Nov 12 Adjusting Entry BAF3M
advertisement

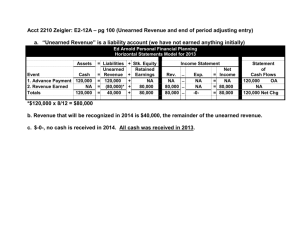
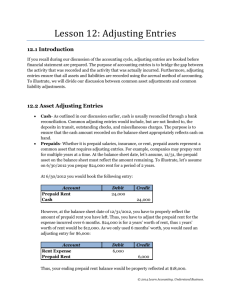
Chapter 8! The Accounting Cycle Unit 3 Test (cover chapter 6, 7 and 8, but we will cover only some portion of chapter 8) will be Tuesday Nov 17 Financial Statement must be…. Relevant: Readers want to see a current picture value of a business’ important features. (= Nobody likes old or outdated information) Reliable: Readers want the information to be based on solid evidence. Comparable: Readers want to compare from one year to the next and one company to another company. Meeting the objectives of relevancy, reliability and comparability requires the input of senior accounting professionals. Accrual Accounting vs Cash basis Accounting Accrual Accounting means recording revenues and expenses when they happen, regardless of whether cash is received or paid. (honors GAAP and IFRS) Cash basis Accounting means recording transactions only when cash is received or paid. (violates GAAP and IFRS) In reality, nobody uses cash basis accounting any more. People used to use cash basis accounting long time ago. Financial Statement Comparability The Time Period Concept ensures that the Comparability objective in accounting is met. This means that reporting period must be consistent such as one year, one month or one quarter Some revenues and expenses occur continuously, and accrural accounting require accounting clerks to record them as they happen. (even if the cash was not exchanged) Adjusting Entry Accounting clerks make entries only when there is source document. This is why senior accountants must step in at the end of a fiscal period to deal with the revenue and expenses which have been accruing but have not yet been recorded. Adjusting Entry There are many different types of adjusting entries accountants make at the end of the fiscal period: Prepaid Expense Prepaid Insurance Supplies adjustment Unearned Revenue Late-Arriving Purchase Invoice Adjusting Entry for Unearned Revenue Sometimes customer pays for service before the end of the fiscal period. Then the business owes service or goods to the customer on the last day. Then the business provides the service (or goods) next year. Then Revenue Recognition says that accountant must make an adjusting entry, which defers the recording of revenue to next fiscal period. (because revenue is not earned yet.) Adjusting Entry for Unearned Revenue For example, a customer (Mathew) paid $600 on August 1, which covers 1 year membership. (= $50 per month) Goodlife is a public corporation, so their fiscal period ends on September 30. On August 1st, the bookkeeper would make the following journal entry: Dr. Cr. Aug 1 Bank 600 Fees earned (Rev) 600 Received annual membership fee Adjusting Entry for Unearned Revenue On September 30, the accountant would make the following adjusting entry: Dr. Cr. Sep 30 Fees earned 600 Prepaid fee(liab) 600 Adjusting Entry for annual membership fee Note: Prepaid fee = Unearned revenue account Adjusting Entry for Unearned Revenue Since we used up two months of the membership fee revenue : 2 * $50 per month is 100$ On September 30, the accountant would also make the following journal entry: Dr. Cr. Sep 30 Prepaid fee 100 Fees earned 100 Adjusting Entry: Recognizing two months of revenue T account for Unearned Revenue Classwork Review Questions – pg 275 #3, 4 Page 278 #5 (a, b and d) Page 278 #6