Brain dissection
advertisement

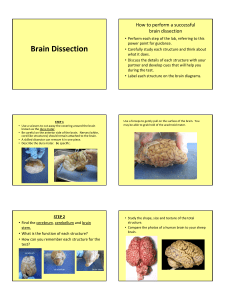
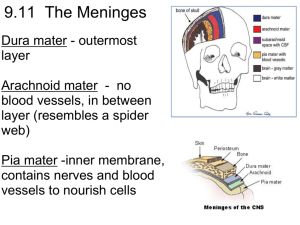
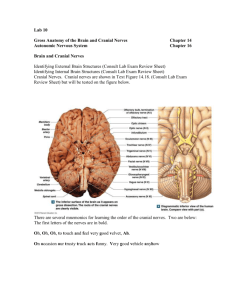
Brain Dissection How to perform a successful brain dissection • Perform each step of the lab, referring to this power point for guidance. • Carefully study each structure and think about what it does. • Discuss the details of each structure with your partner and develop cues that will help you during the test. • Label each structure on the brain diagrams. • • • • STEP 1 Use a scissors to cut away the covering around the brain known as the dura mater. Be careful on the anterior side of the brain. Nerves (white, cord-like structures) should remain attached to the brain. A skilled dissector can remove it in one piece. Describe the dura mater. Be specific. Use a forceps to gently pull on the surface of the brain. You may be able to grab hold of the arachnoid mater. STEP 2 • Find the cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem. • What is the function of each structure? • How can you remember each structure for the test? cerebrum cerebellum Brain stem • Study the shape, size and texture of the total structure. • Compare the photos of a human brain to your sheep brain. STEP 3 • Notice the ridges and grooves in the cerebrum. • What scientific names are given to these structures? • What is their purpose? • Find the longitudinal fissure on the dorsal side of the brain? • What is a fissure? STEP 4 • Observe the ventral side of the brain and begin at the anterior end. You will see some of the major nerves associated with your senses. • Find the olfactory bulbs . • Use your text to find out the sense associated with the olfactory bulbs. • What is a tract? (See page 232 in your text) • • • • Observe the optic nerves. What sense are these nerves associated with? The optic nerves cross as the optic chiasma. Use the internet to find out the importance of the crossing of optic fibers. Optic nerve Oculomotor nerve • Observe some of the other anterior structures. You will need to find the function of the mammillary body on the internet. -mammillary body -the pons STEP 5 • Now make a midsagittal cut through the brain. • Find and label the corpus callosum. What is its function? • Find the ventricles: This is a picture of the lateral ventricle. • What is the function of a ventricle? • The 4th ventricle is connected to the 3rd ventricle by the cerebral aqueduct. • How do you think the cerebral aqueduct got its name? 4th ventricle Cerebral aqueduct • Find the thalamus and label it on your diagram. • Describe its position in the brain. • Find the structures of the brain stem: label the medulla oblongata, pons and midbrain. Spinal cord STEP 6 Make a coronal (frontal) section perpendicular to the longitudinal fissure. • Find the gray matter and white matter. • The gray matter (also called the cortex) gets its colors from what neuron structure? • How does the white matter get its color? Can you figure out the name of these openings? STEP 7 Explore!!!!! Myelinated axons This brain was attached to the nasal bone. Note how the nasal cavities fit over the olfactory bulbs in real life. Nasal cavities Olfactory bulbs STEP 8 • Throw the brain parts in the garbage. • Wash and dry your dissection tray and tools.