finds the midpoint value in a range MIN calculates the minimum value in a range MAX calculates the maximum value in a range COUNT counts the number of values within a range COUNT • Statistical Functions – COUNT, COUNTA • COUNT function counts the number of cells in a range that contain numerical data. • COUNTA function counts the number of cells in a range that are not blank. • COUNTBLANK counts the number of blanks in the given range. • Ex: COUNT(C6:C24) COUNTA(E2:E10) COUNTBLANK(J9:J16) DATE/TIME FUNCTIONS Function Syntax Description =TODAY() Displays today’s date: month, day, year =NOW() Displays today’s date and current military time =DATE(year,month,day) Returns serial number for a date =EDATE(start_date,months) Displays serial number of a date a specified number of months in future or past =DAY(serial_number) Displays the day within a month for a serial number =MONTH(serial_number) Returns the month for a serial number =YEAR(serial_number) Identifies the year for a serial number LOGICAL FUNCTIONS • IF function • Logical Operators Operator Description = Equal to <> Not equal to < Less than > Greater than <= Less than or equal to >= Greater than or equal to IF FUNCTION • Used to determine whether a given condition has been satisfied or not • When the condition is met, the formula performs one task; when it is not met, the formula performs another task • Has three arguments: – a condition tested to determine if it is true or false – the resulting value if the condition is true – the resulting value if the condition is false IF (CONTD.) • Syntax: IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false) Value when condition is false Value when condition is true Condition is true or false • IF(H4=100, “Good”, “Bad”)