Comparative Anatomy Nervous System
advertisement

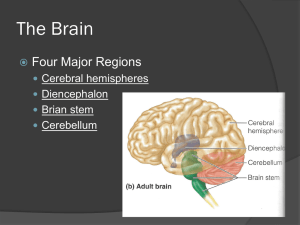
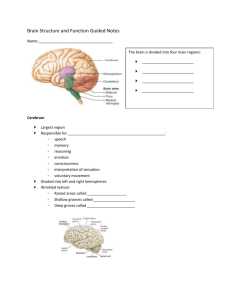
Comparative Anatomy Nervous System Kardong Chapter 16 Part 15 Primary Brain Vesicles Prosencephalon (Forebrain) Smell Mesoncephalon (Midbrain) Vision Rhombencephalon (Hindbrain) Hearing Figure 15.1. Primary brain vesicles (book figure 16.25). Primary Brain Vesicles (cont.) Figure 15.2. Basic brain plan. Figure 15.3. Brain divisions. Hindbrain Myelencephalon Medulla oblongata Involuntary reflexes Vagal lobe Metencephalon Cerebellum Roof of metencephalon Reflex control of skeletal muscle Pons - Floor of metencephalon - relay station of sensory and motor tracts between spinal cord and cerebrum Figure 15.4. Regional divisions of the brain (book figure 16.25). Hindbrain (cont.) 4th ventricle Cavity of hindbrain Posterior choroid plexus Roof in hindbrain 4th ventricle tissue Cerebrospinal fluid Tela choroidea Roof of medulla Thin membrane Figure 15.5. Choroid plexus shown in a larval anuran. Brain Divisions/Vesicles Figure 15.6. Regions of the vertebrate brain (Fig. 16.32) Midbrain No subdivisions Roof – tectum; floor - tegmentum Optic lobes Optic reflex centers Well developed in birds Auditory lobes Caudal to optic lobes Superior (optic) and inferior (auditory) colliculi- when lobes occur together Corpora quadrigemina collectively Figure 15.7. Mesencephalon and tectum region. Midbrain (cont.) 3rd ventricle Cavity of midbrain Cerebral aqueduct Restricted passageways Conduit between 3rd and 4th ventricle Aqueduct of Sylvius when restricted further Figure 15.8. Cerebral aqueduct and ventricles of brain. Forebrain - Diencephalon Optic chiasma Pituitary gland Two optic nerves cross Caudal to optic chiasma Saccus vasculosus Posterior to pituitary in some fish Depth receptor Figure 15.9. Regions of the diencephalon of a shark with third ventricle in red. Forebrain- Diencephalon (cont.) Hypothalamus Floor of diencephalon Thalamus Walls of diencephalon 3rd ventricle cavity Communicates with lateral ventricles Foramen of Monro (actually 2 foramina) Figure 15.10. Medial view of the brain showing thalamus and hypothalamus of the diencephalon. Forebrain- Diencephalon (cont.) Epithalamus Several evaginations Roof of diencephalon Paraphysis anteriorly Epiphyseal complex Figure 15.11. Epithalamus; gross midsagittal section of the human brain. Pineal Photoreceptors Parapineal Pineal eye (3rd eye) Figure 15.12. Pineal in detail (see book figure 16.37). Forebrain- Telencephalon Cerebral hemispheres posterior Rhinencephalon anterior Olfaction Lower vertebrates Rhinencephalon prominent Hemisphere smaller Higher vertebrates Hemispheres increase in size Olfactory get smaller Figure 15.13. Frontal section of cerebral hemisphere formation. Evolution of Vertebrate Brain Figure 15.14. Phylogenetic enlargement of vertebrate brains (see Fig. 16.33). Vertebrate Brains (cont.) Figure 15.15. Dorsal view of vertebrate brains. Telencephalon Terminology Fish Cerebrum Primitive sensory Pallium- dorsal area Motor area Subpallium- ventral area Globus pallidus (striatum) Figure 15.16. Embryonic development of the telencephalon (Book figure 16.42. Amphibian Cerebrum Similar pallium and globus pallidus Split left and right hemispheres Figure 15.17. Globus pallidus of amphibian; left cerebral hemisphere. Reptile Cerebrum Cerebrum is huge compared to amphibians Increase of lateral walls Pushes into lateral ventricle Dorsal ventricular ridge forms Receives visual, auditory, and sensory stimuli Figure 15.18. Globus pallidus of reptile and bird; left cerebral hemisphere. Bird Cerebrum Similar to reptiles Avian ridge (hyperstriatum) Stratum of neurons that capped ridge Processes visual information Important to instinctive stereotypic behavior Migration and courtship Figure 15.19. Globus pallidus of reptile and bird; left cerebral hemisphere. Mammalian Cerebrum Lateral ventricles extremely expanded Neocortex Higher mental facilities Grooves (sulci) Folds (gyrae) Figure 15.20. Neocortex of mammalian brain. Mammalian Cerebrum (cont.) Figure 15.21. Ventral view of human brain (see book Fig 16.36). Mammalian Cerebrum (cont.) Portion of primitive brain retained Ventral medially Hippocampus- ancient olfactory pallium Memory storage? Globus pallidum pushed interiorly Basal ganglia Changes in basal ganglia motor dysfunction Parkinson’s Disease Figure 15.22. Globus pallidus of human; left cerebral hemisphere Mammalian Cerebrum (cont.) Figure 15.23. Sagittal section of the human brain (book Fig. 16.37). Cranial Nerves Amniotes have 12 Anamniotes have 10 Terminal nerve (Nerve 0)- uncommon in humans Associated with pheromone receptors Figure 15.24. Cranial nerve locations on the brain. Figure 15.25. Cranial nerve innervation (book Fig. 16.15). Figure 15.26. Cranial nerve innervation (book Fig. 16.15). Cranial Nerves (cont.) Figure 15.27. Cranial nerves in 6th week embryo. Figure 15.28. Head organization in 4th week embryo (book figure 16.39). Cranial Nerves (cont.) Cranial Nerves (cont.)