"Chapter 10 & 11 Review"

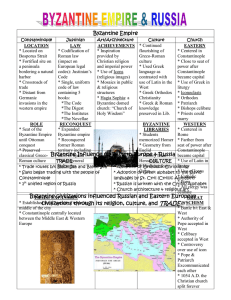
Chapter 10 Review
Places
Byzantium: Founded by the Greek colonists in the 600s
Constantinople: the empire was divided into eastern and western and Constantinople was the capital of the
Eastern Empire.
Hagia Sophia: It is one of the best surviving examples of Eastern Orthodox churches. And greatly influenced the beginnings of the Italian Renaissance during the 13 th and 14 th .
Terms
Christendom: The portion of the World in which Christianity was dominant.
Justinian Code: Codification of existing Roman law, which he combined with Biblical principles.
Greek fire: a byzantine secret weapon similar to a flame thrower.
Iconoclastic Controversy: image destroyer.
Icon: an abstract, simplified image or picture of Christ, Mary or one of the saints.
Cyrillic Alphabet: A Slavic script based on the Greek Alphabet.
Byzantine text: The byzantine church’s greatest contribution to civilization was the preservation of the Greek
New Testament.
Identification
The Roman Empire was permanently divided in 395
The battle of Manzekirt was won by the Seljuk Turks and it was in 1071
The Fourth crusade sacked Constantinople
The fall of Constantinople was on May 19 1453
Cyril was the apostle to the Slavs.
The Byzantine church’s greatest contribution was the preservation of the greek new testament.
Chapter 11 Review
Places
Papal States: the alliance between the Frankish rulers and the papacy, initiated by the conversion of Clovis, and consummated by Pepin the Short was to influence the course of European History not only during the
Middle Ages but well into the modern Age.
Lorraine: this land would become the subject of intense disputes between the French and Germans.
Hungary: the Magyars finally settled down in the area known since as Hungary.
Scandinavia: where the countries of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway are located today.
Normandy: these Normans later became subjects of the French king and accepted the religion of Rome.
Holy Roman Empire: when Charlemagne was crowned emperor of the romans he gave birth to it.
Canossa: means submitting to the Pope, eventually made it possible for the Reformation to take firm Root
Avignon: a part of France into with the papal court was moved
Terms
Bishop: leader of the Roman Catholic Church. It means overseer or superintendent in Greek.
Apostolic Succession: that Christ had appointed apostles -> bishops -> successor, in unbrkn line
Petrine Theory: That Christ founded his church upon peter, that he made him the visible head.
Roman Catholic Church: that the Roman Catholic Church is supreme over all other churches.
Pope: the bishop of Rome became the most powerful of all. Latin papa “father”
Sacraments: means to get grace,
Latin Vulgate: the Latin translation completed by the church leader Jerome in 405
Council of Toulouse: Forbade anyone except a clergyman to own a Bible.
Breviary: Psalms and the lesson of Scripture
Monasticism: withdrawing from the society to live in solitude.
Monk: a man who practices monasticism
Nun: a woman who practices monasticism
Hermit: the earliest monks lived who lived in the wilderness.
Monasteries: religious communities isolated from the rest of society.
Orders: the rules that the monks in a monastery followed.
Abbot, friar: abbot was the head of the monastery, friars where monks that preached.
Mayor of the Palace: chief official of the royal household that actually had the power.
Donation of Pepin: when the Franks defeated the Lombards and gave the central Italy to pope
Missi Dominici: the king’s envoys. They checked on local officials, and hear complaints
Carolingian minuscule: the basis for modern handwriting styles as well as the Roman type face.
Treaty of Verdun: divided the empire into three parts. South, central, and north.
Duchy: lands of Germany divided into small territories.
Cardinals: the ones who had the ability to choose popes according to Hildebrand.
Fourth Lateran Council: a council which sanctioned the dogma of transubstantiation.
Babylonian Captivity of the papacy: when King Philip the Fair captured Boniface VIII.
Great Schism: the rival popes and cardinals created it
Identification
The two swords doctrine stated that the civil and the ecclesiastical power were to be separated it was issued in 494
Two orders were the Franciscans -> St. Francis, and the Dominicans -> St. Dominic
The date Clovis and his soldiers were baptized into the church was Christmas Day 498
The Frankish army under Martel won in 732.
Charlemagne’s empire was the greatest empire in the west since A.D. 300
Charlemagne was crowned emperor on the Christmas day of 800
The treaty of Verdun was in 843
Otto the great was crowned emperor of the Romans in 962