File
advertisement

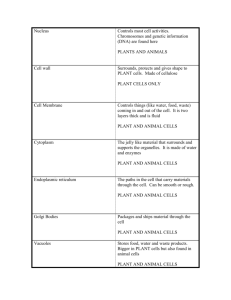
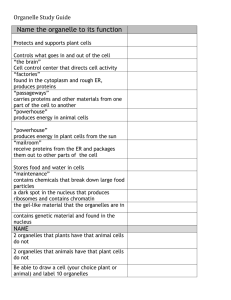
Chemistry Water Macromolecules Organelles Part 1 Organelles Part 2 Molecule Transport Final Exam Jeopardy Organelles Organelles Part 1 Part 2 Molecule Transport Chemistry Water Macromolecules 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Final Jeopardy! $100 Question This is the product of the equation: 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O . $100 Answer What is 2 H2O? Return Daily Double Daily Double Question When an atom has a negative charge, it has gained an extra one of these. Daily Double Answer What is an electron? Return $300 Question Electrons are arranged in this form within an atom. $300 Answer What is within an electron “cloud”? Return $400 Question This type of bond is created when one atom donates an electron to another atom. $400 Answer What is an ionic bond? Return $500 Question This happens to atoms in chemical reactions. $500 Answer What is rearranged? Return $100 Question The word hydrophobic means this. $100 Answer What is “water-fearing”? Return $200 Question Because water has a slight negative charge and a slight positive charge, allowing for hydrogen bonds to form, it is referred to as this type of molecule. $200 Answer What is a polar molecule? Return $300 Question The hydrogen and oxygen in a single water molecule create this type of bond with each other. $300 Answer What is a covalent bond? Return $400 Question Cohesion in water occurs due to this. $400 Answer What are hydrogen bonds? Return $500 Question Hydrogen bonds between water molecules occur due to this quality in water. $500 Answer What is polarity? Return $100 Question This is the function carbohydrates serve for an organism. $100 Answer What is to provide energy? Return $200 Question This is the name for a chain of simple sugars. (It creates a carbohydrate.) $200 Answer What is a polysaccharide? Return $300 Question This macromolecule is known to control chemical reactions in the cell, build muscles, and defend the body. $300 Answer What are proteins? Return $400 Question Enzymes are known to lower this in chemical reactions. $400 Answer What is the activation energy? Return $500 Question This type of reaction occurs when a monomer or polymer is removed from a chain, through the addition of a water molecule. $500 Answer What is a hydrolysis reaction? Return $100 Question This organelle is stores the cell’s DNA and directs activities in the cell. $100 Answer What is a nucleus? Return $200 Question This organelle is the site of photosynthesis in the plant cell. $200 Answer What is the chloroplast? Return Daily Double Daily Double Question These begin at the ribosome, travel to the rough ER, bud off in a vesicle, travel to the Golgi, and are given directions in the Golgi to be transferred to either lysosomes, vacuoles, or vesicles. Daily Double Answer What are proteins? Return $400 Question This organelle is responsible for modifying and folding the protein before sending it to its final destination. $400 Answer What is the Golgi apparatus? Return $500 Question This organelle is a membrane-bound sac that moves products into or out of the cell. $500 Answer What is the vesicle? Return Daily Double Daily Double Question The rough ER is characterized by having this organelle attached to its surface. Daily Double Answer What are ribosomes? Return $200 Question This refers to the network of fibers that extend through the cytoplasm. $200 Answer What is the cytoskeleton? Return $300 Question This organelle refers to the area between the cell membrane and the nucleus. $300 Answer What is the cytoplasm? Return $400 Question This organelle digests worn out organelles. $400 Answer What is the lysosome? Return $500 Question These are organelles on the outer surface of the cell that aid with cell movement. $500 Answer What are the flagella and cilia? Return $100 Question This process refers to the diffusion of water. $100 Answer What is osmosis? Return $200 Question This refers to the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. $200 Answer What is diffusion? Return $300 Question The channels within the cell membrane are made of this. $300 Answer What are proteins? Return $400 Question This refers to the process that occurs when energy is used to move molecules against their concentration gradient (from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration). $400 Answer What is active transport? Return $500 Question Due to the qualities of the phospholipid bilayer, this molecule cannot simply diffuse across the membrane. It must use a transport protein to enter or leave the cell. $500 Answer What is water? Return Final Jeopardy Topic MACROMOLECULES Final Jeopardy Question Name each of the four types of macromolecules, along with an example of each type. Final Jeopardy Answer What are: 1. Carbohydrates (sugars) 2. Lipids (fats, oils, steroids) 3. Proteins (enzymes) 4. Nucleic Acids (DNA) Thank you for playing!